‘How to develop Pythonic coding rather than Python coding – Logic Perspective’
- 1. Online Workshop on ‘How to develop Pythonic coding rather than Python coding – Logic Perspective’ 21.7.20 Day 1 session 2 Dr. S.Mohideen Badhusha Professor/ CSE department Alva’s Institute Engineering and Technology Mijar, Moodbidri, Mangalore 1
- 3. 3 To acquire knowledge of iteration and string in Python To comprehend the concept of looping statements in Python To practice the simple problems in iteration and string Objectives of the Day 1 session 2
- 4. 4 Iteration for loop for var in <collection>: <statements> where collection is iterable obj like list, tuple,dictionary,string and range a = [’i’, ’say’, ’hello’] # a list of string elements for i in range(len(a)): print (i,end=’ ’) print (a[i]) Output 0 I 1 say 2 hello
- 5. 5 Iteration while loop while condition : <Statements> i=0 while (i < 10): print( i) i += 1 o/p 0 1 2 . 9
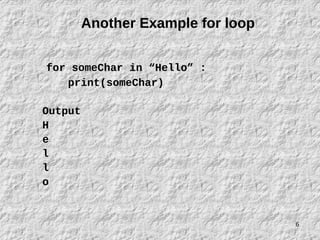
- 6. 6 Another Example for loop for someChar in “Hello” : print(someChar) Output H e l l o
- 7. 7 d=[(1,'a'),(2,'b'),(3,'c'),(4,'d'),(5,'e')] for (x, y) in d : print (x,y) o/p 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 d 5 e
- 8. 8 for loop using range() for x in range(5): print x o/p 0 1 2 3 4
- 9. 9 Python program but not Pythonic def traverse(string): index = 0 while index < len(string): letter = string[index] print(letter) index += 1 traverse('Monty Python') Output ?
- 10. 10 def traverse(string): for letter in string: print (letter) traverse('Monty Python’) Pythonic program
- 11. 11 in operator in is a boolean operator that checks membership within a sequence It is also called membership operator. 'a' in 'banana' True 'o' in 'banana' False
- 13. 13 String handling functions s=’HELLO’ s.lower() # hello s1=’hello’ s1.upper() # HELLO s.strip() -- returns a string with whitespace removed from the start and end s=’ I am happy ‘ s.strip() # I am happy ( no front and back spaces) s.isalpha()# True s.isdigit() # False s.isspace() #False
- 14. 14 split() and join() functions s.split('delim') - returns a string into a list of words separated by delim Ex: 'aaa,bbb,ccc'.split(',') -> ['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc']. Defalut delim is space s.join(list) -- opposite of split(), joins the elements in the given list together using the string as the delimiter. Ex: '---'.join(['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc']) -> ‘aaa---bbb---ccc’ 14
- 15. 15 String Formatting Operator: % The operator % allows strings to be built out of many data items in a “fill in the blanks” fashion. x = “Ram” y = 34 print(“%s’s age is %d” % (x, y)) o/p Ram’s age is 34 The tuple following the % operator is used to fill in the blanks in the original string marked with %s %g %d to represent string, float and integer values
- 16. 16 Converting anything to a String The built-in str() function can convert an instance of any data type into a string Ex: print(“Hello ” + str(2)) o/p Hello 2
- 17. 17 Slicing strings A segment of a string is called a slice. Selecting a slice is similar to selecting a character: Ex: s = 'Monty Python' print(s[0:5]) Monty print(s[6:12]) Python
- 19. 19 String Indexing print(s[-1]) o/p 'o' #last char (1st from the end) print(s[-4]) o/p 'e' # 4th from the end print(s[:-3]) o/p 'He' – from starting, going up to but not including the last 3 chars. s[-3:] is 'llo' -- starting with the 3rd char from the end and extending to the end of the string.
- 20. 20 s[1:4] is 'ell' -- chars starting at index 1 and extending up to but not including index 4 s[1:] is 'ello' -- omitting either index defaults to the start or end of the string s[:] is 'Hello' -- omitting both always gives us a copy of the whole thing s[1:100] is 'ello' -- an index that is too big is truncated down to the string length
- 21. 21 Concluding Tips for loop in Python is entirely different from other programming languages[ for var in collection] while loop in Python is similar to the programming constructs in other languages There is no do… while loop existing in Python To be Pythonic, we should use data structures and PEP 8 rules in Python In slicing of string, st[i:n], we have to consider from i th index to n-1 . st[:n] from 0 th index to n-1. st[i:] from i th index to end of the string




![4
Iteration
for loop
for var in <collection>:
<statements>
where collection is iterable obj like list, tuple,dictionary,string
and range
a = [’i’, ’say’, ’hello’] # a list of string elements
for i in range(len(a)):
print (i,end=’ ’)
print (a[i])
Output
0 I
1 say
2 hello](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-4-320.jpg)

![7
d=[(1,'a'),(2,'b'),(3,'c'),(4,'d'),(5,'e')]
for (x, y) in d :
print (x,y)
o/p
1 a
2 b
3 c
4 d
5 e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-7-320.jpg)

![9
Python program but not Pythonic
def traverse(string):
index = 0
while index < len(string):
letter = string[index]
print(letter)
index += 1
traverse('Monty Python')
Output ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-9-320.jpg)




![14
split() and join() functions
s.split('delim') - returns a string into a list of
words separated by delim
Ex:
'aaa,bbb,ccc'.split(',') -> ['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc'].
Defalut delim is space
s.join(list) -- opposite of split(), joins the
elements in the given list together using the
string as the delimiter.
Ex:
'---'.join(['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc']) -> ‘aaa---bbb---ccc’
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-14-320.jpg)


![17
Slicing strings
A segment of a string is called a slice.
Selecting a slice is similar to selecting a
character:
Ex:
s = 'Monty Python'
print(s[0:5])
Monty
print(s[6:12])
Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-17-320.jpg)
![18
String Indexing
print(s[:3])
o/p
Hel
print(s[3:])
o/p
lo
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-18-320.jpg)
![19
String Indexing
print(s[-1])
o/p
'o' #last char (1st from the end)
print(s[-4])
o/p
'e' # 4th from the end
print(s[:-3])
o/p
'He' – from starting, going up to but not
including the last 3 chars.
s[-3:] is 'llo' -- starting with the 3rd char from
the end and extending to the end of the string.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-19-320.jpg)
![20
s[1:4] is 'ell' -- chars starting at index 1 and
extending up to but not including index 4
s[1:] is 'ello' -- omitting either index defaults
to the start or end of the string
s[:] is 'Hello' -- omitting both always gives
us a copy of the whole thing
s[1:100] is 'ello' -- an index that is too big is
truncated down to the string length](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-20-320.jpg)
![21
Concluding Tips
for loop in Python is entirely different from
other programming languages[ for var in
collection]
while loop in Python is similar to the
programming constructs in other languages
There is no do… while loop existing in Python
To be Pythonic, we should use data
structures and PEP 8 rules in Python
In slicing of string, st[i:n], we have to consider
from i th index to n-1 .
st[:n] from 0 th index to n-1.
st[i:] from i th index to end of the string](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day1session2-250427170618-603461c6/85/How-to-develop-Pythonic-coding-rather-than-Python-coding-Logic-Perspective-21-320.jpg)