Java essentials for hadoop
- 1. Java Essentials for Hadoop
- 2. Agenda What is Java ? Features of Java How Java Works Java Data Types Java Operators Statements & Blocks in Java Java Class Java Basic Constructs Creating an Object Arrays
- 3. What is Java ? Java is a high level programming language developed by Sun Microsystems and released in November 1995. Java can be used to create complete applications that may run on a single computer or be distributed among servers and clients in a network. Java is Object-Oriented and follows the principal of “write once run anywhere” codes.
- 4. Features of Java Simple Object Oriented Multithreaded Distributed Platform Independent Secure Robust
- 5. What is JDK and JRE ? JDK + Development tools Compiler Debugger JRE JVM Utility Classes
- 6. How Java Works ? Source Code Byte Code JVM JIT Compiler Java Interpreter Runtime System Output of the program Java Compiler Hexadecimal format It is used to speed up the execution Converts total byte code into machine code
- 7. Data Types Data Type Size Default value Boolean 1 bit False char 2 bytes 'u0000' byte 1 byte 0 short 2 bytes 0 int 4 bytes 0 long 8 bytes 0L float 4 bytes 0.0f double 8 bytes 0.0d String(any object) - null Primitive Data Types Non-primitive Data Types (Reference type) 1. Class Type 2. Interface Type 3. Array type
- 8. Operators Provide a way to perform different operations on variables. Operator Type operators Assignment = Arithmetic + , - , * , / Relational < , > , <= , >= , == , != Logical && , || , ! Bitwise &, |, ^, >>, << Unary ++ , --, +, -, !
- 9. Statements & Blocks in JAVA Statements are always terminated by a semi-colon(;) A block is a compound statement enclosed in curly brackets. Statement forms a complete command to be executed. class Stat { Boolean flag ; //statement 1 Int x = 20 ; //Statement 2 . . } Open braces for a block End of block, using close braces
- 10. A class can be defined as a template/blue print that describes the behaviors and states that object of its type support. Objects have states and behaviors. Example: Bicycles have state (current gear, current pedal cadence, two wheels, number of gears) and behavior (braking, accelerating, slowing down, changing gears). An object is an instance of a class. Java Class
- 11. Example of a class public class hello { public static void main(String[] args) { int number = 10; //variable System.out.println("Hello"); System.out.println(number); } } class Myclass { //data members //constructors // methods or member functions }
- 12. Method Public static void myFunction(arg1, arg2, arg3) { } Modifier Java keyword return type function name Any number of arguments //Body of the method
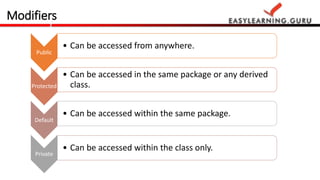
- 13. Public • Can be accessed from anywhere. Protected • Can be accessed in the same package or any derived class. Default • Can be accessed within the class only. Private • Can be accessed within the same package. Modifiers
- 14. Java Basic Constructs If…else case Switch Case Loops in Java – for loop, while loop, do while loop
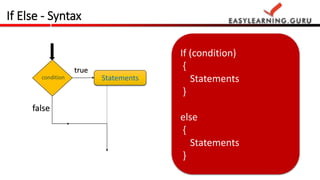
- 15. If Else - Syntax If (condition) { Statements } else { Statements } Statements true false condition
- 16. Switch - Syntax Switch(x) { Case 1: Statements Case 2: Statements default : Statements } Case 1 Statements Statements Case 2 true false true false default End of the switch Statement
- 17. For Loop - Syntax for (initialization; condition; increment/decrement;) { statement 1; statement 2; … } Initialization Inside the for loop true false Increment/ decrement End of for loop condition
- 18. While Loop - Syntax while (<condition>) { statement1; … } Initialization Inside the for loop true false Increment/ decrement End of for loop condition
- 19. Do While Loop Syntax do { statement 1; statement 2; …… } while (<condition>) ; Initialization Inside the do while loop true false Increment/ decrement End of for loop condition condition
- 20. Creation of the Object Class_name object_name = new class_name(); Name of the class Creates a reference object Allocate memory Constructor of the class Creates a new object
- 21. An array is a list of similar elements. An array has a fixed: - name - type - length These must be declared when the array is created. Array size cannot be changed during the execution of the code. Arrays










![Example of a class
public class hello {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int number = 10; //variable
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println(number);
}
}
class Myclass
{
//data members
//constructors
// methods or member functions
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaessentialsforhadoop-140825015659-phpapp02/85/Java-essentials-for-hadoop-11-320.jpg)