Java file
- 1. 1 1. WAP to print following series: 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 1 2 1 class Serie1 { public static void main(String args[]) { for(int i=5;i>=1;i--) { for(int j=1;j<=i;j++) { System.out.print(j); } System.out.println("n"); } } }
- 2. 2 Output:
- 3. 3 2. WAP to print following series: 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 3 4 5 4 5 5 class Serie2 { public static void main(String args[]) { for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) { for(int j=i;j<=5;j++) { System.out.print(j); } System.out.println("n"); } } }
- 4. 4 Output:
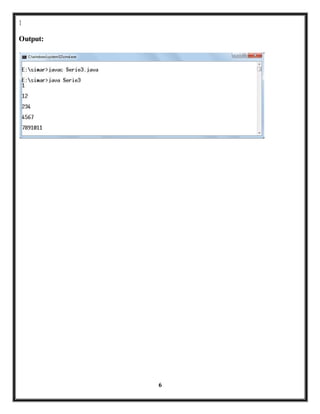
- 5. 5 3. WAP to print following series: 1 1 2 2 3 4 4 5 6 7 7 8 9 10 11 class Serie3 { public static void main(String args[]) { int n=1; for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=i;j++) { System.out.print(n); n++; } System.out.println("n"); n--; } }
- 6. 6 } Output:
- 7. 4.WAP to illustrate the use of io package to receive input for different datatypes. 7 import java.io.*; class Testio { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.println("enter int value"); String s=br.readLine(); int i=Integer.parseInt(s); System.out.println("enter short value"); String a=br.readLine(); short sh=Short.parseShort(a); System.out.println("enter long value"); String x=br.readLine(); long l=Long.parseLong(x); System.out.println("enter float value"); String y=br.readLine(); float f=Float.parseFloat(y); System.out.println("enter double value"); String n=br.readLine(); double d=Double.parseDouble(n); System.out.println("enter string value");
- 8. 8 String z=br.readLine(); String st=z; System.out.println("enter boolean value"); String t=br.readLine(); boolean b=Boolean.parseBoolean(t); System.out.println("int i ="+i); System.out.println("short sh ="+sh); System.out.println("long l ="+l); System.out.println("float f ="+f); System.out.println("double d ="+d); System.out.println("String st ="+st); System.out.println("boolean b ="+b); } }
- 9. 9 Output:
- 10. 5.WAP to illustrate the use of StringTokenizer class of util package. 10 import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class Testst { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); System.out.println("enter Name,Age,Salary"); String str=br.readLine(); StringTokenizer st=new StringTokenizer(str,","); String s1=st.nextToken(); String s2=st.nextToken(); String s3=st.nextToken(); String name=s1; int age=Integer.parseInt(s2); float sal=Float.parseFloat(s3); System.out.println("Name = "+name); System.out.println("Age = "+age); System.out.println("Salary = "+sal); } }
- 11. 11 Output:
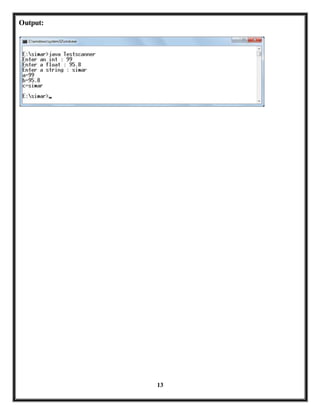
- 12. 6.WAP to illustrate the use of Scanner class. 12 import java.util.Scanner; class Testscanner { public static void main(String args[]) { int a; float b; String c; Scanner ob=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter an int : "); a=ob.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter a float : "); b=ob.nextFloat(); System.out.print("Enter a string : "); c=ob.next(); System.out.println("a="+a); System.out.println("b="+b); System.out.println("c="+c); } }
- 13. 13 Output:
- 14. 7. WAP to receive two inputs from user of different data types at same time and print it using Scanner class. 14 import java.util.Scanner; class Testms { public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner br=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("enter Name,Age"); String n=br.next(); int a=br.nextInt(); System.out.println("Name = "+n); System.out.println("Age = "+a); } } Output:
- 15. 8. WAP to receive one number from user and print table of that number. 15 import java.util.Scanner; public class Table { public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("enter any number : "); int n=obj.nextInt(); for(int j=1;j<=10;j++) { System.out.print(n+"t"+"*"+"t"+j+"t"+"="+"t"+j*n); System.out.print("n"); } } } Output:
- 16. 9. WAP to receive one number from user and print tables up to that number. 16 import java.util.Scanner; public class Table1 { public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("enter any number : "); int n=obj.nextInt(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) { System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+j*i); System.out.print("n"); } } } }
- 17. 17 Output:
- 18. 10. WAP to except three numbers from the user and print largest among them using if else if statement. 18 import java.util.Scanner; public class Largest { public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("enter 1st number : "); int a=obj.nextInt(); System.out.print("enter 2nd number : "); int b=obj.nextInt(); System.out.print("enter 3rd number : "); int c=obj.nextInt(); if(a>b && a>c) System.out.print(a+" is greatest number "); else if(b>a && b>c) System.out.print(b+" is greatest number "); else System.out.print(c+" is greatest number "); } }
