Implementing dr w. hyper v clustering
- 1. Implementing Affordable Disaster Recovery with Hyper-V andMulti-Site ClusteringGreg Shields, MVPPartner and Principal Technologistwww.ConcentratedTech.com
- 2. This slide deck was used in one of our many conference presentations. We hope you enjoy it, and invite you to use it within your own organization however you like.For more information on our company, including information on private classes and upcoming conference appearances, please visit our Web site, www.ConcentratedTech.com. For links to newly-posted decks, follow us on Twitter:@concentrateddon or @concentratdgregThis work is copyright ©Concentrated Technology, LLC
- 3. What Makes a Disaster?Which of the following would you consider a disaster?
- 4. A naturally-occurring event, such as a tornado, flood, or hurricane, impacts your datacenter and causes damage. That damage causes the entire processing of that datacenter to cease.
- 5. A widespread incident, such as a water leakage or long-term power outage, that interrupts the functionality of your datacenter for an extended period of time.
- 6. A problem with a virtual host creates a “blue screen of death”, immediately ceasing all processing on that server.
- 7. An administrator installs a piece of code that causes problems with a service, shutting down that service and preventing some action from occurring on the server.
- 8. An issue with power connections causes a server or an entire rack of servers to inadvertently and rapidly power down.What Makes a Disaster?Which of the following would you consider a disaster?
- 9. A naturally-occurring event, such as a tornado, flood, or hurricane, impacts your datacenter and causes damage. That damage causes the entire processing of that datacenter to cease.
- 10. A widespread incident, such as a water leakage or long-term power outage, that interrupts the functionality of your datacenter for an extended period of time.
- 11. A problem with a virtual host creates a “blue screen of death”, immediately ceasing all processing on that server.
- 12. An administrator installs a piece of code that causes problems with a service, shutting down that service and preventing some action from occurring on the server.
- 13. An issue with power connections causes a server or an entire rack of servers to inadvertently and rapidly power down.DISASTER!JUST A BAD DAY!
- 14. What Makes a Disaster?Your decision to “declare a disaster” and move to “disaster ops” is a major one.The technologies used for disaster protection are different than those used for high-availability.More complex.More expensive.
- 15. What Makes a Disaster?Your decision to “declare a disaster” and move to “disaster ops” is a major one.The technologies used for disaster protection are different than those used for high-availability.More complex.More expensive.Failover and failback processes involve more thought.You might not be able to just “fail back” with a click of a button.
- 16. A Disastrous PollWhere are We? Who Here is…Planning a DR Environment?In Process of Implementing One?Already Enjoying One?What’s a “DR Environment” ???
- 17. Multi-Site Hyper-V == Single-Site Hyper-VDON’T PANIC: Multi-site Hyper-V looks very much the same as single-site Hyper-V.Microsoft has not done a good job of explaining this fact!Some Hyper-V hosts.Some networking and storage.Virtual machines that Live Migrate around.
- 18. Multi-Site Hyper-V == Single-Site Hyper-VDON’T PANIC: Multi-site Hyper-V looks very much the same as single-site Hyper-V.Microsoft has not done a good job of explaining this fact!Some Hyper-V hosts.Some networking and storage.Virtual machines that Live Migrate around.But there are some major differences too…VMs can Live Migrate across sites.Sites typically have different subnet arrangements.Data in the primary site must be replaced with the DR site.Clients need to know where your servers go!
- 19. Constructing Site-Proof Hyper-V:Three Things You NeedAt a very high level, Hyper-V disaster recovery is three things:A storage mechanismA replication mechanismA set of target servers and a cluster to receive virtual machines and their dataOnce you have these three things, layering Hyper-V atop is easy.
- 20. Constructing Site-Proof Hyper-V:Three Things You NeedReplication MechanismStorage Device(s)Target Servers
- 21. Thing 1:A Storage MechanismTypically, two SANs in two different locationsFibre Channel , iSCSI, FCoE, heck JBOD.Often similar model or manufacturer. This similarity can be necessary (although not required) for some replication mechanisms to function property.
- 22. Thing 1:A Storage MechanismTypically, two SANs in two different locationsFibre Channel , iSCSI, FCoE, heck JBOD.Often similar model or manufacturer. This similarity can be necessary (although not required) for some replication mechanisms to function property.Backup SAN doesn’t necessarily need to be of the same size or speed as the primary SANReplicated data isn’t always full set of data.You may not need disaster recovery for everything.DR Environments: Where Old SANs Go To Die.
- 23. Thing 2:A Replication MechanismReplication between SANs must occur.There are two commonly-accepted ways to accomplish this….
- 24. Thing 2:A Replication MechanismReplication between SANs must occur.There are two commonly-accepted ways to accomplish this….SynchronouslyChanges are made on one node at a time. Subsequent changes on primary SAN must wait for ACK from backup SAN.AsynchronouslyChanges on backup SAN will eventually be written. Changes queued at primary SAN to be transferred at intervals.
