Induction treatment in Kidney transplantation chaken 2017
- 2. Scope § T-cell mediated rejection and immunosuppression § Definition and purpose of induction therapy § Classification § Depleting agents § Non depleting agents § Mechanism / Dose / Side effect / clinical study support § KDIGO,TCC guideline
- 11. Sites of actions of immunosuppression
- 12. Scope § T-cell mediated rejection and immunosuppression § Definition and purpose of induction therapy § Classification § Depleting agents § Non depleting agents § Mechanism / Dose / Side effect / Trial support § KDIGO,TCC guideline
- 13. Definition of induction therapy § Treatment with a biologic agent before or at the time or immediately after transplantation KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients.Am JTransplant 2009; 9 Suppl 3:S1.
- 14. Purpose of induction therapy § To deplete or modulate T-cell responses at time of antigen presentation § Reducing acute rejection § Allowing reduction of other components, such as CNIs or corticosteroids KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients.Am JTransplant 2009; 9 Suppl 3:S1.
- 15. Scope § T-cell mediated rejection and immunosuppression § Definition and purpose of induction therapy § Classification § Depleting agents § Non depleting agents § Mechanism / Dose / Side effect / Trial support § KDIGO,TCC guideline
- 16. Classification of induction agents Polyclonal Thymoglobulin ATGAM Monoclonal Basiliximab Daclizumab Alemtuzumab OKT3 Non-depleting agents Basiliximab Daclizumab Depleting agents Thymoglobulin Alemtuzumab OKT3
- 17. Induction Antibodies Monoclonal Polyclonal Homogenous Heterogenous Murine hybridoma techniques Or genetic engineered for chimeric or humanized modifications. Harvesting serum from animals previously inoculated with human thymocytes or lymphocytes Predictability Variable reaction Smaller dose Large dose More susceptible for immune elimination Less susceptible for immune elimination Mary Ann Lim, et al..Transplantation Reviews 31 (2017) 10–17
- 18. Development of Monoclonal Ab
- 19. Depleting agents Thymoglobulin, OKT-3, Alemtuzumab § T-cell lysis and/or clearance circulating lymphocytes § Extensive release of cytokines due to cell destruction § Reconstitution of immune system in long time § Responsible for many adverse effects like infections and malignancy.
- 21. Anti-Thymoglobuline § Preparation made by immunization of animals with human lymphoid tissue § Rabbits ➠ § Thymoglobulin (Genzyme) § Anti-T-lymphocyte immune globulin (ATG- Fresinius) § Horses ➠ ATGAM Handbook of kidney transplantation / edited by Gabriel M. Danovitch - 5th ed.
- 22. Types of ATG
- 23. § Depletion of thymus produced lymphocytes through CD2, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD11a, and CD18 an multiple of mechanisms § Complement-dependent lysis (Major pathway) § Opsonization § Phagocystosis § Repopulation leads to expansion of regulatory- suppressor functions Kirk AD. Induction immunosuppression.Transplantation. 2006; 82:593–602 Lopez M et al . J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17:2844–53 ATG: mechanism of action
- 24. ATG: Dosage/administration § 1.5 mg/kg/day (range 1-4 ) given in 5 days § Infuse slowly 4 – 8 hrs via central vein § Premedication to prevent adverse effects ➪ methylprednisolone ➪ diphenhydramine ➪ acetaminophen
- 25. Anti-Thymocyte globulin § First dose in OR before allograft perfusion to prevent ischemic reperfusion injury and reduction of DGF § Less frequent intervals if § platelet 50,000–75,000 platelets/mm3 § WBC 2,000–3,000 cells/mm3. § Discontinuation : platlet < 50,000/mm3 or WBC <2,000 cells/mm3.
