Lecture 1-introduction to distributed computing.pptx
- 1. Distributed and Cloud Computing DR. ABDULRAHMAN ALSABRI ALSABRI374@GMAIL.COM
- 2. Computing Systems Types of Computing Systems: Centralized Systems Decentralized Systems Distributed Systems Distributed Computing : A field of computer science /engineering that studies distributed systems.
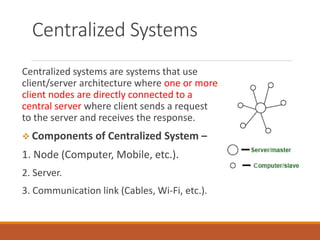
- 4. Centralized Systems Centralized systems are systems that use client/server architecture where one or more client nodes are directly connected to a central server where client sends a request to the server and receives the response. Components of Centralized System – 1. Node (Computer, Mobile, etc.). 2. Server. 3. Communication link (Cables, Wi-Fi, etc.).
- 5. Characteristics of Centralized System Presence of a global clock: As the entire system consists of a central node(a server/ a master) and many client nodes(a computer/ a slave), all client nodes sync up with the global clock(the clock of the central node). One single central unit: One single central unit which serves/coordinates all the other nodes in the system. Dependent failure of components: Central node failure causes entire system to fail. This makes sense because when the server is down, no other entity is there to send/receive response/requests
- 6. Advantages of Centralized System Easy to physically secure. It is easy to secure and service the server and client nodes by virtue of their location Smooth and elegant personal experience – A client has a dedicated system which he uses(for example, a personal computer) and the company has a similar system which can be modified to suit custom needs Dedicated resources (memory, CPU cores, etc) More cost efficient for small systems upto a certain limit – As the central systems take less funds to set up, they have an edge when small systems have to be built Quick updates are possible – Only one machine to update. Easy detachment of a node from the system. Just remove the connection of the client node from the server and voila! Node detached.
- 7. Disadvantages of Centralized System Highly dependent on the network connectivity – System can fail if the nodes lose connectivity as there is only one central node. No graceful degradation of system – abrupt failure of the entire system Less possibility of data backup. If the server node fails and there is no backup, you lose the data straight away Difficult server maintenance – There is only one server node and due to availability reasons, it is inefficient and unprofessional to take the server down for maintenance. So, updates have to be done on-the- fly(hot updates) which is difficult and the system could break.
- 8. Applications of Centralized System Application development : Very easy to setup a central server and send client requests. Data analysis – Easy to do data analysis when all the data is in one place and available for analysis Personal computing
- 9. Use Cases Centralized databases – all the data in one server for use. Single player games like Need For Speed, GTA Vice City – entire game in one system(commonly, a Personal Computer) Application development by deploying test servers leading to easy debugging, easy deployment, easy simulation Personal Computers
- 11. Decentralized Systems Is an interconnected information system in which no single entity is the sole authority. Every node makes its own decision. The final behavior of the system is the aggregate of the decisions of the individual nodes. Components of Centralized System: 1. Nodes (Computer, Mobile, etc.). 2. Servers 3. Communication link (Cables, Wi-Fi, etc.).
- 12. Ingredients of a Distributed System Middleware Network OS Component-1 Component-n … Host-1 Hardware Middleware Network OS Component-1 Component-n … Host-3 Hardware Middleware Network OS Component-1 Component-n … Host-n Hardware Middleware Network OS Component-1 Component-n … Host-2 Hardware Network
- 13. Characteristics of Decentralized System Lack of a global clock: Every node is independent of each other and hence, have different clocks that they run and follow. Multiple central units (Computers/Nodes/Servers): More than one central unit which can listen for connections from other nodes Dependent failure of components: one central node failure causes a part of system to fail; not the whole system
- 14. Architecture of Decentralized System Peer-to-peer architecture : all nodes are peers of each other. No one node has supremacy over other nodes Master-slave architecture : One node can become a master by voting and help in coordinating of a part of the system but this does not mean the node has supremacy over the other node which it is coordinating
- 15. Advantages of Decentralized System Minimal problem of performance bottlenecks occurring : The entire load gets balanced on all the nodes; leading to minimal to no bottleneck situations. High availability: Some nodes(computers, mobiles, servers) are always available/online for work, leading to high availability. More autonomy and control over resources : As each node controls its own behavior, it has better autonomy leading to more control over resources
- 16. Disadvantages of Decentralized System Difficult to achieve global big tasks : No chain of command to command others to perform certain tasks Difficult to know which node failed : Each node must be pinged for availability checking and partitioning of work has to be done to actually find out which node failed by checking the expected output with what the node generated Difficult to know which node responded : When a request is served by a decentralized system, the request is actually served by one of the nodes in the system but it is actually difficult to find out which node indeed served the request.
- 17. Applications of Decentralized System Private networks : peer nodes joined with each other to make a private network. Cryptocurrency: (Blockchain ) Nodes joined to become a part of a system in which digital currency is exchanged without any trace and location of who sent what to whom. Decentralized databases : Entire database split in parts and distributed to different nodes for storage and use.
- 19. DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS A distributed system is a collection of autonomous hosts that are connected through a computer network each host executes components and coordinated via middleware. Components of Distributed System – 1. Node (Computer, Mobile, etc.) 2. Communication link (Cables, Wi-Fi, etc.)
- 20. Characteristics of Distributed System Concurrency of components: Nodes apply consensus protocols to agree on same values/transactions/commands/logs. A global clock is not required : All nodes maintain their own clock. Independent failure of components: In a distributed system, nodes fail independently without having a significant effect on the entire system.
