Java Programming - 04 object oriented in java
- 1. Module 04 – Object Oriented in Java Danairat T. Line ID: Danairat FB: Danairat Thanabodithammachari +668-1559-1446
- 2. Fundamental Java Programming The Course Outline Module 01 – Introduction to Java Module 02 – Basic Java Programming Module 03 – Control Flow and Exception Handling Module 04 – Object Oriented in Java Module 05 – Java Package and Access Control Module 06 – Java File IO Module 07 – Java Networking Module 08 – Java Threading
- 3. Module 04 – Object Oriented in Java • Java Class • Java Object • Java Variable • Java Method and Constructor • Abstraction • Encapsulation • Inheritance • Polymorphism
- 4. Java Class A class is a blueprint or prototype from which objects are created. This section defines a class that models the state and behavior of a real-world object. It intentionally focuses on the basics, showing how even a simple class can cleanly model state and behavior.
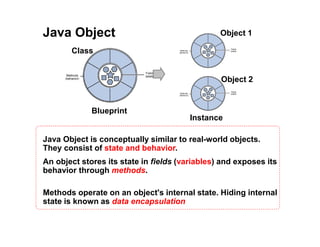
- 5. Java Object Java Object is conceptually similar to real-world objects. They consist of state and behavior. An object stores its state in fields (variables) and exposes its behavior through methods. Methods operate on an object's internal state. Hiding internal state is known as data encapsulation Class Object 1 Object 2 Blueprint Instance
- 6. Java Class Syntax ["public"] ["abstract"|"final"]"class" Class_name ["extends" object_name] ["implements" interface_name] "{" // properties declarations // behavior declarations "}"
- 7. Class Members Class consists from two main members:- • Variable • Method Variable Member variables in a class—these are called fields. - Class – static member - Object – instance member Variables in a method or block of code—these are called local variables. Variables in method declarations—these are called parameters.
- 8. Method [ "public" | "private" | "protected" ] [ "final" ] [ "static" | "abstract" ] return_data_type method_name "(" parameter_list ")" "{" // some defining actions "}" public static void example1() {} public static int add2(int x) {x+=2; return x;} public static double example3(int x, double d) {return x*d;} public static void example4(int x, int y, boolean flag) {} public static void example5(int arr[]) {} // note: this is object
- 9. Type of Java Method 1. Constructor methods These allow class objects to be created with fields initialized to values as determined by the methods' parameters. This allows objects to start with values appropriate to use public Box() {length=0;width=0;height=0;} // default is point public Box(int l,int w,int h) // allows giving initial size {length=l; width=w; height=h;} 2. Accessor (or observer) methods read property (ie. field variable) values and are conventionally named getField() or whatever the property is called. 3. Mutator (or transformer) methods set property values and are often named setField() etc. Mutators can be used to ensure that the property's value is valid in both range and type. 4. Helper methods support modular of code structure in a unit of working.
- 10. Overloading Method The Java programming language supports overloading methods, and Java can distinguish between methods with different method signatures (Method Name, Argument Type, Number of Argument). public class TouchPointer { ... public void draw(int i) { ... } public void draw(double f) { ... } public void draw(int i, int j) { ... } }
- 11. Constructor When you create a new instance (a new object) of a class using the new keyword, a constructor for that class is called. Constructors are used to initialize the instance variables (fields) of an object. Constructors are similar to methods, but with some important differences. • Constructor name is class name. Eg. YourClassName() {} • Default constructor. If you don't define a constructor for a class, a default parameterless constructor is automatically created by the compiler. The default constructor calls the default parent constructor (super()) and initializes all instance variables to default value. • Default constructor is created only if there are no constructors. If you define any constructor for your class, no default constructor is automatically created.
- 12. Differences between methods and constructors 1. There is no return type given in a constructor signature (header). The value is this object itself so there is no need to indicate a return value. 2. There is no return statement in the body of the constructor. 3. The first line of a constructor must either be a call on another constructor in the same class (using this), or a call on the superclass constructor (using super). If the first line is neither of these, the compiler automatically inserts a call to the parameterless super class constructor.