- 26. ATG: Adverse effects § Severe first dose reaction (Cytokine release syndrome) § Chills, fever, arthralgias § Hypotension § Thrombophleblitis/ peripheral vein thrombosis § Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia § Infection esp CMV § Anaphylaxis § Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) risk factors include : § Repeated courses of depleting antibodies § EBV Ab D+/R-
- 27. Graft survival in ATG induction Vs No induction D.Thibaudin , et al; Nephrol DialTransplant (1998) 13: 711–715 Post –Transplantation (Days) Probability of graft survival Decreased the incidence of acute rejection Increased graft survival Improved graft function ATG NO induction RR 0.6 (0.4-0.9)
- 28. Three arms study comparing induction ATG Vs Tacrolimus § Rate of biopsy-proven acute rejection over 6 mo B. Charpentier et al;Transplantation 75(6):844-51 · March 2003 Acute rejection was significantly lower in ATG-Tac More hematologic and infectious events in both ATG induction ATG groups CMV infection was significantly higher
- 29. rATG VS ATGAM in adult KTRs Brennan DC et al Transplantation 67(7):1011-8 · May 1999
- 30. rATG VS ATGAM in adult KTRs Brennan DC et al Transplantation 67(7):1011-8 · May 1999 rATG less frequent and less severe rejection, a better event-free survival, less CMV disease, fewer serious adverse events, but more frequent early leukopenia
- 31. Brennan DC et al; N Engl J Med. 2006 Nov 9;355(19):1967-77.
- 32. Rabbit ATG versus Basilliximab in High risk patients Brennan DC et al; N Engl J Med. 2006 Nov 9;355(19):1967-77. Donor risk factors - Acute tubular necrosis, - High-dose inotropic support Recipient risk factors - Repeated transplantation - PRA>20% - Black race - MM ≥ 1
- 33. Rabbit ATG versus Basilliximab in High risk patients Brennan DC et al; N Engl J Med. 2006 Nov 9;355(19):1967-77. In CDKT ,high risk pts : ATG reduced incidence of acute rejection But SAME incidence of DGF , patient and graft survival
- 34. Frequency of Adverse Events at 12 Months Brennan DC et al; N Engl J Med. 2006 Nov 9;355(19):1967-77.
- 35. ATG for induction in KTRs 2010-2016:9studies8956participants § Prevented acute graft rejection and improvement in graft survival (RR 0.63) compare with no treatment § Benefits on graft rejection similar with or w/o CNI. § Increased CMV infection, leucopenia and thrombocytopenia (RR 1.55) § Uncertain effects on DGF, PTLD and NODAT Penny Hill and Cross Cochrane Kidney andTransplant Group ,The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by JohnWiley ; Jan 2017
- 37. IL-2 RA: Mechanism of action § Binds the CD25 antigen (interleukin-2 receptor alpha- chain) at surface of activated Tlymphocytes )
- 38. IL-2 RA § Humanized Anti-CD25 monoclonal antibodies § Basiliximab (Simulect) § Chimeric, 75% human 25% murine origin § Daclizumab (Zenapex) § Humanized, 90% human 10% murine origin
- 39. IL2RA(Anti CD25 Ab) : Dose Basiliximab: § 20 mg IV given 2 hours prior to KT transplant, followed by a second 20 mg dose on post-op day 4. § Complete saturation of CD25 receptor for 30-45 days Daclizumab: § 1 mg/kg within 24 hours of KT plus additional 4 doses of 1 mg/kg at a schedule of every 2 weeks after KT. § Causes receptor saturation that lasts up to 120 days
- 40. IL2RA(Anti CD25 Ab) : Side effect § Common insomnia , tremor , headache § Low immunogenicity, not induce first-dose reaction § Lack of risk of infection or cancer § Daclizumab was “retired” from market by the manufacturer at the end of 2009 § Basiliximab will remain the only IL-2RA in the market
- 41. Clinically diagnosed acute allograft rejection at 1 year after KT IL-2Ra versus placebo/no treatment. Interleukin 2 receptor antagonists for renal transplant recipients: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Webster AC, et al,Transplantation 77(2):166-76 · February 2004 Seven patients would need treatment with I2Ra in addition to standard therapy, to prevent one patient from undergoing rejection
- 42. Cost-effectiveness of induction immunosuppression in KT Rachael L. Morton Et al Nephrol DialTransplant (2009) 24 (7): 2258-2269.
