Introduction to RFID
- 1. Radio Frequency IDentification PRESENTED BY ILA SHARMA MTECH ECE 102001
- 2. OUTLINE • DEFINITION • HISTORY • COMPONENTS • RFID SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE • ELECTRONIC PRODUCT CODE(EPC) • RFID VS BARCODE • BENEFITS OF RFID • ISSUES/ CONCERNS
- 3. INTRODUCTION TO RFID • RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that enables the electronic and wireless labeling and identification of objects, humans and animals. • An alternative to Barcode. • RFID is also called dedicated short range communication (DSRC).
- 4. HISTORY • Invented in 1948 by Harry Stockman. • Initial application was during World War II-The United Kingdom used RFID devices to distinguish returning English airplanes from inbound German ones. RADAR was only able to signal the presence of a plane, not the kind of plane it was.. • Came into commercial use only in 1990s.
- 5. COMPONENTS • Tag (Transponder) – Chip – Antenna • Reader (Interrogator) – RF Module (Transmitter and Receiver) – Antenna • Host Computer – Middleware
- 6. Components of RFID(cont’d) • A RFID tag is an object that can be stuck on or incorporated into a product, animal, or person for the purpose of identification using radio waves . • Tags ( Chip + Antenna). -Tag types -Active. -Passive. -Frequency at which these tags are used -Between 125 to 134 kilohertz. -At 13.56 megahertz. -Between 868 to 956 megahertz. -At 2.45 gigahertz.
- 7. Tags Characteristic • Means by which transponder is powered • Data carrying options • Data read rates • Physical forms • Costs
- 8. Active and Passive Tags • Active tags – Powered by an internal battery – Finite lifetime (because of battery) – Greater range – Better noise immunity – Higher data transmission rates
- 9. Active and Passive Tags • Passive tags – Operate without battery – Derive power from the field generate by the reader – Less expensive – Unlimited life – Subject to noise – Require more powerful readers
- 10. Components of RFID(cont’d) • Interrogator ( Antenna + Reader ) : Interrogator are used to read the tags. • Middleware: Middleware is the needed interface between the existing company databases & information management software. • Middleware provides a range of functions: -Data filtering -System monitoring -Multiple reader co-ordination.
- 12. RFID Operation • Host Manages Reader(s) and Issues Commands • Reader and tag communicate via RF signal • Carrier signal generated by the reader (upon request from the host application) • Carrier signal sent out through the antennas • Carrier signal hits tag(s) • Tag receives and modifies carrier signal – “sends back” modulated signal. • Antennas receive the modulated signal and send them to the Reader • Reader decodes the data – Results returned to the host application
- 13. Electronic Product Code Header - Tag version number EPC Manager - Manufacturer ID Object class - Manufacturer’s product ID Serial Number - Unit ID With 96 bit code, 268 million companies can each categorize 16 million different products where each product category contains up to 687 billion individual units
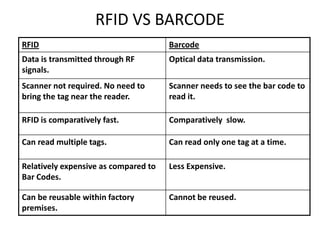
- 14. RFID VS BARCODE RFID Barcode Data is transmitted through RF Optical data transmission. signals. Scanner not required. No need to Scanner needs to see the bar code to bring the tag near the reader. read it. RFID is comparatively fast. Comparatively slow. Can read multiple tags. Can read only one tag at a time. Relatively expensive as compared to Less Expensive. Bar Codes. Can be reusable within factory Cannot be reused. premises.
- 15. BENEFITS OF RFID • Increased stock visibility and availability. • Reduced theft in the supply chain. • Improved Product Selection • Easier Identification on Recalls • Unifying Auto-ID technology • Line of sight is not required • Longer read ranges • Faster: hundreds of items can be scanned in one read
- 16. Issues / Concerns • Cost of RFID technology. • Active RFID life – 2 to 4 years. • Extreme weather. • Security concerns-illegal tracking of RFID tags. • Global standardization. • Environmental concern- recycling
- 17. Uses of RFID • Used where unique identification is needed. • Large Retail companies – Product Tracking. • Hospitals & Nursing Homes – Patient Tagging • Airports – Baggage Tracking. • RFID Sensors to sense temperature, movement, radiation, food quality. • Passports-UK, Australia, Finland, Ireland. • RFID is used in Libraries. • Replacing Barcodes
- 18. Initiatives in RFID • Patni Computer Systems Lab – Implemented Animal Tracking System • Wipro Technologies - Member of the Electronic Product Code (EPC) - Setting up a lab to study RFID - Working on pilot projects • TCS have tied up with Hyderabad university to produce RFID tagged mark sheets & degrees to deter use of fake degree. • Intel icon - pilot project for BEL Bangalore, tags installed on employee buses. Buses inside the BEL campus were tracked with the aim of gauging employee punctuality.
- 19. Some links… • www.rfidjournal.com • www.computerworld.com • www.rfidusa.com • RFID Handbook • www.uh.edu/gartner
- 20. THANK YOU