Load distribution of analytical query workloads for database cluster architecture
- 1. Review on Load Distribution of Analytical Query Workloads For Database Cluster Architectures Research Paper by Thomas Phan Yahoo!, Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA Wen-Syan Li IBM Almaden Research Center, San Jose, CA, USA
- 2. Introduction Database Cluster - A group of databases Ex: a company may have two identical database systems, one as a production system for online transactions and one as a hot standby. And also some additional database systems which have a subset of base tables for various day today applications. These systems have their dedicated missions in the day time, but they could be left idle or under-utilized in the evening when batch workloads are processed. In such systems, query workloads can be distributed across different servers for better performance. Load Distribution of Analytical Query Workloads For Database Cluster Architectures
- 3. Introduction Cont. • Online query workloads - touch a relatively small region of the data on the disk. Such queries are said to be selective • Analytical Query Workloads - Touch large volumes of the disk. • On Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) OLAP is an approach to answer multi-dimensional analytical (MDA) queries swiftly. OLAP is part of the broader category of business intelligence, which also encompasses relational database, report writing and data mining. MQTs are required in OLAP applications as the query workloads tend to have complex structures and syntax. • Materialized query tables (MQT) MQT is a table whose definition is based on the result of a query, and whose data is in the form of pre-computed results that are taken from one or more tables.
- 4. Idea of the Research Framework for coordinating and optimizing execution of OLAP query workloads across a cluster of database servers with shared-nothing architecture. For a database cluster, such an optimization is achieved when, the maximum completion time of the workloads across all database servers is minimized Completion time at each database server includes, MQT and index building time + query workload execution time Expected Outcome : Server – MQT – Query mapping mechanism where workload execution time is minimized
- 5. Current Scenario Load distribution by dividing the workload into multiple sub-workloads and assign each sub-workload to a database server in some greedy manner, such as a round robin distribution. Problems Identified ‽ Queries routed to a database server may not be collocated with their needed MQTs ‽ Some MQTs may not t in the data server that has a limited disk space ‽ Some sub-workloads may be more expensive to execute than others, so some server may be idle while other servers are still busy ‽ Some servers may be more powerful than others
- 7. Proposed Methodology Cont. Key component - Scheduler (operates on the queries and the MQTs produced by an existing MQT Advisor product) Scheduler distributes the workload's queries and MQTs according to query- to-server and MQT-to-server mappings. Distribution problem number of different distribution combinations = Even for small parameters, the solution space grows exponentially, making an exhaustive search infeasible
- 8. Approach To search through the solution space, Genetic Algorithm (GA) search heuristic is used which finds a near-optimal mapping of • queries-to-servers • MQTs-to-servers and also • query-to-MQTs requirement mapping Other options may had used • Tabu search • Simulated annealing • Steepest-ascent hill climbing The justification for using GA as the searching algorithm instead of other methods, is not sufficient.
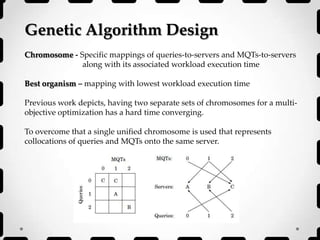
- 9. Genetic Algorithm Design Chromosome - Specific mappings of queries-to-servers and MQTs-to-servers along with its associated workload execution time Best organism – mapping with lowest workload execution time Previous work depicts, having two separate sets of chromosomes for a multi- objective optimization has a hard time converging. To overcome that a single unified chromosome is used that represents collocations of queries and MQTs onto the same server.
- 11. GA Evaluation Function • Initialize the execution times for all servers in the chromosome. • Check to see what MQTs have been materialized and at what server and accordingly adds these materialization times to the respective servers. • key loop that looks across all collocations. • If a query needs a particular MQT, the query's execution with the MQT is added to the execution time if the query and MQT are collocated. If they are not collocated, then the query's execution time without the MQT is added • The function returns the maximum execution time among the servers. • And it is omitted from the chromosome, go for next generation.
- 12. Mapping Optimization Developed Genetic Algorithm is compared with an exhaustive search and three standard greedy algorithms. And the paper shows that GA is a better solution in finding optimal mapping mechanism. Narrowing down the research in to OLAP query workloads and usage of MQTs is not clearly justified. And also there are some problems in the method followed to find the better solution.
- 13. Literature Review 1. Need to justify the single server approach Vs database cluster approach • Only describes the use of QCC (Query Cost Calibrator) in federated systems and not in database clusters 2. No enough evidence to emphasize the relativity of GA to solve optimization problem e.g. Evolutionary Optimization of File Assignment for a Large-Scale Video- on- Demand System by Jun Guo 3. Reasons for the use of scheduler algorithms for experiment is not clearly mentioned 4. Purpose for the use of OLAP is not identified • OLAP is used because MQTs are required OLAP 5. No review on the preparation of greedy algorithms e.g. Valuated matroids: a new look at the greedy algorithm by Andreas W.M. Dress, Walter Wenzel
- 14. What’s new on this topic ? • IQuery Performance Prediction for Analytical Workloads by Jennie Duggan Uses a combination of isolated and concurrent query execution samples, as well as new query workload features and metrics that can capture how different query classes behave for various levels of resource availability and contention. • Dynamic Prioritization of Database Queries by Sivaramakrishnan Narayanan, Florian Waas Presents a mechanism that continuously determines and re-computes the ideal target velocity of concurrent database processes based on their run-time statistics to achieve prioritization. In this scheme, every process autonomously adjusts its resource consumption using basic control theory principles.
- 15. Sources and data collection •5 types of scheduler algorithms GA Exhaustive Greedy1-MQTs-then-queries Greedy2-queries-then-MQTs Greedy3-no-MQTs •2 data sources workload produced by the standard TPC benchmark H generator synthetic benchmark based on the queries and MQTs from the TPC benchmarks Tests implemented in standard C++ and run on an off the shelf desk top computer running Red Hat Linux. GA run for 100 generations with a population size of 100 chromosomes.
- 16. Workload running time with increasing number of queries Exhaustive search and GA Comparison against exhaustive search shows that GA gives very close results as in exhaustive search which implies accuracy.
- 17. Workload running time with increasing number of servers GA, exhaustive search, greedy1, 2, 3 Workload running time with increasing number of queries
- 18. Issues •Assumption as having infinite disk space But disk space is limited •Tested for homogeneous servers only But if heterogeneous!!! •Scalability tested up to limited number queries only But when increased??? •Emphasis on the suitability of GA from the very beginning. But results show Greedy 2 is also significant
- 19. Conclusion -problem identification is successful -prior conclusions of results??? -further improvements for algorithms is needed
- 20. Thank You !
Editor's Notes
- #4: You can think of an MQT as a kind of materialized view. Both views and MQTs are defined on the basis of a query. The query on which a view is based is run whenever the view is referenced; however, an MQT actually stores the query results as data, and you can work with the data that is in the MQT instead of the data that is in the underlying tables.