Lecture 14 (inheritance basics)
- 1. INHERITANCE BASICS 1. Reusability is achieved by INHERITANCE 2. Java classes Can be Reused by extending a class. Extending an existing class is nothing but reusing properties of the existing classes. 3. The class whose properties are extended is known as super or base or parent class. 4. The class which extends the properties of super class is known as sub or derived or child class 5. A class can either extends another class or can implement an interface
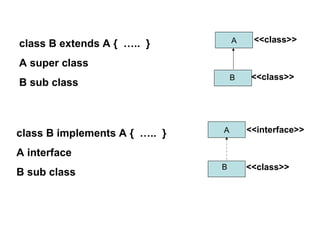
- 2. A B class B extends A { ….. } A super class B sub class A B <<class>> <<class>> <<class>> <<interface>>class B implements A { ….. } A interface B sub class
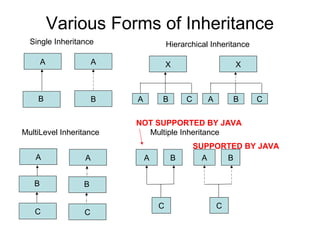
- 3. Various Forms of Inheritance A B Single Inheritance A B Hierarchical Inheritance X A B C X A B C MultiLevel Inheritance A B C A B C A B C Multiple Inheritance NOT SUPPORTED BY JAVA A B C SUPPORTED BY JAVA
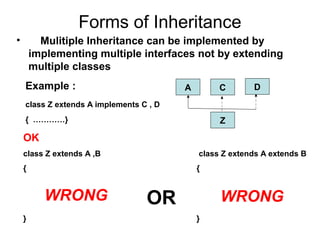
- 4. Forms of Inheritance • Mulitiple Inheritance can be implemented by implementing multiple interfaces not by extending multiple classes Example : class Z extends A implements C , D { …………} OK class Z extends A ,B class Z extends A extends B { { OR } } A C D Z WRONG WRONG
- 5. Defining a Subclass Syntax : class <subclass name> extends <superclass name> { variable declarations; method declarations; } • Extends keyword signifies that properties of the super class are extended to sub class • Sub class will not inherit private members of super class
- 6. Access Control Access Modifiers Access Location public protected friendly private Same Class Yes Yes Yes Yes sub classes in same package Yes Yes Yes No Other Classes in Same package Yes Yes Yes No Subclasses in other packages Yes Yes No No Non-subclasses in other packages Yes No No No
- 7. 1. Whenever a sub class object is created ,super class constructor is called first. 2. If super class constructor does not have any constructor of its own OR has an unparametrized constructor then it is automatically called by Java Run Time by using call super() 3. If a super class has a parameterized constructor then it is the responsibility of the sub class constructor to call the super class constructor by call super(<parameters required by super class>) 4. Call to super class constructor must be the first statement in sub class constructor Inheritance Basics
- 8. Inheritance Basics When super class has a Unparametrized constructor class A { A() { System.out.println("This is constructor of class A"); } } // End of class A class B extends A { B() { super(); System.out.println("This is constructor of class B"); } } // End of class B Optional Cont…..
- 9. class inhtest { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(); } } OUTPUT This is constructor of class A This is constructor of class B
- 10. class A { A() { System.out.println("This is class A"); } } class B extends A { B() { System.out.println("This is class B"); } } class inherit1 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(); } } /* E:Java>java inherit1 This is class A This is class B E:Java> */ File Name is xyz.java
- 11. class A { private A() { System.out.println("This is class A"); } } class B extends A { B() { System.out.println("This is class B"); } } class inherit2 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(); } } /* E:Java>javac xyz1.java xyz1.java:12: A() has private access in A { ^ 1 error
- 12. class A { private A() { System.out.println("This is class A"); } A() { System.out.println("This is class A"); } } class B extends A { B() { System.out.println("This is class B"); } } class inherit2 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(); } } /* E:Java>javac xyz2.java xyz2.java:7: A() is already defined in A A() ^ xyz2.java:16: A() has private access in A { ^ 2 errors */
- 13. When Super class has a parametrized constructor. class A { private int a; A( int a) { this.a =a; System.out.println("This is constructor of class A"); } } class B extends A { private int b; private double c; B(int b,double c) { this.b=b; this.c=c; System.out.println("This is constructor of class B"); } } D:javabin>javac inhtest.java inhtest.java:15: cannot find symbol symbol : constructor A() location: class A { ^ 1 errors B b1 = new B(10,8.6);
- 14. class A { private int a; A( int a) { this.a =a; System.out.println("This is constructor of class A"); } } class B extends A { private int b; private double c; B(int a,int b,double c) { super(a); this.b=b; this.c=c; System.out.println("This is constructor of class B"); } } B b1 = new B(8,10,8.6); OUTPUT This is constructor of class A This is constructor of class B
- 15. class A { private int a; protected String name; A(int a, String n) { this.a = a; this.name = n; } void print() { System.out.println("a="+a); } } class B extends A { int b; double c; B(int a,String n,int b,double c) { super(a,n); this.b=b; this.c =c; } void show() { //System.out.println("a="+a); print(); System.out.println("name="+name); System.out.println("b="+b); System.out.println("c="+c); } } a is private in class A Call to print() from super class A Accessing name field from super class (super.name)
- 16. class xyz3 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(10,"OOP",8,10.56); b1.show(); } } E:Java>java xyz3 a=10 name=OOP b=8 c=10.56
- 17. USE OF super KEYWORD • Can be used to call super class constrctor super(); super(<parameter-list>); • Can refer to super class instance variables/Methods super.<super class instance variable/Method>
- 18. class A { private int a; A( int a) { this.a =a; System.out.println("This is constructor of class A"); } void print() { System.out.println("a="+a); } void display() { System.out.println("hello This is Display in A"); } } // End of class A class B extends A { private int b; private double c; B(int a,int b,double c) { super(a); this.b=b; this.c=c; System.out.println("This is constructor of class B"); } void show() { print(); System.out.println("b="+b); System.out.println("c="+c); } } // End of class B
- 19. class inhtest1 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(10,8,4.5); b1.show(); } } /* OutPUt D:javabin>java inhtest1 This is constructor of class A This is constructor of class B a=10 b=8 c=4.5 */
- 20. class A { private int a; A( int a) { this.a =a; System.out.println("This is constructor of class A"); } void show() { System.out.println("a="+a); } void display() { System.out.println("hello This is Display in A"); } } class B extends A { private int b; private double c; B(int a,int b,double c) { super(a); this.b=b; this.c=c; System.out.println("This is constructor of class B"); } void show() { super.show(); System.out.println("b="+b); System.out.println("c="+c); display(); } }
- 21. class inhtest1 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(10,8,4.5); b1.show(); } } /* OutPut D:javabin>java inhtest1 This is constructor of class A This is constructor of class B a=10 b=8 c=4.5 hello This is Display in A */
- 22. class A { int a; A( int a) { this.a =a; } void show() { System.out.println("a="+a); } void display() { System.out.println("hello This is Display in A"); } } class B extends A { int b; double c; B(int a,int b,double c) { super(a); this.b=b; this.c=c; } void show() { //super.show(); System.out.println("a="+a); System.out.println("b="+b); System.out.println("c="+c); } }
- 23. class inhtest2 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(10,20,8.4); b1.show(); } } /* D:javabin>java inhtest2 a=10 b=20 c=8.4 */
- 24. class A { int a; A( int a) { this.a =a; } } class B extends A { // super class variable a hides here int a; int b; double c; B(int a,int b,double c) { super(100); this.a = a; this.b=b; this.c=c; } void show() { System.out.println("Super class a="+super.a); System.out.println("a="+a); System.out.println("b="+b); System.out.println("c="+c); } }
- 25. class inhtest2 { public static void main(String args[]) { B b1 = new B(10,20,8.4); b1.show(); } } /* Out Put D:javabin>java inhtest2 Super class a=100 a=10 b=20 c=8.4 */