- 25. Thing 2:A Replication MechanismSynchronouslyChanges are made on one node at a time. Subsequent changes on primary SAN must wait for ACK from backup SAN.
- 26. Thing 2:A Replication MechanismAsynchronouslyChanges on backup SAN will eventually be written. Are queued at primary SAN to be transferred at intervals.
- 27. Class DiscussionWhich would you choose? Why?Class DiscussionWhich would you choose? Why?
- 28. Synchronous
- 29. Assures no loss of data.
- 30. Requires a high-bandwidth and low-latency connection.
- 31. Write and acknowledgement latencies impact performance.
- 32. Requires shorter distances between storage devices.
- 33. Asynchronous
- 34. Potential for loss of data during a failure.
- 35. Leverages smaller-bandwidth connections, more tolerant of latency.
- 37. Potential to stretch across longer distances.
- 38. Your Recovery Point Objective makes this decision…Thing 2½:Replication Processing LocationThere are also two locations for replication processing…
- 39. Thing 2½:Replication Processing LocationThere are also two locations for replication processing…Storage LayerReplication processing is handled by the SAN itself.Agents are often installed to virtual hosts or machines to ensure crash consistency.Easier to set up, fewer moving parts. More scalable.Concerns about crash consistency.OS / Application LayerReplication processing is handled by software in the VM OS.This software also operates as the agent.More challenging to set up, more moving parts. More installations to manage/monitor. Scalability and cost are linear.Fewer concerns about crash consistency.
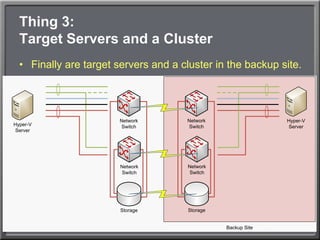
- 40. Thing 3:Target Servers and a ClusterFinally are target servers and a cluster in the backup site.
- 41. Clustering’s Sordid HistoryWindows NT 4.0Microsoft Cluster Service “Wolfpack”.“As the corporate expert in Windows clustering, I recommend you don’t use Windows clustering.”
- 42. Clustering’s Sordid HistoryWindows NT 4.0Microsoft Cluster Service “Wolfpack”.“As the corporate expert in Windows clustering, I recommend you don’t use Windows clustering.”Windows 2000Greater availability, scalability. Still painful.Windows 2003Added iSCSI storage to traditional Fibre Channel.SCSI Resets still used as method of last resort (painful).
- 43. Clustering’s Sordid HistoryWindows NT 4.0Microsoft Cluster Service “Wolfpack”.“As the corporate expert in Windows clustering, I recommend you don’t use Windows clustering.”Windows 2000Greater availability, scalability. Still painful.Windows 2003Added iSCSI storage to traditional Fibre Channel.SCSI Resets still used as method of last resort (painful).Windows 2008Eliminated use of SCSI Resets.Eliminated full-solution HCL requirement.Added Cluster Validation Wizard and pre-cluster tests.Clusters can now span subnets (ta-da!)
- 44. Clustering’s Sordid HistoryWindows NT 4.0Microsoft Cluster Service “Wolfpack”.“As the corporate expert in Windows clustering, I recommend you don’t use Windows clustering.”Windows 2000Greater availability, scalability. Still painful.Windows 2003Added iSCSI storage to traditional Fibre Channel.SCSI Resets still used as method of last resort (painful).Windows 2008Eliminated use of SCSI Resets.Eliminated full-solution HCL requirement.Added Cluster Validation Wizard and pre-cluster tests.Clusters can now span subnets (ta-da!)Windows 2008 R2Improvements to Cluster Validation Wizard and Migration Wizard.Additional cluster services.Cluster Shared Volumes (!) and Live Migration (!)
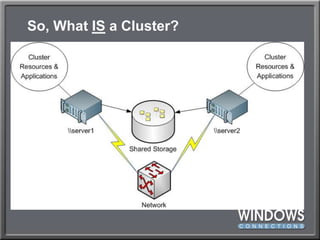
- 45. So, What IS a Cluster?
- 46. So, What IS a Cluster?Quorum Drive & Storage for Hyper-V VMs
- 47. So, What IS a Multi-Site Cluster?
- 48. Quorum: Windows Clustering’s Most Confusing ConfigurationEver been to a Kiwanis meeting…?
- 49. Quorum: Windows Clustering’s Most Confusing ConfigurationEver been to a Kiwanis meeting…?A cluster “exists” because it has quorum between its members. That quorum is achieved through a voting process.Different Kiwanis clubs have different rules for quorum.Different clusters have different rules for quorum.
- 50. Quorum: Windows Clustering’s Most Confusing ConfigurationEver been to a Kiwanis meeting…?A cluster “exists” because it has quorum between its members. That quorum is achieved through a voting process.Different Kiwanis clubs have different rules for quorum.Different clusters have different rules for quorum.If a cluster “loses quorum”, the entire cluster shuts down and ceases to exist. This happens until quorum is regained.This is much different than a resource failover, which is the reason why clusters are implemented.Multiple quorum models exist.