- 19. 19 Output:
- 20. 11. WAP to except three numbers from the user and print largest among them using nested if statement. 20 import java.util.Scanner; public class Largestn { public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("enter 1st number : "); int a=obj.nextInt(); System.out.print("enter 2nd number : "); int b=obj.nextInt(); System.out.print("enter 3rd number : "); int c=obj.nextInt(); if(a>b) { if(a>c) { System.out.print(a+" is greatest number "); } else { System.out.print(c+" is greatest number ");
- 21. 21 } } if(b>a) { if(b>c) { System.out.print(b+" is greatest number "); } else { System.out.print(c+" is greatest number "); } } } } Output:
- 22. 12. WAP to except three numbers from the user and print largest among them using nested if statement. 22 import java.util.Scanner; public class Largestm { public static void main(String [] args) { Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("enter 1st number : "); int a=obj.nextInt(); System.out.print("enter 2nd number : "); int b=obj.nextInt(); System.out.print("enter 3rd number : "); int c=obj.nextInt(); if (a>b && a>c) { System.out.println("largest number is "+a); } if(b>a && b>c) { System.out.println("largest number is "+b); } if(c>a && c>b)
- 23. 23 { System.out.println("largest number is "+c); } } } Output:
- 24. 13. WAP to show the use of command line arguments. 24 class Democa { public static void main(String args[]) { for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++) { System.out.println("args["+i+"]: "+args[i]); } } } Output:
- 25. 14. WAP to illustrate the use of String class methods. 25 class Teststr { public static void main(String args[]) { String s = " HELLO WORLD "; String s2 = "HELLO"; int l=s.length(); System.out.println("lenth():"); System.out.println("lenth="+l); System.out.println("charAt():"); System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); System.out.println("trim():"); System.out.println(s.trim()); System.out.println("toLowerCase():"); System.out.println(s.toLowerCase()); System.out.println("substring():"); System.out.println(s.substring(3,9)); System.out.println("indexOf():"); System.out.println(s.indexOf("L")); System.out.println("equals():"); if(s2.equals("HELLO")) System.out.println("HELLO"); else System.out.println("donot match"); System.out.println("compareTo():"); int ans1,ans2,ans3;
- 26. 26 ans1=s2.compareTo("ANNU"); ans2=s2.compareTo("HELLO"); ans3=s2.compareTo("SIMAR"); System.out.println(ans1); System.out.println(ans2); System.out.println(ans3); } } Output:
- 27. 15. WAP to shows the use of array of object in java. 27 import java.util.Scanner; class Student { int r; int m[] = new int[5]; String n; Scanner o= new Scanner(System.in); void getdata() { System.out.print("enter rollno: "); r=o.nextInt(); System.out.print("enter name: "); n=o.next(); System.out.println("enter marks in 5 subjects"); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { m[i]=o.nextInt(); } } void putdata() { int sum=0; System.out.println("rollno: "+r); System.out.println("name: "+n); System.out.println("list of marks");
- 28. 28 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { System.out.println("marks in sub"+(i+1)+" :"+m[i]); sum=sum+m[i]; } int per=((sum*100)/500); if(per<40) { System.out.println("sorry! you are fail"); } else if(per>40 && per<=60) { System.out.println("Division: Third"); } else if(per>60 && per<=80) { System.out.println("Division: second"); } else if(per>80 && per<=100) { System.out.println("Division: first"); } else if(per>100) { System.out.println("invalid result"); } }
- 29. 29 } class T { public static void main(String args[]) { Student obj[]=new Student[2]; for(int i=0;i<2;i++) { obj[i]=new Student(); obj[i].getdata(); } for(int i=0;i<2;i++) { obj[i].putdata(); } } }
- 30. 30 Output:
- 31. 16. WAP to enter the size of row and column for two dimension array, accept values from the user accordingly and print them along with column wise total. 31 import java.util.Scanner; class Carray { public static void main(String args[]) { int r,c; Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("enter size of row"); r=obj.nextInt(); System.out.println("enter size of column"); c=obj.nextInt(); int a[][]=new int[r][c]; System.out.println("enter"+r*c+"values"); for(int i=0;i<r;i++) { for(int j=0;j<c;j++) { a[i][j]=obj.nextInt(); } } int s[]=new int[r];
- 32. 32 System.out.println("Matrix is:"); for(int i=0;i<r;i++) { s[i]=0; for(int j=0;j<c;j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j]+"t"); s[i]=s[i]+a[j][i]; } System.out.print("nn"); } System.out.println("Columnwise total:"); for(int i=0;i<r;i++) { System.out.print(s[i]+"t"); } } }
- 33. 33 Output:
- 34. 17. WAP to enter the size of row and column for two dimension array, accept values from the user accordingly and print them along with diagonal total. 34 import java.util.Scanner; class Diagnal { public static void main(String args[]) { int r,c; Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("enter size of row"); r=obj.nextInt(); System.out.println("enter size of column"); c=obj.nextInt(); int a[][]=new int[r][c]; System.out.println("enter"+r*c+"values"); for(int i=0;i<r;i++) { for(int j=0;j<c;j++) { a[i][j]=obj.nextInt(); } } System.out.println("Matrix is: ");
- 35. 35 int s=0; for(int i=0;i<r;i++) { for(int j=0;j<c;j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j]+"t"); if(i==j) s=s+a[i][j]; } System.out.print("n"); } System.out.println("Sum of diagnal: "+s); } }
- 36. 36 Output:
- 37. 18. WAP to enter the size of row and column for two dimension array, accept values from the user accordingly and print them along with row wise total. 37 import java.util.Scanner; class Rarray { public static void main(String args[]) { int r,c; Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("enter size of row"); r=obj.nextInt(); System.out.println("enter size of column"); c=obj.nextInt(); int a[][]=new int[r][c]; System.out.println("enter"+r*c+"values"); for(int i=0;i<r;i++) { for(int j=0;j<c;j++) { a[i][j]=obj.nextInt(); } } System.out.println("Matrix is: ");
- 38. 38 for(int i=0;i<r;i++) { int s=0; for(int j=0;j<c;j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j]+"t"); s=a[i][j]+s; } System.out.print("="+s); System.out.print("n"); } } } Output:
- 39. 39 19. WAP to show the use of static variable. class Testn { int n; static int count; void getdata(int x) { n=x; count++; } void getcount() { System.out.println("count: "+count); } } class Testd { Test o1=new Test(); Test o2=new Test(); Test o3=new Test(); o1.getcount(); o2.getcount(); o3.getcount();
- 40. 40 o1.getdata(10); o2.getdata(20); o3.getdata(30); o1.getcount(); o2.getcount(); o3.getcount(); } Output:
- 41. 41 20. WAP to show the use of static method. class Mathoperation { static int mul(int a,int b) { return(a*b); } static int mul(int a,int b,int c) { return(a*b*c); } } class Statictest { public static void main(String args[]) { int f1=Mathoperation.mul(10,20); int f2=Mathoperation.mul(10,20,4); System.out.println("1st multiplication = "+f1); System.out.println("2nd multiplication = "+f2); } }
- 42. 42 Output:
- 43. 21. WAP to show the use of parameterized constructor. 43 class A { int a; A(int a) { this.a=a; System.out.println("This is a constructor of class A"); } } class B extends A { int b,c; B(int a,int b,int c) { super(a); this.b=b; this.c=c; System.out.println("This is a constructor of class B"); } void display() { System.out.println("a="+a);
- 44. 44 System.out.println("b="+b); System.out.println("c="+c); } } class ParCons { public static void main(String args[]) { B obj=new B(10,20,30); obj.display(); } } Output:
- 45. 22. WAP to show the use of default constructor. 45 class A { A() { System.out.println("This is a constructor of class A"); } } class B extends A { B() { super(); System.out.println("This is a constructor of class B"); } } class DefCons { public static void main(String args[]) { B obj=new B(); } }
- 46. 46 Output:
- 47. 23. WAP to show the use of overriding method. 47 class One { void show() { System.out.println("I am method of class One"); } } class Two extends One { void show() { System.out.println("I am method of class Two"); } } class Testoverriding { public static void main(String args[]) { One o=new One(); Two t=new Two(); o.show(); t.show();
- 48. 48 } } Output:
- 49. 24. WAP to show the use of method overloading. 49 class Mathoperation { static int mul(int a,int b) { return(a*b); } static int mul(int a,int b,int c) { return(a*b*c); } static float mul(int a,float b) { return(a*b); } } class Testoverloading { public static void main(String args[]) { int f1=Mathoperation.mul(10,20); int f2=Mathoperation.mul(10,20,4); float f3=Mathoperation.mul(10,20.4f);
- 50. 50 System.out.println("1st multiplication = "+f1); System.out.println("2nd multiplication = "+f2); System.out.println("3rd multiplication = "+f3); } } Output:
- 51. 51 25. WAP to show the use of final method. class One { final void show() { System.out.println("i am belong to class One"); } final void show(int a) { System.out.println("i am variable of class one = "+a); } } class Two extends One { void show1() { System.out.println("i am belong to class Two"); } } class Testfinal { public static void main(String args[]) {
- 52. 52 Two t1 = new Two(); t1.show1(); t1.show(); t1.show(10); } } Output:
- 53. 53 26. WAP to show the use of final variable. class One { final int x=5; } class Two extends One { void show() { System.out.println("x = "+x); } } class Testfinalvar { public static void main(String args[]) { Two t1 = new Two(); t1.show(); } }
- 54. 54 Output:
- 55. 55 27. WAP to show the use of final class. class One { void show() { System.out.println("I am method of final class."); } } class Testfinalclass { public static void main(String args[]) { One t1 = new One(); t1.show(); } } Output:
- 56. 28. WAP to show the use of abstract method. 56 abstract class Demo { abstract public void calculate(int x); } class Second extends Demo { public void calculate(int x) { System.out.println("square of "+x+" is "+(x*x)); } } class Third extends Demo { public void calculate(int x) { System.out.println("cube of "+x+" is "+(x*x*x)); } } class Testdemo { public static void main(String args[]) {
- 57. 57 Second s =new Second(); s.calculate(10); Third t =new Third(); t.calculate(10); Demo d; d=s; d.calculate(10); d=t; t.calculate(10); } } Output:
- 58. 29. WAP to show the use of package in classes. 58 package mypack; import java.util.Scanner; public class Student { String n; Scanner o=new Scanner(System.in); public void getname() { System.out.println("enter name"); n=o.next(); } public void putname() { System.out.println("Name = "+n); } } import java.util.Scanner; import mypack.*; class Test1 { Scanner o= new Scanner(System.in); int s[]= new int[3]; void getdata()
- 59. 59 { System.out.println("enter the data in 3 subjects:"); for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { s[i]=o.nextInt(); } } void putdata() { int sum=0; System.out.println("marks in 3 subjects:"); for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { System.out.println("s["+i+"]:"+s[i]); sum=sum+s[i]; } System.out.println("Total = "+sum); int per=(sum*100)/300; System.out.println("percentage = "+per); if(per>80) System.out.println("First"); else if(per<80 && per>60) System.out.println("Second");
- 60. 60 else if(per>50 && per<60) System.out.println("Third"); else System.out.println("Sorry!you are fail"); } } class My { public static void main(String args[]) { Student o1=new Student(); Test1 m=new Test1(); o1.getname(); o1.putname(); m.getdata(); m.putdata(); } }
- 61. 61 Output:
- 62. 30. WAP to demonstrate the use of interface which contains two methods one can accept the input and second for displaying input. 62 interface One { void getdata(int x,int y); void display(); } class Super implements One { int a,b; public void getdata(int x,int y) { a=x; b=y; } public void display() { System.out.println("a = "+a); System.out.println("b = "+b); } } class Testinterface {
- 63. 63 public static void main(String args[]) { Super s=new Super(); One o; o=s; o.getdata(10,20); o.display(); } } Output:
- 64. 31. WAP in which you can implement an interface which contain one method and variable. 64 interface Area { float pi=3.14f; float compute(float x,float y); } class Rectangle implements Area { public float compute(float x, float y) { return(x*y); } } class Circle implements Area { public float compute(float x,float y) { return(pi*x*x); } } class Interfacetest {
- 65. 65 public static void main(String args[]) { Rectangle r=new Rectangle(); Circle c=new Circle(); System.out.println("Area of rectangle = " + r.compute(10.1f,20.2f)); System.out.println("Area of circle = " + c.compute(10.0f,0)); } } Output:
- 66. 32. WAP to show the use of predefined exception. 66 class Testpre { public static void main(String args[]) { try { int n = args.length; int a = 45 / n; System.out.println("The value of a is :"+a); } catch(ArithmeticException ae) { System.out.println(ae); System.out.println("Arguments are required"); } finally { System.out.println("End of program"); } } }
- 67. 67 Output:
- 68. 33. WAP to show the use of user defined exception. 68 import java.util.Scanner; class MyException2 extends Exception { static Scanner o=new Scanner(System.in); static int a[] =new int[5]; MyException2(String str) { super(str); } public static void main(String args[]) { try { System.out.println("enter 5 numbers"); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { a[i]=o.nextInt(); if(a[i]>0) System.out.println("a["+i+"] : "+a[i]); else { MyException2 me= new MyException2("enter positive number");
- 69. 69 throw me; } } } catch(MyException2 me) { me.printStackTrace(); } } } Output:
- 70. 70 34. WAP to show the use of multi threading. class Mythread implements Runnable { String str; Mythread(String str) { this.str = str; } public void run() { for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { System.out.println(str+i); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException ie) { ie.printStackTrace(); } } }
- 71. 71 } class Theatre { public static void main(String args[]) { Mythread obj1 = new Mythread("Cut the ticket"); Mythread obj2 = new Mythread("Show the seat"); Thread t1 = new Thread(obj1); Thread t2 = new Thread(obj2); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } Output:
![1
1. WAP to print following series:
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4
1 2 3
1 2
1
class Serie1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
for(int i=5;i>=1;i--)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println("n");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-1-320.jpg)

