Lambda Expressions Java 8 Features usage
- 1. Lambda Expressions – Java 8
- 2. Content • Understanding Lambdas • Using Lambdas • Functional Interface • Method references • Collections improvements
- 3. Why Lambdas? • Enables Functional Programming • Readable and concise code • Enables us to write better APIs and libraries which are easier to use • Support for parallel processing
- 4. Functional Programming VS OOP • Functional programming allow you to write more readable and maintainable code.(in some cases) • Problems in OOP • Everything is object - all code blocks are "associated" with class and objects , which is a problem some time • We cannot have a independent functions , it have to be a part of function. • Also allow us to use functions as values.
- 5. Function as a value aBlockOfCode = public void () { System.out.println("Hello World"); } perfom -> aBlockOfCode = () -> { System.out.println("Hello World"); } aBlockOfCode = () -> System.out.println("Hello World");
- 6. Type Inference • Your lambda Expression infer type of function and its return type from the interface(functional interface). public static void main(String[] args) { //StringLengthLambda myStringLenthLambda = (String s) -> s.length(); //StringLengthLambda myStringLenthLambda = (s) -> s.length(); StringLengthLambda myStringLenthLambda = s -> s.length(); System.out.println("String Length :: " + myStringLenthLambda.getLength("Hello World!!")); } interface StringLengthLambda { int getLength(String s); }
- 7. Lambda Vs Interface Implementation • We can implement the functional interface in two ways. • By Implementing the lambda Expression • By Creating the Anonymous class implementation Greeting innerClassGreeting = new Greeting() { @Override public void perfom() { System.out.println("Hello World"); } }; innerClassGreeting.perfom(); Greeting myLambdaFunction = () -> System.out.println("Hello World"); myLambdaFunction.perfom();
- 8. Lambda Vs Interface Implementation • For the most purposes you can think of the lambda expression as the shortcut for creating these kind of anonymous inner classes but its not exactly true. • There are things that inner class does which is different from what these lambda expressions do. • In case of lambda expression its not exactly creating an anonymous class, will look at those differences in a further slides.
- 9. Runnable Using Lambdas • You can use lambda in order to create Runnable. • Implement Using anonymous inner class • Implement Using Lambda Expression public static void main(String[] args) { Thread myThread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Printed inside runnable"); } }); myThread.start(); } Thread myLambdaThread = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("Printed inside Lambda Runnable")); myLambdaThread.start();
- 10. Functional Interface • Any interface with a SAM(Single Abstract Method) is a functional interface • Interface can have multiple default methods but it should have only one abstract method(Java 8) • its implementation may be treated as lambda expressions. • It's recommended that all functional interfaces have an informative @FunctionalInterface annotation. • Add @FunctionalInterface on Greeting
- 11. Implementation Of Lambda Expression • Lets do some hands on exercise to understand advantages of lambda expression with collections.
- 12. Predicate Interface • Represents a predicate (boolean-valued function) of one argument. • This is a functional interface whose functional method is test(Object).
- 13. Consumer Interface • Represents an operation that accepts a single input argument and returns no result. • This is a functional interface whose functional method is accept(Object).
- 14. Exception Handling in lambda Expression • Create a lambda expression which X in an array of integers and a key which is and do the mathematical operation for each element in array given a key.
- 15. Closers in Lambda Expressions • Understand what is effectively final. • Understand the freeze value in lambda expression
- 16. Difference between lambda and Anonymous Inner Class. • In an anonymous inner class when using the this reference , it overwrite the this reference to the anonymous inner class instance. • In the case of a lambda that does not happen. It still refers to the instance that it points to the outside of the lambda(no overriding of this reference that happens). • Lets have an example in eclipse.
- 17. Streams • A sequence of elements supporting sequential and parallel aggregate operations. • Stream Operations • Intermediate Operations (Return Stream Object) • Map • Filter • Sorted • Terminal Operations • Collect • forEach • Reduce • Stream Operations don’t change the source.
- 18. Optional • The purpose of the class is to provide a type-level solution for representing optional values instead of null references • Static methods of Optional class • empty() • of() • isPresent()
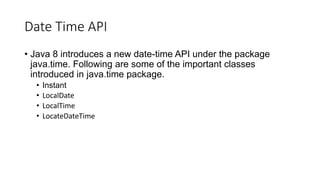
- 19. Date Time API • Java 8 introduces a new date-time API under the package java.time. Following are some of the important classes introduced in java.time package. • Instant • LocalDate • LocalTime • LocateDateTime





![Type Inference
• Your lambda Expression infer type of function and its return type
from the interface(functional interface).
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//StringLengthLambda myStringLenthLambda = (String s) -> s.length();
//StringLengthLambda myStringLenthLambda = (s) -> s.length();
StringLengthLambda myStringLenthLambda = s -> s.length();
System.out.println("String Length :: " + myStringLenthLambda.getLength("Hello World!!"));
}
interface StringLengthLambda
{
int getLength(String s);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lambdaexpressionsjava8-240317115916-d80f9f7e/85/Lambda-Expressions-Java-8-Features-usage-6-320.jpg)


![Runnable Using Lambdas
• You can use lambda in order to create Runnable.
• Implement Using anonymous inner class
• Implement Using Lambda Expression
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread myThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Printed inside runnable");
}
});
myThread.start();
}
Thread myLambdaThread = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("Printed inside Lambda Runnable"));
myLambdaThread.start();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lambdaexpressionsjava8-240317115916-d80f9f7e/85/Lambda-Expressions-Java-8-Features-usage-9-320.jpg)