Lec8_Java Advanced class features_Part 1V.ppt
- 1. Java Advanced Class Features Interfaces and Packages Lecturer: Jackline Ssanyu
- 2. In this class, we will cover: •Introduction to interfaces •Defining and implementing interfaces •Extending interfaces •Implementing multiple inheritance •Use of packages •Packages and member access
- 3. Interfaces •An interface is just like a java class, but it only has static constants and abstract methods. •A class implements an interface, thereby inheriting the abstract methods of the interface. •Purpose of interfaces is to specify a contract that must be fulfilled by any class that implements the interface. •Java uses Interface to implement multiple inheritance. A Java class can implement multiple Java Interfaces. All methods in an interface are implicitly public and abstract. •Interfaces are syntactically like abstract classes. However, in an interface, no method can include a body. That is, an interface provides no implementation whatsoever. •Once an interface is defined, any number of classes can implement it. Also, one class can implement any number of interfaces.
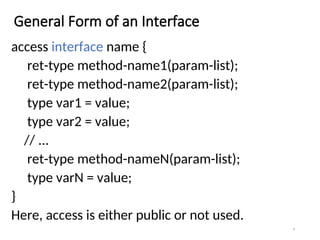
- 4. General Form of an Interface access interface name { ret-type method-name1(param-list); ret-type method-name2(param-list); type var1 = value; type var2 = value; // ... ret-type method-nameN(param-list); type varN = value; } Here, access is either public or not used. 4
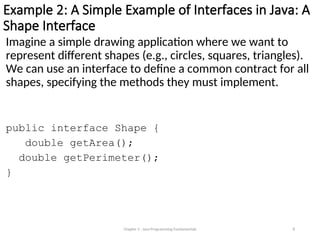
- 8. Example 2: A Simple Example of Interfaces in Java: A Shape Interface Imagine a simple drawing application where we want to represent different shapes (e.g., circles, squares, triangles). We can use an interface to define a common contract for all shapes, specifying the methods they must implement. public interface Shape { double getArea(); double getPerimeter(); } Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 8
- 9. Example 2 Continued…. public class Circle implements Shape { private double radius; public Circle(double radius){ this.radius = radius; } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI * radius * radius; } @Override public double getPerimeter() { return 2 * Math.PI * radius; } } Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 9
- 10. Example 2 Continued…. public class Square implements Shape { private double sideLength; public Square(double sideLength) { this.sideLength = sideLength; } @Override public double getArea() { return sideLength * sideLength; } @Override public double getPerimeter() { return 4 * sideLength; } } Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 10
- 11. Example 2 Continued….. public class DrawingApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { Shape circle = new Circle(5.0); Shape square = new Square(10.0); System.out.println("Circle area: " + circle.getArea()); System.out.println("Circle perimeter: “ + circle.getPerimeter()); System.out.println("Square area: " + square.getArea()); System.out.println("Square perimeter: “ + square.getPerimeter()); } } Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 11
- 12. Rulebook for interface 12 •An interface is 100% abstract class and has only abstract methods and constants. •Class can implement any number of interfaces.
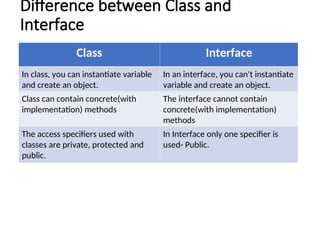
- 13. Difference between Class and Interface Class Interface In class, you can instantiate variable and create an object. In an interface, you can't instantiate variable and create an object. Class can contain concrete(with implementation) methods The interface cannot contain concrete(with implementation) methods The access specifiers used with classes are private, protected and public. In Interface only one specifier is used- Public.
- 14. When to use Interface and Abstract Class? • Use an abstract class when a template needs to be defined for a group of subclasses • Use an interface when a role needs to be defined for other classes, regardless of the inheritance tree of these classes, and multiple inheritance 14
- 15. Must know facts about Interface 15 •A Java class can implement multiple Java Interfaces. It is necessary that the class must implement all the methods declared in the interfaces. •Class should override all the abstract methods declared in the interface •All methods in an interface are implicitly public and abstract •An interface cannot be instantiated •An interface can extend from one or many interfaces. Class can extend only one class but implement any number of interfaces
- 16. Extending Interfaces 16 •One interface can inherit another by use of the keyword extends. The syntax is the same as for inheriting classes. •When a class implements an interface that inherits another interface, it must provide implementations for all methods defined within the interface inheritance chain.