![3
2. WAP to print following series:
1 2 3 4 5
2 3 4 5
3 4 5
4 5
5
class Serie2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
for(int j=i;j<=5;j++)
{
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println("n");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-3-320.jpg)

![5
3. WAP to print following series:
1
1 2
2 3 4
4 5 6 7
7 8 9 10 11
class Serie3
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n=1;
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print(n);
n++;
}
System.out.println("n");
n--;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-5-320.jpg)
![4.WAP to illustrate the use of io package to receive input for different datatypes.
7
import java.io.*;
class Testio
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("enter int value");
String s=br.readLine();
int i=Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println("enter short value");
String a=br.readLine();
short sh=Short.parseShort(a);
System.out.println("enter long value");
String x=br.readLine();
long l=Long.parseLong(x);
System.out.println("enter float value");
String y=br.readLine();
float f=Float.parseFloat(y);
System.out.println("enter double value");
String n=br.readLine();
double d=Double.parseDouble(n);
System.out.println("enter string value");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-7-320.jpg)


![5.WAP to illustrate the use of StringTokenizer class of util package.
10
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Testst
{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("enter Name,Age,Salary");
String str=br.readLine();
StringTokenizer st=new StringTokenizer(str,",");
String s1=st.nextToken();
String s2=st.nextToken();
String s3=st.nextToken();
String name=s1;
int age=Integer.parseInt(s2);
float sal=Float.parseFloat(s3);
System.out.println("Name = "+name);
System.out.println("Age = "+age);
System.out.println("Salary = "+sal);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-10-320.jpg)