- 13. LAB – ConstructTest1 public class ConstructTest { int value1; int value2; ConstructTest() { value1 = 10; value2 = 20; System.out.println("Inside Constructor"); } public void display() { System.out.println("Value1 === " + value1); System.out.println("Value2 === " + value2); } public static void main(String[] args) { ConstructTest c1 = new ConstructTest(); c1.display(); } } Inside Constructor Value1 === 10 Value2 === 20 Creating Object HereCreating Reference Activating Method
- 14. LAB - Constructor Overloading class ConstrutOverloadDemo { int value1; int value2; ConstrutOverloadDemo() { value1 = 10; value2 = 20; System.out.println("Inside 1st Constructor"); } ConstrutOverloadDemo(int a) { value1 = a; System.out.println("Inside 2nd Constructor"); } ConstrutOverloadDemo(int a, int b) { value1 = a; value2 = b; System.out.println("Inside 3rd Constructor"); } public void display() { System.out.println("Value1 === " + value1); System.out.println("Value2 === " + value2); } public static void main(String[] args) { ConstrutOverloadDemo c1 = new ConstrutOverloadDemo(); ConstrutOverloadDemo c2 = new ConstrutOverloadDemo(30); ConstrutOverloadDemo c3 = new ConstrutOverloadDemo(30, 40); c1.display(); c2.display(); c3.display(); } }
- 15. LAB - Constructor Chain class ConstrucChainDemo{ int value1; int value2; ConstrucChainDemo(){ value1 = 1; value2 = 2; System.out.println("Inside 1st Parent Constructor"); } ConstrucChainDemo(int a, int b){ value1 = a; value2 = b; Syastem.out.println("Inside 2nd Parent Constructor"); } } class ConstrucChild extends ConstrucChainDemo{ int value3; int value4; ConstrucChild(){ super(11,22); value3 = 3; value4 = 4; System.out.println("Inside the Constructor of Child"); } public void display(){ System.out.println("Value1 === "+value1); System.out.println("Value2 === "+value2); System.out.println("Value3 === "+value3); System.out.println("Value4 === "+value4); } } public static void main(String args[]){ ConstrucChild c1 = new ConstrucChild(); c1.display(); }
- 16. Object Oriented History The sense of object-oriented programming term seems to make their first appearance at MIT in the late 1950s Object-oriented programming is modeled on how in the real world objects are made up of many kinds of smaller objects. The Smalltalk language, which was developed at Xerox PARC (by Alan Kay and others) in the 1970s, introduced the term object-oriented programming to represent the pervasive use of objects and messages as the basis for computation.
- 17. Abstraction Abstraction(hiding implementation) focuses on the outside view of an object.. (i.e. the interface) Abstraction is an essential element for OO which manages the complexity. In a sense when someone works on a computer not necessary that he should know the working of each and every part of the computer. interface Customer { void printCustomer (int i); }
- 18. Encapsulation Encapsulation (hiding information) prevents clients from seeing its inside view, where the behavior of the abstraction is implemented It is the mechanism that binds together state and behavior in manipulates and keeps both safe from outside interference and misuse. class Customer { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
- 19. Inheritance It is the process by which one object acquires the properties of another object. This supports the hierarchical classification. Without the use of hierarchies each object would need to define all its characteristics explicitly. However by use of inheritance, an object need only define those qualities that make it unique within its class. Java use “extend” keyword to inherit properties and behavior from super to its sub class. class Customer { String name; public String getName() { } } class MemberCustomer extends Customer { int collectedPoints; }
- 20. Polymorphism The ability of the object design to group object behavior from different types. So by using this, one object can be treated like another even it came from difference hierarchy. The programmers can focus on selected behavior by no need to know the exact type of object in advance and this is being implemented at runtime.