- 17. Extending an Interface - Example
- 18. Extending an Interface – Example… 18
- 19. Implementing Multiple Inheritance 19 • Multiple inheritance in Java programming is achieved or implemented using interfaces. • Java does not support multiple inheritance using classes. In simple term, a class can inherit only one class and multiple interfaces in a java programs. • In java terminology, we can say that: “ A class can extend only one class but it can implement multiple interfaces”
- 20. Multiple Inheritance - Example 20
- 21. Multiple Inheritance – Example… 21
- 22. Multiple Inheritance – Example… 22
- 23. Multiple Inheritance – Example… 23 }
- 24. Multiple Inheritance – Example… 24
- 25. Example 2: Multiple Inheritance in Java Using Interfaces: A Vehicle Rental System Imagine a vehicle rental system where vehicles can be classified by both their type (car, truck, motorcycle) and their fuel type (gasoline, diesel, electric). We want to represent this classification using multiple inheritance, which is not directly supported in Java but can be achieved using interfaces. public interface Vehicle { double getRentalRatePerHour(); } public interface GasolineVehicle { double getFuelEfficiency(); } public interface DieselVehicle { double getFuelEfficiency(); } public interface ElectricVehicle { double getBatteryCapacity();} Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 25
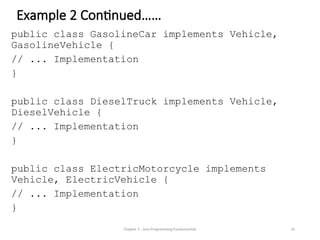
- 26. Example 2 Continued…… public class GasolineCar implements Vehicle, GasolineVehicle { // ... Implementation } public class DieselTruck implements Vehicle, DieselVehicle { // ... Implementation } public class ElectricMotorcycle implements Vehicle, ElectricVehicle { // ... Implementation } Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 26
- 27. Example 2 Continued….. public class RentalSystem { public static void main(String[] args) { GasolineCar gasolineCar = new GasolineCar(); DieselTruck dieselTruck = new DieselTruck(); ElectricMotorcycle electricMotorcycle = new ElectricMotorcycle(); // Access methods from both Vehicle and // GasolineVehicle interfaces System.out.println("Gasoline car rental rate: " + gasolineCar.getRentalRatePerHour()); System.out.println("Gasoline car fuel efficiency: " + gasolineCar.getFuelEfficiency()); // ... similar for other vehicles } } Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 27
- 28. Sample Implementation of class GasolineCar public class GasolineCar implements Vehicle, GasolineVehicle { private double RRPH; //rentalRatePerHour private double FE; //fuelEfficiency public GasolineCar(double RRPH, double FE) { this.RRPH = RRPH; this.FE = FE; } public double getRRPH() { return RRPH; } public double getFE() { return FE; } // Additional methods specific to gasoline cars (e.g., //calculate fuel cost) public double calculateFuelCost(int rentalHours) { // Assume a fuel price of $3.50 per gallon double fuelPricePerGallon = 3.50; double totalMiles = rentalHours * 50; // Assuming an average of 50 miles per hour double gallonsUsed = totalMiles / fuelEfficiency; return gallonsUsed * fuelPricePerGallon; }} Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 28
- 29. Java Packages •A package in Java is a namespace for organizing classes and interfaces in a logical manner. •Helps to avoid name conflicts and maintain a structured codebase. •Package in java can be categorized in two form • Built-in packages: Provided by Java (e.g., java.util, java.io). • User-defined packages: Created by users to structure their code. 29
- 30. Advantage of Java Package •Java package is used to categorize the classes and interfaces so that they can be easily maintained. •Java package provides access protection. •Java package removes naming collision. 30
- 31. Example of java package 31
- 32. Simple example of java package •The package keyword is used to create a package in java. //save as Simple.java package mypack; public class Simple{ public static void main(String args[]){ System.out.println("Welcome to package"); } } Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 32
- 33. Packages and Member Access •The visibility of an element is determined by its access specification: private, public, protected, or default, and the package in which it resides. •Thus, the visibility of an element is determined by its visibility within a class and its visibility within a package. Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 33
- 34. Packages and Member Access 34 •Access Modifiers and their effect on package-level access: •Public: Members are accessible from anywhere, even from outside the package. •Private: Members are only accessible within the same class. •Protected: Members are accessible within the same package and subclasses. •Default (no modifier): Members are accessible only within the same package.