![6.WAP to illustrate the use of Scanner class.
12
import java.util.Scanner;
class Testscanner
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a;
float b;
String c;
Scanner ob=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter an int : ");
a=ob.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter a float : ");
b=ob.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter a string : ");
c=ob.next();
System.out.println("a="+a);
System.out.println("b="+b);
System.out.println("c="+c);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-12-320.jpg)
![7. WAP to receive two inputs from user of different data types at same time and print it
using Scanner class.
14
import java.util.Scanner;
class Testms
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner br=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter Name,Age");
String n=br.next();
int a=br.nextInt();
System.out.println("Name = "+n);
System.out.println("Age = "+a);
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-14-320.jpg)
![8. WAP to receive one number from user and print table of that number.
15
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Table
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("enter any number : ");
int n=obj.nextInt();
for(int j=1;j<=10;j++)
{
System.out.print(n+"t"+"*"+"t"+j+"t"+"="+"t"+j*n);
System.out.print("n");
}
}
} Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-15-320.jpg)
![9. WAP to receive one number from user and print tables up to that number.
16
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Table1
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("enter any number : ");
int n=obj.nextInt();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+j*i);
System.out.print("n");
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-16-320.jpg)

![10. WAP to except three numbers from the user and print largest among them using if
else if statement.
18
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Largest
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("enter 1st number : ");
int a=obj.nextInt();
System.out.print("enter 2nd number : ");
int b=obj.nextInt();
System.out.print("enter 3rd number : ");
int c=obj.nextInt();
if(a>b && a>c)
System.out.print(a+" is greatest number ");
else if(b>a && b>c)
System.out.print(b+" is greatest number ");
else
System.out.print(c+" is greatest number ");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-18-320.jpg)

![11. WAP to except three numbers from the user and print largest among them using
nested if statement.
20
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Largestn
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("enter 1st number : ");
int a=obj.nextInt();
System.out.print("enter 2nd number : ");
int b=obj.nextInt();
System.out.print("enter 3rd number : ");
int c=obj.nextInt();
if(a>b)
{
if(a>c)
{
System.out.print(a+" is greatest number ");
}
else
{
System.out.print(c+" is greatest number ");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-20-320.jpg)

![12. WAP to except three numbers from the user and print largest among them using
nested if statement.
22
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Largestm
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Scanner obj=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("enter 1st number : ");
int a=obj.nextInt();
System.out.print("enter 2nd number : ");
int b=obj.nextInt();
System.out.print("enter 3rd number : ");
int c=obj.nextInt();
if (a>b && a>c)
{
System.out.println("largest number is "+a);
}
if(b>a && b>c)
{
System.out.println("largest number is "+b);
}
if(c>a && c>b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-22-320.jpg)

![13. WAP to show the use of command line arguments.
24
class Democa
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++)
{
System.out.println("args["+i+"]: "+args[i]);
}
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-24-320.jpg)
![14. WAP to illustrate the use of String class methods.
25
class Teststr
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s = " HELLO WORLD ";
String s2 = "HELLO";
int l=s.length();
System.out.println("lenth():");
System.out.println("lenth="+l);
System.out.println("charAt():");
System.out.println(s.charAt(3));
System.out.println("trim():");
System.out.println(s.trim());
System.out.println("toLowerCase():");
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());
System.out.println("substring():");
System.out.println(s.substring(3,9));
System.out.println("indexOf():");
System.out.println(s.indexOf("L"));
System.out.println("equals():");
if(s2.equals("HELLO"))
System.out.println("HELLO");
else
System.out.println("donot match");
System.out.println("compareTo():");
int ans1,ans2,ans3;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-25-320.jpg)