- 21. Architecture of Distributed System peer-to-peer : all nodes are peer of each other and work towards a common goal client-server : some nodes are become server nodes for the role of coordinator, arbiter, etc. n-tier architecture : different parts of an application are distributed in different nodes of the systems and these nodes work together to function as an application for the user/client
- 22. Advantages of Distributed System Economics:- ◦ Computers harnessed together give a better price/performance ratio than mainframes. Speed:- ◦ A distributed system may have more total computing power than a mainframe. Reliability:- ◦ If one machine crashes, the system as a whole can still survive if you have multiple server machines and multiple storage devices (redundancy). Extensibility and Incremental Growth:- ◦ Possible to gradually scale up (in terms of processing power and functionality) by adding more sources (both hardware and software). This can be done without disruption to the rest of the system.
- 23. Disadvantages of Distributed System Complexity :- ◦ Lack of experience in designing, and implementing a distributed system. E.g. which platform (hardware and OS) to use, which language to use etc. Network problem:- ◦ If the network underlying a distributed system saturates or goes down, then the distributed system will be effectively disabled thus negating most of the advantages of the distributed system. Security:- ◦ Security is a major hazard since easy access to data means easy access to secret data as well.
- 24. Applications of Distributed System Cluster computing – a technique in which many computers are coupled together to work so that they achieve global goals. The computer cluster acts as if they were a single computer Grid computing – All the resources are pooled together for sharing in this kind of computing turning the systems into a powerful supercomputer; essentially.
- 25. Issues and Challenges Heterogeneity of components :- ◦ variety or differences that apply to computer hardware, network, OS, programming language and implementations by different developers. Openness:- ◦ System can be extended and re-implemented in various ways. Transparency:- ◦ make certain aspects of distribution are invisible to the application programmer ; focus on design of their particular application. ◦ They not concern the locations and details of how it operate, either replicated or migrated.
- 26. Issues and Challenges cont… Security:- ◦ Security for information resources in distributed system have 3 components : a. Confidentiality : protection against disclosure to unauthorized individuals. b. Integrity : protection against alteration/corruption c. Availability : protection against interference with the means to access the resources. Concurrency :- ◦ Where applications/services process concurrency, it will effect a conflict in operations with one another and produce inconsistence results. ◦ Each resource must be designed to be safe in a concurrent environment.
- 27. Distributed Systems Architecture Client-server 3-tier architecture Peer-to-peer
- 28. Client/Server Architecture Client/server architecture is a computing model in which the server hosts, delivers and manages most of the resources and services to be consumed by the client. Components Server Hosts Services Client Request Service Communication Media for message exchange
- 29. Peer-to-Peer Architecture (P2P Architecture) Peer-to-peer architecture (P2P architecture) is a commonly used computer networking architecture in which each workstation, or node, has the same capabilities and responsibilities.
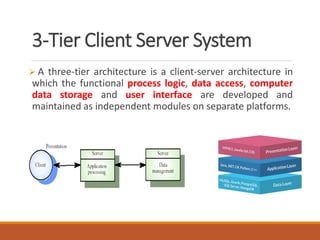
- 30. 3-Tier Client Server System A three-tier architecture is a client-server architecture in which the functional process logic, data access, computer data storage and user interface are developed and maintained as independent modules on separate platforms.
- 31. 3-Tier Client Server System Presentation Tier- The presentation tier is the front end layer in the 3-tier system and consists of the user interface. Application Tier- The application tier contains the functional business logic . Data Tier- The data tier comprises of the database/data storage system and data access layer.
- 32. 21-Oct-22 COMP28112 LECTURE 3 32 Client-Server vs P2P Client-Server ◦ Widely Used ◦ Functional Specialisation ◦ Asymmetrical ◦ Tends to be centralised ◦ Tends to scale poorly P2P ◦ Symmetrical, computers have same “rights” ◦ Truly Distributed ◦ Share / exploit resources with a large number of participants ◦ Resource discovery is a challenge
- 34. Cluster Computing A collection of similar processors (PCs, workstations) running the same operating system, connected by a high- speed LAN. Each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. Parallel computing capabilities using inexpensive PC hardware High degree of distribution transparency (single system image)(SSI) Processes can migrate between nodes dynamically and preemptively
- 35. Components of Cluster CPU CPU CPU … High Speed Local Network Cluster Middle ware Cluster … Nodes(master+computing) Network OS Cluster middleware: Middleware such as MPI which permits compute clustering programs to be portable to a wide variety of clusters
- 36. Grid Computing Systems Similar to clusters but processors are more loosely coupled, tend to be heterogeneous, and are not all in a central location. Highly heterogeneous with respect to hardware, software, networks, security policies, etc. A collaboration of users who pool resources (servers, storage, databases, clusters,..) and share them Can handle workloads similar to those on supercomputers, but grid computers connect over a network (Internet?) and supercomputers’ CPUs connect to a high-speed internal bus/network. Each user should have a single login account to access all resources. Resources may be owned by diverse organizations. .
- 37. Architecture for Grid Systems Fabric layer: interfaces to local resources at a specific site Connectivity layer: protocols to support usage of multiple resources for a single application; e.g., access a remote resource or transfer data between resources; and protocols to provide security Resource layer manages a single resource, using functions supplied by the connectivity layer Collective layer: resource discovery, allocation, scheduling, etc. Applications: use the grid resources The collective, connectivity and resource layers together form the middleware layer for a grid . A layered architecture for grid computing systems
- 38. Cloud computing Is the delivery of computing services—servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics and more—over the Internet Is the delivery of on-demand computing services -- from applications to storage and processing power -- typically over the internet and on a pay-as-you-go basis. is an information technology (IT) paradigm that enables ubiquitous access to shared pools of virtualized and configurable system resources and higher-level services that can be rapidly provisioned with minimal management effort, often over the Internet.