![class inhtest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B();
}
}
OUTPUT
This is constructor of class A
This is constructor of class B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-9-320.jpg)
![class A
{
A()
{
System.out.println("This is class A");
}
}
class B extends A
{
B()
{
System.out.println("This is class B");
}
}
class inherit1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B();
}
}
/*
E:Java>java inherit1
This is class A
This is class B
E:Java>
*/
File Name is xyz.java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-10-320.jpg)
![class A
{
private A()
{
System.out.println("This is class A");
}
}
class B extends A
{
B()
{
System.out.println("This is class B");
}
}
class inherit2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B();
}
}
/*
E:Java>javac xyz1.java
xyz1.java:12: A() has private access
in A
{
^
1 error](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-11-320.jpg)
![class A
{
private A()
{
System.out.println("This is class A");
}
A()
{
System.out.println("This is class A");
}
}
class B extends A
{
B()
{
System.out.println("This is class B");
}
}
class inherit2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B();
} }
/*
E:Java>javac xyz2.java
xyz2.java:7: A() is already defined in
A
A()
^
xyz2.java:16: A() has private access
in A
{
^
2 errors
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-12-320.jpg)



![class xyz3
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B(10,"OOP",8,10.56);
b1.show();
}
}
E:Java>java xyz3
a=10
name=OOP
b=8
c=10.56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-16-320.jpg)


![class inhtest1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B(10,8,4.5);
b1.show();
}
}
/* OutPUt
D:javabin>java inhtest1
This is constructor of class A
This is constructor of class B
a=10
b=8
c=4.5
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-19-320.jpg)

![class inhtest1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B(10,8,4.5);
b1.show();
}
}
/* OutPut
D:javabin>java inhtest1
This is constructor of class A
This is constructor of class B
a=10
b=8
c=4.5
hello This is Display in A
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-21-320.jpg)

![class inhtest2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B(10,20,8.4);
b1.show();
}
}
/*
D:javabin>java inhtest2
a=10
b=20
c=8.4
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-23-320.jpg)

![class inhtest2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B b1 = new B(10,20,8.4);
b1.show();
}
}
/* Out Put
D:javabin>java inhtest2
Super class a=100
a=10
b=20
c=8.4
*/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture14inheritancebasics-130806210922-phpapp01/85/Lecture-14-inheritance-basics-25-320.jpg)