![15. WAP to shows the use of array of object in java.
27
import java.util.Scanner;
class Student
{
int r;
int m[] = new int[5];
String n;
Scanner o= new Scanner(System.in);
void getdata()
{
System.out.print("enter rollno: ");
r=o.nextInt();
System.out.print("enter name: ");
n=o.next();
System.out.println("enter marks in 5 subjects");
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
m[i]=o.nextInt();
}
}
void putdata()
{
int sum=0;
System.out.println("rollno: "+r);
System.out.println("name: "+n);
System.out.println("list of marks");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-27-320.jpg)
![28
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println("marks in sub"+(i+1)+" :"+m[i]);
sum=sum+m[i];
}
int per=((sum*100)/500);
if(per<40)
{
System.out.println("sorry! you are fail");
}
else if(per>40 && per<=60)
{
System.out.println("Division: Third");
}
else if(per>60 && per<=80)
{
System.out.println("Division: second");
}
else if(per>80 && per<=100)
{
System.out.println("Division: first");
}
else if(per>100)
{
System.out.println("invalid result");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-28-320.jpg)
![29
}
class T
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student obj[]=new Student[2];
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
obj[i]=new Student();
obj[i].getdata();
}
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
obj[i].putdata();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-29-320.jpg)

![16. WAP to enter the size of row and column for two dimension array, accept values from
the user accordingly and print them along with column wise total.
31
import java.util.Scanner;
class Carray
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int r,c;
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter size of row");
r=obj.nextInt();
System.out.println("enter size of column");
c=obj.nextInt();
int a[][]=new int[r][c];
System.out.println("enter"+r*c+"values");
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
{
a[i][j]=obj.nextInt();
}
}
int s[]=new int[r];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-31-320.jpg)
![32
System.out.println("Matrix is:");
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
s[i]=0;
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
{
System.out.print(a[i][j]+"t");
s[i]=s[i]+a[j][i];
}
System.out.print("nn");
}
System.out.println("Columnwise total:");
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
System.out.print(s[i]+"t");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-32-320.jpg)

![17. WAP to enter the size of row and column for two dimension array, accept values from
the user accordingly and print them along with diagonal total.
34
import java.util.Scanner;
class Diagnal
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int r,c;
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter size of row");
r=obj.nextInt();
System.out.println("enter size of column");
c=obj.nextInt();
int a[][]=new int[r][c];
System.out.println("enter"+r*c+"values");
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
{
a[i][j]=obj.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Matrix is: ");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-34-320.jpg)
![35
int s=0;
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
{
System.out.print(a[i][j]+"t");
if(i==j)
s=s+a[i][j];
}
System.out.print("n");
}
System.out.println("Sum of diagnal: "+s);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-35-320.jpg)

![18. WAP to enter the size of row and column for two dimension array, accept values from
the user accordingly and print them along with row wise total.
37
import java.util.Scanner;
class Rarray
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int r,c;
Scanner obj = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter size of row");
r=obj.nextInt();
System.out.println("enter size of column");
c=obj.nextInt();
int a[][]=new int[r][c];
System.out.println("enter"+r*c+"values");
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
{
a[i][j]=obj.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Matrix is: ");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-37-320.jpg)
![38
for(int i=0;i<r;i++)
{
int s=0;
for(int j=0;j<c;j++)
{
System.out.print(a[i][j]+"t");
s=a[i][j]+s;
}
System.out.print("="+s);
System.out.print("n");
}
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-38-320.jpg)


![41
20. WAP to show the use of static method.
class Mathoperation
{
static int mul(int a,int b)
{
return(a*b);
}
static int mul(int a,int b,int c)
{
return(a*b*c);
}
}
class Statictest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int f1=Mathoperation.mul(10,20);
int f2=Mathoperation.mul(10,20,4);
System.out.println("1st multiplication = "+f1);
System.out.println("2nd multiplication = "+f2);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-41-320.jpg)


![44
System.out.println("b="+b);
System.out.println("c="+c);
}
}
class ParCons
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj=new B(10,20,30);
obj.display();
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-44-320.jpg)
![22. WAP to show the use of default constructor.
45
class A
{
A()
{
System.out.println("This is a constructor of class A");
}
}
class B extends A
{
B()
{
super();
System.out.println("This is a constructor of class B");
}
}
class DefCons
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj=new B();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-45-320.jpg)

![23. WAP to show the use of overriding method.
47
class One
{
void show()
{
System.out.println("I am method of class One");
}
}
class Two extends One
{
void show()
{
System.out.println("I am method of class Two");
}
}
class Testoverriding
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
One o=new One();
Two t=new Two();
o.show();
t.show();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-47-320.jpg)