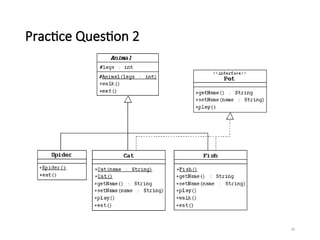
- 37. Practice Question 2 … In this exercise you will create a hierarchy of animals that is rooted in an abstract class Animal. Several of the animal classes will implement an interface called Pet. You will experiment with variations of these animals, their methods, and polymorphism. 1)Create the Animal class, which is the abstract superclass of all animals. • Declare a protected integer attribute called legs, which records the number of legs for this animal. • Define a protected constructor that initializes the legs attribute. • Declare an abstract method eat. • Declare a concrete method walk that prints out something about how the animals walks (include the number of legs). 37
- 38. Practice Question 2 … 2) Create the Spider class. • The Spider class extends the Animal class. • Define a default constructor that calls the superclass constructor to specify that all spiders have eight legs. • Implement the eat method. 3) Create the Pet interface specified by the UML diagram. • Create the Cat class that extends Animal and implements Pet. • This class must include a String attribute to store the name of the pet. • Define a constructor that takes one String parameter that specifies the cat's name. This constructor must also call the superclass constructor to specify that all cats have four legs. • Define another constructor that takes no parameters. Have this constructor call the previous constructor (using the this keyword) and pass an empty string as the argument. • Implement the Pet interface methods. • Implement the eat method. 38
- 39. Practice Question 2 … 4) Create the Fish class. Override the Animal methods to specify that fish can't walk and don't have legs. 5) Create and TestAnimals program. Have the main method create and manipulate instances of the classes you created above. Start with: • Fish d = new Fish(); • Cat c = new Cat("Fluffy"); • Animal a = new Fish(); • Animal e = new Spider(); • Pet p = new Cat(); Experiment by: a) calling the methods in each object b) casting objects, c) using polymorphism, and d) using super to call super class methods. 39








![Example 2 Continued…..
public class DrawingApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape circle = new Circle(5.0);
Shape square = new Square(10.0);
System.out.println("Circle area: " +
circle.getArea());
System.out.println("Circle perimeter: “
+ circle.getPerimeter());
System.out.println("Square area: " +
square.getArea());
System.out.println("Square perimeter: “
+ square.getPerimeter());
}
}
Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec8javaadvancedclassfeaturespart1v-250803043814-9306c99f/85/Lec8_Java-Advanced-class-features_Part-1V-ppt-11-320.jpg)













![Example 2 Continued…..
public class RentalSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GasolineCar gasolineCar = new GasolineCar();
DieselTruck dieselTruck = new DieselTruck();
ElectricMotorcycle electricMotorcycle = new
ElectricMotorcycle();
// Access methods from both Vehicle and
// GasolineVehicle interfaces
System.out.println("Gasoline car rental rate: " +
gasolineCar.getRentalRatePerHour());
System.out.println("Gasoline car fuel efficiency: " +
gasolineCar.getFuelEfficiency());
// ... similar for other vehicles
}
}
Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec8javaadvancedclassfeaturespart1v-250803043814-9306c99f/85/Lec8_Java-Advanced-class-features_Part-1V-ppt-27-320.jpg)




![Simple example of java package
•The package keyword is used to create a package in
java.
//save as Simple.java
package mypack;
public class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Welcome to package");
}
}
Chapter 3 - Java Programming Fundamentals 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec8javaadvancedclassfeaturespart1v-250803043814-9306c99f/85/Lec8_Java-Advanced-class-features_Part-1V-ppt-32-320.jpg)