- 21. Defining the Behavior public interface IFace_Printable { public void printNow(); }
- 22. Defining Classes which are the same behavior public class CustomerInfo implements IFace_Printable{ @Override public void printNow() { System.out.println("Read Customer Table... CustomerInfo. Done."); } } public class ProductInfo implements IFace_Printable{ @Override public void printNow() { System.out.println("Reading Product Table... ProductInfo. Done."); } }
- 23. Create Polymorphic Method public class PrintServer { private IFace_Printable iFacePrintable; PrintServer(IFace_Printable iFacePrintable){ this.iFacePrintable = iFacePrintable; } public void printNowWraper(){ iFacePrintable.printNow(); } }
- 24. Create Test Client for the Polymorphic Method public class PrintClientApplication { private static CustomerInfo customerInfo = new CustomerInfo(); private static ProductInfo productInfo = new ProductInfo(); public static void main(String [] args) { new PrintServer(customerInfo).printNowWraper(); new PrintServer(productInfo).printNowWraper(); } }
- 25. Danairat T. Line ID: Danairat FB: Danairat Thanabodithammachari +668-1559-1446 Thank you




![Java Class Syntax
["public"] ["abstract"|"final"]"class" Class_name
["extends" object_name] ["implements"
interface_name]
"{"
// properties declarations
// behavior declarations
"}"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04objectorientedinjavav1-151031160616-lva1-app6892/85/Java-Programming-04-object-oriented-in-java-6-320.jpg)

![Method
[ "public" | "private" | "protected" ] [ "final" ]
[ "static" | "abstract" ]
return_data_type method_name "(" parameter_list ")"
"{"
// some defining actions
"}"
public static void example1() {}
public static int add2(int x) {x+=2; return x;}
public static double example3(int x, double d) {return x*d;}
public static void example4(int x, int y, boolean flag) {}
public static void example5(int arr[]) {} // note: this is object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04objectorientedinjavav1-151031160616-lva1-app6892/85/Java-Programming-04-object-oriented-in-java-8-320.jpg)




![LAB – ConstructTest1
public class ConstructTest {
int value1;
int value2;
ConstructTest() {
value1 = 10;
value2 = 20;
System.out.println("Inside Constructor");
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Value1 === " + value1);
System.out.println("Value2 === " + value2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConstructTest c1 = new ConstructTest();
c1.display();
}
}
Inside Constructor
Value1 === 10
Value2 === 20
Creating Object HereCreating
Reference
Activating Method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04objectorientedinjavav1-151031160616-lva1-app6892/85/Java-Programming-04-object-oriented-in-java-13-320.jpg)
![LAB - Constructor Overloading
class ConstrutOverloadDemo {
int value1;
int value2;
ConstrutOverloadDemo() {
value1 = 10;
value2 = 20;
System.out.println("Inside 1st Constructor");
}
ConstrutOverloadDemo(int a) {
value1 = a;
System.out.println("Inside 2nd Constructor");
}
ConstrutOverloadDemo(int a, int b) {
value1 = a;
value2 = b;
System.out.println("Inside 3rd Constructor");
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("Value1 === " + value1);
System.out.println("Value2 === " + value2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConstrutOverloadDemo c1 = new
ConstrutOverloadDemo();
ConstrutOverloadDemo c2 = new
ConstrutOverloadDemo(30);
ConstrutOverloadDemo c3 = new
ConstrutOverloadDemo(30, 40);
c1.display();
c2.display();
c3.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04objectorientedinjavav1-151031160616-lva1-app6892/85/Java-Programming-04-object-oriented-in-java-14-320.jpg)
![LAB - Constructor Chain
class ConstrucChainDemo{
int value1;
int value2;
ConstrucChainDemo(){
value1 = 1;
value2 = 2;
System.out.println("Inside 1st Parent Constructor");
}
ConstrucChainDemo(int a, int b){
value1 = a;
value2 = b;
Syastem.out.println("Inside 2nd Parent Constructor");
}
}
class ConstrucChild extends ConstrucChainDemo{
int value3;
int value4;
ConstrucChild(){
super(11,22);
value3 = 3;
value4 = 4;
System.out.println("Inside the Constructor of Child");
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("Value1 === "+value1);
System.out.println("Value2 === "+value2);
System.out.println("Value3 === "+value3);
System.out.println("Value4 === "+value4);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
ConstrucChild c1 = new ConstrucChild();
c1.display();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04objectorientedinjavav1-151031160616-lva1-app6892/85/Java-Programming-04-object-oriented-in-java-15-320.jpg)








![Create Test Client for the Polymorphic Method
public class PrintClientApplication {
private static CustomerInfo customerInfo = new CustomerInfo();
private static ProductInfo productInfo = new ProductInfo();
public static void main(String [] args) {
new PrintServer(customerInfo).printNowWraper();
new PrintServer(productInfo).printNowWraper();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04objectorientedinjavav1-151031160616-lva1-app6892/85/Java-Programming-04-object-oriented-in-java-24-320.jpg)