![24. WAP to show the use of method overloading.
49
class Mathoperation
{
static int mul(int a,int b)
{
return(a*b);
}
static int mul(int a,int b,int c)
{
return(a*b*c);
}
static float mul(int a,float b)
{
return(a*b);
}
}
class Testoverloading
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int f1=Mathoperation.mul(10,20);
int f2=Mathoperation.mul(10,20,4);
float f3=Mathoperation.mul(10,20.4f);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-49-320.jpg)

![51
25. WAP to show the use of final method.
class One
{
final void show()
{
System.out.println("i am belong to class One");
}
final void show(int a)
{
System.out.println("i am variable of class one = "+a);
}
}
class Two extends One
{
void show1()
{
System.out.println("i am belong to class Two");
}
}
class Testfinal
{
public static void main(String args[])
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-51-320.jpg)

![53
26. WAP to show the use of final variable.
class One
{
final int x=5;
}
class Two extends One
{
void show()
{
System.out.println("x = "+x);
}
}
class Testfinalvar
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Two t1 = new Two();
t1.show();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-53-320.jpg)

![55
27. WAP to show the use of final class.
class One
{
void show()
{
System.out.println("I am method of final class.");
}
}
class Testfinalclass
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
One t1 = new One();
t1.show();
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-55-320.jpg)
![28. WAP to show the use of abstract method.
56
abstract class Demo
{
abstract public void calculate(int x);
}
class Second extends Demo
{
public void calculate(int x)
{
System.out.println("square of "+x+" is "+(x*x));
}
}
class Third extends Demo
{
public void calculate(int x)
{
System.out.println("cube of "+x+" is "+(x*x*x));
}
}
class Testdemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-56-320.jpg)

![29. WAP to show the use of package in classes.
58
package mypack;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Student
{
String n;
Scanner o=new Scanner(System.in);
public void getname()
{ System.out.println("enter name");
n=o.next();
}
public void putname()
{
System.out.println("Name = "+n);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
import mypack.*;
class Test1
{
Scanner o= new Scanner(System.in);
int s[]= new int[3];
void getdata()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-58-320.jpg)
![59
{
System.out.println("enter the data in 3 subjects:");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
s[i]=o.nextInt();
}
}
void putdata()
{
int sum=0;
System.out.println("marks in 3 subjects:");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
System.out.println("s["+i+"]:"+s[i]);
sum=sum+s[i];
}
System.out.println("Total = "+sum);
int per=(sum*100)/300;
System.out.println("percentage = "+per);
if(per>80)
System.out.println("First");
else if(per<80 && per>60)
System.out.println("Second");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-59-320.jpg)
![60
else if(per>50 && per<60)
System.out.println("Third");
else
System.out.println("Sorry!you are fail");
}
}
class My
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student o1=new Student();
Test1 m=new Test1();
o1.getname();
o1.putname();
m.getdata();
m.putdata();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-60-320.jpg)


![63
public static void main(String args[])
{
Super s=new Super();
One o;
o=s;
o.getdata(10,20);
o.display();
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-63-320.jpg)

![65
public static void main(String args[])
{
Rectangle r=new Rectangle();
Circle c=new Circle();
System.out.println("Area of rectangle = " + r.compute(10.1f,20.2f));
System.out.println("Area of circle = " + c.compute(10.0f,0));
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-65-320.jpg)
![32. WAP to show the use of predefined exception.
66
class Testpre
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
int n = args.length;
int a = 45 / n;
System.out.println("The value of a is :"+a);
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println(ae);
System.out.println("Arguments are required");
}
finally
{
System.out.println("End of program");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-66-320.jpg)

![33. WAP to show the use of user defined exception.
68
import java.util.Scanner;
class MyException2 extends Exception
{
static Scanner o=new Scanner(System.in);
static int a[] =new int[5];
MyException2(String str)
{
super(str);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
System.out.println("enter 5 numbers");
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
a[i]=o.nextInt();
if(a[i]>0)
System.out.println("a["+i+"] : "+a[i]);
else
{
MyException2 me= new MyException2("enter positive number");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-68-320.jpg)


![71
}
class Theatre
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mythread obj1 = new Mythread("Cut the ticket");
Mythread obj2 = new Mythread("Show the seat");
Thread t1 = new Thread(obj1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(obj2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-file-141113220027-conversion-gate01/85/Java-file-71-320.jpg)