- 43. Rabbit ATG versus Basilliximab in High risk patients Brennan DC et al; N Engl J Med. 2006 Nov 9;355(19):1967-77. In CDKT ,high risk pts : ATG reduced incidence of acute rejection But SAME incidence of DGF , patient and graft survival
- 44. Meta analysis of IL- 2 RA for kidney transplantation § IL-2 RA Vs Placebo : § No difference in mortality rate § 25% reduction in graft loss ( inc death with functioning graft ) at one year § 24 studies, 4672 par- ticipants: RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.62 to 0.90 § IL-2 RA Vs ATG : § No difference in mortality rate , graft loss (inc death with function at any time point) § 25% increased in BPAR for IL2Ra over ATG but fewer side effects and less cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease and malignancy. § 8 studies, 1106 participants: RR 1.30 95% CI 1.01 to 1.67 § IL-2 RA Vs other mono or polyclonal Ab § No difference in treatment effect compared with muromonab-CD3 § Muromonab-CD3 increased adverse reactions over IL2Ra § No difference in effect demonstrated for IL2Ra compared versus alemtuzumab and rituximab for mortality, graft loss, acute rejection or CMV infection Webster AC, Ruster LP, et al.. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010; :CD003897.
- 46. MUROMONAB- CD3(OKT3) § OKT3 is a murine monoclonal antibody directed against the CD3 receptor. § Inert T-cell , removed via opsonization / phagocytosis. § A substantial T-cell loss could occur within the first few hours after an initial dose. § As T-cell fall, several T-cell derived cytokines (eg,TNF, IL-2, and IFN-γ) are released into circulation.
- 47. MUROMONAB- CD3(OKT3) Dosage § Dosage: 5mg iv bolus, daily for 10 days .
- 48. MUROMONAB- CD3(OKT3) Side effect § Cytokine release syndrome typically 45 min. after injection. § Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema § Neurologic complications § mild headache, § aseptic meningitis § severe encephalopathy § Neutralizing Ab (anti-OKT3) seen in 50% of pts.
- 49. ALEMTUZUMAB
- 50. Alemtuzumab: Action § Recombinant DNA-derived humanized monoclonal antibody directed against CD52 § CD52 is present on all B- and T-cells macrophages, NK cells § Trigger antibody-dependent lysis of T cell § FDA approved in refractory B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment
- 51. Alemtuzumab: Dosage Dosing: § 20-30 mg on the day of transplantation infused 4-8 hr (over peripheral line)
- 52. Alemtuzumab: Side effect § Neutropenia (70%) § Thrombocytopenia (52%) § Anemia (47%) § Nausea , vomiting (41%), § Diarrhea (22%) § Cytokine release syndrome (less than ATG) § AIHA(<5%) § Autoimmune thyroid disease (5%) Hanaway MJ, et al; N Engl J Med. 2011;364(20):1909-1919
- 53. Hanaway MJ, et al; N Engl J Med. 2011;364(20):1909-1919
- 54. Alemtuzumab Induction in KT Hanaway MJ, et al; N Engl J Med. 2011;364(20):1909-1919 Conclusion: biopsy-confirmed acute rejection lower than with conventional only in low immunological risk • N= 474 • Prospective RCT • Alemtuzumab Vs Convention therapy • Follow up 36 mo INTAC STUDY
- 55. Alemtuzumab Induction in KT Hanaway MJ, et al; N Engl J Med. 2011;364(20):1909-1919 Late acute rejection (after first 12 months) was more common with alemtuzumab, but this was not statistically significant (10 versus 2 percent), • N= 474 • Prospective RCT • Alemtuzumab Vs Convention therapy • Follow up 36 mo
- 56. Alemtuzumab induction in KT: A meta-analysis and systemic review § 6 RCTs were included § Lower incidence of BPAR over traditional Ab (RR 0.63, CI 0.45–0.87, p=0.005) on low risk patients § No significance in terms of DGF , death, graft loss, and safety profile X. Zhang et al. /Transplant Immunology 27 (2012) 63–68
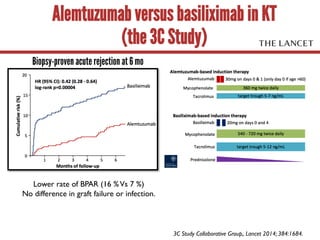
- 57. Alemtuzumab versus basiliximab in KT (the 3C Study) Biopsy-proven acute rejection at 6 mo Lower rate of BPAR (16 %Vs 7 %) No difference in graft failure or infection. 3C Study Collaborative Group,. Lancet 2014; 384:1684.