- 51. Four Options for QuorumNode and Disk MajorityNode MajorityNode and File Share MajorityNo Majority: Disk Only
- 52. Four Options for QuorumNode and Disk MajorityNode MajorityNode and File Share MajorityNo Majority: Disk Only
- 53. Four Options for QuorumNode and Disk MajorityNode MajorityNode and File Share MajorityNo Majority: Disk Only
- 54. Four Options for QuorumNode and Disk MajorityNode MajorityNode and File Share MajorityNo Majority: Disk Only
- 55. Quorum in Multi-Site ClustersNode and Disk MajorityNode MajorityNode and File Share MajorityNo Majority: Disk OnlyMicrosoft recommends using the Node and File Share Majority model for multi-site clusters.This model provides the best protection for a full-site outage.Full-site outage requires a file share witness in a third geographic location.
- 56. Quorum in Multi-Site ClustersUse the Node and File Share QuorumPrevents entire-site outage from impacting quorum.Enables creation of multiple clusters if necessary.Third Site for Witness Server
- 57. I Need a Third Site? Seriously?Here’s where Microsoft’s ridiculous quorum notion gets unnecessarily complicated…What happens if you put the quorum’s file share in the primary site?The secondary site might not automatically come online after a primary site failure.Votes in secondary site < Votes in primary siteLet’s count on our fingers…
- 58. I Need a Third Site? Seriously?Here’s where Microsoft’s ridiculous quorum notion gets unnecessarily complicated…What happens if you put the quorum’s file share in the secondary site?A failure in the secondary site could cause the primary site to go down.Votes in secondary site > votes in primary site.More fingers…This problem gets even weirder as time passes and the number of servers changes in each site.
- 59. I Need a Third Site? Seriously?Third Site for Witness Server
- 61. Multi-Site Cluster Tips/TricksInstall servers to sites so that your primary site always contains more servers than backup sites.Eliminates some problems with quorum during site outage.
- 62. Multi-Site Cluster Tips/TricksManage Preferred Owners & Persistent Mode options.Make sure your servers fail over to servers in the same site first.But also make sure they have options on failing over elsewhere.
- 64. Multi-Site Cluster Tips/TricksManage Preferred Owners & Persistent Mode options.Make sure your servers fail over to servers in the same site first.But also make sure they have options on failing over elsewhere.Consider carefully the effects of Failback.Failback is a great solution for resetting after a failure.But Failback can be a massive problem-causer as well.Its effects are particularly pronounced in Multi-Site Clusters.Recommendation: Turn it off, (until you’re ready).
- 66. Multi-Site Cluster Tips/TricksResist creating clusters that support other services.A Hyper-V cluster is a Hyper-V cluster is a Hyper-V cluster.
- 67. Multi-Site Cluster Tips/TricksResist creating clusters that support other services.A Hyper-V cluster is a Hyper-V cluster is a Hyper-V cluster.Use disk “dependencies” as Affinity/Anti-Affinity rules.Hyper-V all by itself doesn’t have an elegant way to affinitize.Setting disk dependencies against each other is a work-around.
- 68. Multi-Site Cluster Tips/TricksResist creating clusters that support other services.A Hyper-V cluster is a Hyper-V cluster is a Hyper-V cluster.Use disk “dependencies” as Affinity/Anti-Affinity rules.Hyper-V all by itself doesn’t have an elegant way to affinitize.Setting disk dependencies against each other is a work-around.Add Servers in PairsEnsures that a server loss won’t cause site split brain.This is less a problem with the File Share Witness configuration.
- 69. Multi-Site Cluster Tips/TricksSegregate traffic!!!
- 70. Most Important!Ensure that networking remains available when VMs migrate from primary to backup site.
- 71. Most Important!Ensure that networking remains available when VMs migrate from primary to backup site.Clustering can span subnets!This is good, but only if you plan for it…Remember that crossing subnets also means changing IP address, subnet mask, gateway, etc, at new site.This can be automatically done by using DHCP and dynamic DNS, or must be manually updated.DNS replication is also a problem. Clients will require time to update their local cache.Consider reducing DNS TTL or clearing client cache.
- 72. Implementing Affordable Disaster Recovery with Hyper-V andMulti-Site ClusteringGreg Shields, MVPPartner and Principal Technologistwww.ConcentratedTech.com
- 73. This slide deck was used in one of our many conference presentations. We hope you enjoy it, and invite you to use it within your own organization however you like.For more information on our company, including information on private classes and upcoming conference appearances, please visit our Web site, www.ConcentratedTech.com. For links to newly-posted decks, follow us on Twitter:@concentrateddon or @concentratdgregThis work is copyright ©Concentrated Technology, LLC