Installing, Programming & Commissioning of Power System Protection Relays and Hardware
- 1. Installing, Programming & Commissioning of Power System Protection Relays and Hardware Technology Training that Works
- 2. Need for protective apparatus For efficiency and economy power system must be kept in operation continuously without major breakdowns Methods to avoid breakdown Implement a system using components, which should not fail and which require minimal maintenance to maintain the continuity of service. However, implementing such a system is neither economical nor feasible, except for small systems. Anticipate any possible effects or failures that may cause a long-term shutdown of a system, which in turn may take a longer time to bring the system back to its normal operation. Restrict the disturbances during such failures to a limited area and maintain power distribution to the remaining areas. www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 3. Basic requirements of protection • main functions: • Safeguard the entire system to maintain continuity of supply. • Minimize damage and repair costs where it senses a fault. • Ensure safety of personnel. • protection must have the following qualities: • Selectivity • Stability • Sensitivity • Speed www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 4. Basic components of protection • Basic components A fuse self destructs and carries the currents in a power circuit continuously and sacrifices itself by blowing under abnormal conditions. Voltage transformers and current transformers measure these basic parameters and are capable of providing accurate measurement during fault conditions without failure. Relays, which in turn isolate the circuits by opening the faulty circuits. circuit breakers are used to isolate the faulty circuits. batteries are used to ensure uninterrupted power to relays and breaker coils www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 5. Simple distribution systems www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 6. Radial distribution systems Advantages: If a fault occurs at T2 then only the protection on one leg connecting T2 is called into operation to isolate this leg. The other consumers are not affected. Disadvantages: If the conductor to T2 fails, then supply to this particular consumer is lost completely and cannot be restored until the conductor is replaced/repaired. www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 7. Radial distribution system with parallel feeders www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 8. Ring main distribution system Advantage : Essentially, meets the requirements of two alternative feeds to give 100% continuity of supply, whilst saving in cabling/copper compared to parallel feeders. Disadvantage : The fault currents in particular could vary depending on the exact location of the fault. www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 9. Active faults Active fault must be cleared as quickly as possible, otherwise there will be: • Increased damage at fault location. Fault energy = I2 × Rf × t where t is time in seconds. • Danger to operating personnel (flashes due to high fault energy sustaining for a long time). • Danger of igniting combustible gas in hazardous areas, such as methane in coal mines which could cause horrendous disaster. • Increased probability of ground faults spreading to healthy phases. • Higher mechanical and thermal stressing of all items of plant carrying the fault current, particularly transformers whose windings suffer progressive and cumulative deterioration because of the enormous electro-mechanical forces caused by multiphase faults proportional to the square of the fault current. • Sustained voltage dips resulting in motor (and generator) instability leading to extensive shutdown at the plant concerned and possibly other nearby plants connected to the system. www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 10. Types of faults on a three-phase system (A) Phase-to-ground fault (B) Phase-to-phase fault (C) Phase-to-phase-to-ground fault (D) Three-phase fault (E) Three-phase-to-ground fault (F) Phase-to-pilot fault* (G) Pilot-to-ground fault* www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 11. Symmetrical and asymmetrical faults www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 12. Total asymmetry factor chart www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 13. System grounding Problems Phase faults: High fault currents. Only limited by inherent impedance of power supply. Ground faults: Solid grounding means high ground fault currents. Only limited by inherent zero sequence impedance of power system. Consequence 1) Heavy currents damage equipment extensively–danger of fire hazard. 2) This leads to long outage times–lost production, lost revenue. 3) Heavy currents in ground bonding gives rise to high touch potentials–dangerous to human life. 4) Large fault currents are more hazardous in igniting gases–explosion hazard. www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 14. Solid grounding Advantages: • Neutral held effectively at ground potential • Phase-to-ground faults of same magnitude as phase-to-phase faults so no need for special sensitive relays • Cost of current limiting device is eliminated • Grading insulation towards neutral point N reduces size and cost of transformers Disadvantages: • As most system faults are phase-to-ground, severe shocks are more considerable than with resistance grounding • Third harmonics tend to circulate between neutrals www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 15. Resistance grounding Advantages: • Limits electrical and mechanical stress on system when a ground fault occurs, but at the same time, current is sufficient to operate normal protection equipment Disadvantages: • Full line-to-line insulation required between phase and ground www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 16. Reactance grounding Arc suppression coil (Petersen coil) Reactance grounding www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 17. Grounding Grounding via neutral grounding compensator www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 18. Fuses Fuses Re-wireable type Cartridge type Disadvantages : 1) Open to abuse due to incorrect rating of replacement elements hence affording incorrect protection 2) Deterioration of element as it is open to the atmosphere www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 19. Selection of fuses Fuse selection depends on a number of factors: • Maximum fault kVA of circuit to be protected • Voltage of circuit Full load current of circuit Factors taken into account while selecting a fuse Degree of overcurrent protection required other protective apparatus level of overcurrent required www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 20. Rules of thumb Transformers, fluorescent lighting circuits Transient switching surges - take next highest rating above full load current. Capacitor circuits Select fuse rating of 25% or greater than the full load rating of the circuit to allow for the extra heating by capacitance effect. Motor circuits Starting current surge normally lasts for 20 seconds. Squirrel cage induction motors: - Direct-on-line takes about 7 times full load current - 75% tap autotransformer takes about 4 times full load current - 60% tap autotransformer takes about 2.5 times full load current - Star/delta starting takes about 2.5 times full load current www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
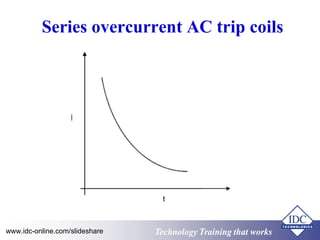
- 21. Series overcurrent AC trip coils www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
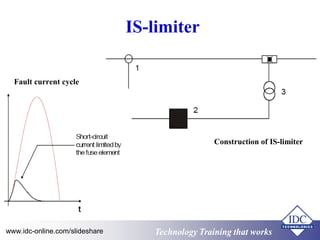
- 22. IS-limiter Construction of IS-limiter www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 23. IS-limiter Construction of IS-limiter Fault current cycle www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
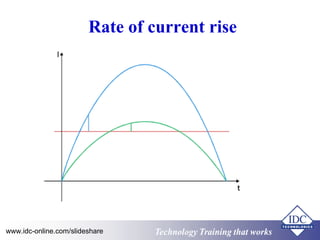
- 24. Rate of current rise www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 25. Practical use of IS-limiter www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 26. Instrument transformers The main tasks of instrument transformers are: • To transform currents or voltages from usually a high value to a value easy to handle for relays and instruments. • To insulate the relays, metering and instruments from the primary high voltage system. • To provide possibilities of standardizing the relays and instruments, etc. to a few rated currents and voltages. www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
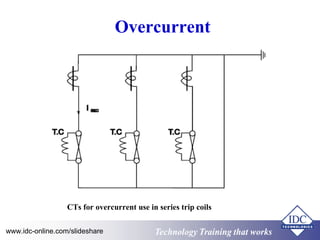
- 27. Overcurrent CTs for overcurrent use in series trip coils www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss
- 28. DO YOU WANT TO KNOW MORE? If you are interested in further training or information, please visit: http://idc-online.com/slideshare www.idc-online.com/slideshare Technology TTrraaiinniinngg tthhaatt WWoorrkkss