- 58. Alemtuzumab for induction in KTRs 2010-2016:9studies8956participants § Alemtuzumab plus steroid minimisation reduced acute rejection compared to ATG at 1 year (RR 0.57) § Alemtuzumab had uncertain effects on death at 1 year, , graft loss and death-censored graft loss compared to ATG § CrCl was lower with alemtuzumab plus steroid minimisation at 2 years (-12.86 mL/min) compared to ATG plus triple maintenance. § The effect of alemtuzumab with steroid minimisation on NODAT was uncertain, compared to ATG with steroid maintenance. Penny Hill and Cross Cochrane Kidney andTransplant Group ,The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by JohnWiley ; Jan 2017
- 59. Rituximab § Increasing evidence B cells may have a role by their ability to act as APS and T-cell activators Mary Ann Lim, et al..Transplantation Reviews 31 (2017) 10–17
- 60. Rituximab § Useful for induction with ABO-incompatible transplantation, with outcomes comparable with splenectomy § There was limited evidence that rituximab reduced rejection and improved survival for HLA- incompatible transplants. Macklin PS, et al.Transplantation 2014; 98:794.
- 61. Scope § T-cell mediated rejection and immunosuppression § Definition and purpose of induction therapy § Classification § Depleting agents § Non depleting agents § Mechanism / Dose / Side effect / Trial support § KDIGO,TCC guideline
- 62. Induction recommendation § We recommend starting a combination of immunosuppressive medications before, or at the time of, kidney transplantation. (1A) § We recommend including induction therapy with a biologic agent as part of the initial immunosuppressive regimen in KTRs. (1A) § We recommend that an IL2-RA be the first line induction therapy. (1B) § We suggest using a lymphocyte-depleting agent, rather than an IL2RA, for KTRs at high immunologic risk. (2B) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients.Am JTransplant 2009; 9 Suppl 3:S1.
- 63. High risk factors for acute rejection § Number of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatches (A) § Younger recipient age (B) § Older donor age (B) § African-American ethnicity (in the United States) (B) § PRA >0% (B) § Presence of a donor-specific antibody (B) § Blood group incompatibility (B) § Delayed onset of graft function (B) § Cold ischemia time >24 hours (C) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients.Am JTransplant 2009; 9 Suppl 3:S1.
- 68. No induction > Basilliximab > ATG Induction regimen Low risk § Zero HLA mismatch § Live donor § Caucasian ethnicity § Low PRA § No DSA § Blood group compatibility § Immediate graft function § Short CIT § First transplant High risk § Increased HLA mismatches § Younger recipient and older donor age § African-American ethnicity § High PRA § Presence of DSA § Blood group incompatability § Delayed graft function § Long CIT § Retransplant
- 69. Conclusion § Immunosuppression is not a one-size-fits-all practice. § Balance the benefit of rejection prevention against risk of over-immunosuppression. § Immunological risk § Co morbid disease of KTRs § Overall efficacy § New studies required for clinically meaningful outcomes