Mbt 1
- 2. The MBT Bracket System • The MBT bracket system is based on a more balanced mix of science,tradition and experience. • It is a bracket system for use with light continuous forces, lacebacks and bendbacks • It is designed ideally to work with sliding mechanics. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 3. Requirements for Providing Quality Orthodontic Care • Good diagnosis and treatment planning. • Best available bracket system. • Correct positioning and repositioning of brackets. • Clear philosophy on arch form. • Effective aligning technique. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 4. • Ability to level the dental arches and control overbite. • Correction of Class II and Class III discrepancies . • Controlled space closure, with sliding mechanics. • Persistence in finishing. • Good retention protocol. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 5. Diagnosis and treatment planning -The Dental VTO DENTAL VTO provides organized and simplified information about direction and amount of dental movement in UL arches. The information includes,the initial position and desired movement of first molars ,the cuspids and the dental midlines. It is helpful in extraction and non-extraction decision and can be referred during regular follow-up. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 6. Midline Molars Right Left INITIAL MIDLINE AND MOLAR POSITION Chart 1www.indiandentalacademy.com
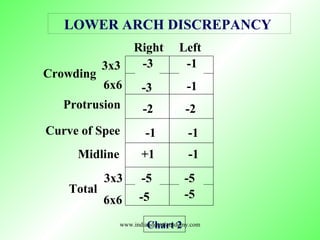
- 7. Right Left 3x3 6x6 Crowding Protrusion Curve of Spee Midline 3x3 Total 6x6 LOWER ARCH DISCREPANCY Chart 2www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 8. Secondary factors to provide additional space. • Interproximal enamel reduction. • Uprighting or distal movement of lower first molars. • Buccal uprighting of lower canines and lower posterior teeth. • Leeway space or ‘E’space. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 10. Case - 1 • 12 year old male patient. • Class II skeletal pattern. • High angle with increased lower facial height • 4mm Class II on right side. • 3.5mm Class II on left side. • Lower midline deviated 1mm to right. • 4mm lower incisor crowding. • 2mm Curve of Spee. • Lower anteriors 6mm in front of A.pog line. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 11. Right 4mm Left 3.5mm INITIAL MIDLINE AND MOLAR POSITION 1mm Chart-1www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 12. Right Left 3x3 6x6 Crowding Protrusion Curve of Spee Midline 3x3 Total 6x6 LOWER ARCH DISCREPANCY Chart 2 -3 -3 -1 -1 -2 -2 -1 -1 +1 -1 -5 -5 -5 -5 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 13. Right Left ANTICIPATED TREATMENT CHANGE (7) (7) 2mm 5mm 1mm 5mm 2mm 2mm 9mm 0 1.5mm8.5mm (7) (7) Chart-3. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 14. Bracket Specification THE FIRST GENERATION PAE • The original SWA was introduced by Andrews in 1972 and it had the features of Siamese edgewise bracket. • He recommended a wide range of brackets. - For extraction cases, anti-tip,anti-rotation, and power arms for control space closure. -Three sets of incisor brackets with varying degrees of torque for different clinical situation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 15. THE SECOND GENERATION PEA • To avoid inventory difficulties or multiple bracket system, ROTH recommended a single appliance system to manage both extraction and non-extraction cases. • The appliance prescriptions developed by Andrews and Roth were based on the treatment mechanics used in their practice. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 16. THE THIRD GENERATION PEA • The MBT has been developed from the combined clinical experience of the authors for more than 70 years. • It also introduced additional research input from Japanese sources to update the scientific input. • It is designed ideally to work with sliding mechanics,with light continuous forces, lacebacks and bendbacks. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 17. The MBT Versatile Appliance System. Victory Series Brackets. Clarity Brackets. Unitek Full-Sized Twin Brackets. Molar bands,molar bonding bases,and buccal tubes. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 18. Design features of a modern bracket system • Range of brackets - Standard size metal brackets. - Mid-size metal brackets. -Esthetic brackets. • Improved i.d system Laser numbering of standard size metal brackets. • Rhomboidal shape Reduces bulk and assists accuracy of bracket placement. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 19. • Torque in base-the CAD factor Using CAD it is possible to program the computer to create the correct relationship between the mid-point on the tooth and the slot base,as with traditional torque-in-base. • Refinement of bracket base design It is incorporated to increase strength and help plaque control in difficult areas. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 20. • Drawing of original SWA bracket. • Dots (upper) and dashes (lower) were used for i.d purposes. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 21. • Drawing of MBT brackets. • Standard size brackets have a rhomboidal form and numerical i.d.system. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 22. • Lower premolar bracket may be offset on specially designed bases,to increase bond strength and reduce the risk of bond failure. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 23. • Tapered bracket bases on lower incisors can help in plaque control in this difficult area. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 24. Tip specification ANTERIOR TIP Reduced anterior tip was incorporated into the appliance to conform to Andrews original research,and to dramatically reduce the anchorage needs of each case. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 25. Incisor Tip Cuspid Tip Upper Central Upper Lateral Lower Central Lower Lateral Upper Lower MBT Versatile+ 4.0° 8.0° 0° 0° 8.0° 3.0° Original SWA3 5.0° 9.0° 2.0° 2.0° 11.0° 5.0° www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 26. UPPER POSTERIOR TIP •Upper bicuspid brackets are provided with 00 tip to keep these teeth in a more upright position . •Upper molar brackets are provided with 00 tip, which when placed parallel to the occlusal plane,introduces 50 tip into the upper molars. www.indiandentalacademy.com
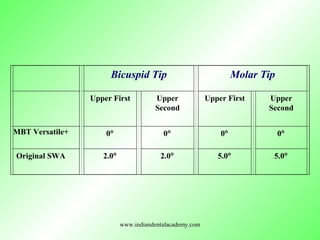
- 27. Bicuspid Tip Molar Tip Upper First Upper Second Upper First Upper Second MBT Versatile+ 0° 0° 0° 0° Original SWA 2.0° 2.0° 5.0° 5.0° www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 28. Upper tip considerations The authors prefer a 00 tip bracket,with the band seated parallel to the buccal cusps.This gives 50 tip. If a 50 bracket is used,the band must be seated more gingivally at the mesial. If a 50 bracket is used,and the band is seated parallel to the buccal cusps,this will result in an effective 100 tip on the molar. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 29. LOWER POSTERIOR TIP •Lower posterior tip in the first and second bicuspid brackets is maintained at 20 , to slightly incline these teeth forward. •For the lower first and second molars, 00 tipped brackets are provided, which when placed parallel to the occlusal plane,introduces 20 of tip to these teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 30. Lower Bicuspid Tip Lower Molar Tip Lower First Lower Second Lower First Lower Second MBT Versatile+ 2.0° 2.0° 0° 0° Original SWA 2.0° 2.0° 2.0° 2.0° www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 31. Torque specification INCISOR TORQUE •Upper incisor brackets are provided with additional palatal root torque;while lower incisor brackets are provided with additional labial root torque. •This adjustment aids in the correction of the most common torque problems occurring in the incisor areas. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 32. Upper central incisor torque • Increased palatal root torque for upper centrals. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 33. Upper lateral incisor torque • Increased palatal root torque for upper lateral incisors. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 34. Lower incisor torque • Increased labial root torque for lower incisors. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 35. Incisor Torque Incisor Torque Upper Central Upper Lateral Lower Central Lower Lateral MBT Versatile+ 17.0° 10.0° -6.0° -6.0° Original SWA 7.0° 3.0° -1.0° -1.0° www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 36. Upper Cuspid ,bicuspid and molar torque. •Upper cuspid and bicuspid brackets are provided with the normal -70 of torque. •Upper molar brackets are provided with an additional 50 of buccal root torque (-90 to -140 ) to reduce palatal cusp interferences with these teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 37. • Upper canine torque. • Available in –70 ,00 , +70 , torque. • The 00 and +70 options are for cases with narrow maxillary bone form andor prominent canine roots,and are often used with archwires in the tapered form. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 38. Upper torque considerations There was a tendency for upper first molar palatal cusps to extrude. A bracket with – 140 of buccal torque gives extra control. In some cases it is necessary to add buccal root torque to the upper archwire ,even when using a –140 torque bracket. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 39. Upper Cuspid, Bicuspid and Molar Torque Upper Cuspids Upper 1st Bicuspids Upper 2nd Bicuspids Upper 1st Molars Upper 2nd Molars MBT Versatile+ -7.0 -7.0 -7.0 -14.0 -14.0 Original SWA -7.0 -7.0 -7.0 -9.0 -9.0 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 40. Lower cuspid,bicuspid and molar torque. •Progressive buccal crown torque is provided in the brackets of the lower posterior segments. •This allows for buccal uprighting of these teeth,which is beneficial in most cases. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 41. • Lower canine torque available in –60 ,00 ,+60 , • The 00 and +60 options are for cases with narrow mandibular bone form or prominent canine roots,or deep bites at start of treatment. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 42. Lower Cuspid, Bicuspid and Molar Torque Lower Cuspids Lower 1st Bicuspids Lower 2nd Bicuspids Lower 1st Molars Lower 2nd Molars MBT Versatile+ -6.0 -12.0 -17.0 -20.0 -10.0 Original SWA -11.0 -17.0 -22.0 -30.0 -35.0 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 43. In-out specification • It is 100% fully expressed. • In upper premolars an alternative bracket which is 0.5mm thicker than normal,is used. • This is helpful in obtaining good alignment of marginal ridges in cases with small upper second premolars. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 44. In-out modifications. • An upper second bicuspid bracket with an additional 0.5mm of in-out compensation is provided for the common situation in which upper second bicuspids are smaller than upper first bicuspids. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 45. Horizontal bracket placement errors • If brackets are placed to the mesial or distal of the vertical long axis of the clinical crown,improper tooth rotation can occur. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 46. Axial or paralleling bracket placement errors • These will occur if the bracket wings do not straddle the vertical long axis of the crown in a parallel manner. • Such errors lead to improper crown tip. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 47. Thickness errors. • Excess bonding agent beneath the bracket base can cause thickness and rotational errors. • Can be eliminated by pressing the bracket against the tooth. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 48. Vertical errors • Vertical errors in bracket placement are caused by placing brackets gingival or incisalocclusal to the center of the clinical crown. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 49. Gingival Concern. • Partially erupted tooth. • It is difficult to visualize the center of the clinical crown on partially erupted teeth,when treating young patients. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 50. Gingival Inflammation • Top:Healthy gingivae. • Bottom :The same case with inflamed gingivae in the upper right quadrant. Gingival inflammation causes foreshortening,effectively reducing the length of the clinical crowns. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 51. Teeth with palatally or lingually displaced roots. • Individual teeth with lingually displaced roots can produce short clinical crowns. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 52. Teeth with facially displaced roots. • Individual teeth with facially displaced roots can produce long clinical crowns. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 53. Incisal or Occlusal concerns. • Incisal crown fractures or tooth wear make it difficult to visualize the center of the clinical crown. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 54. Crowns with long tapered buccal cusps • Cuspids with tapered clinical crowns often do not have adequate contact with the opposing teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 55. Axial/paralleling variation The tip position of the lateral incisor brackets was varied to help root paralleling. In this case a lower incisor has been extracted and root paralleling has been helped by changing axial positions of adjacent brackets. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 56. Palatally positioned lateral incisors. It is important to create adequate space before attempting to move palatally placed incisors. It is beneficial to invert the bracket on instanding lateral incisors,giving –100 torque. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 57. Upper first molar bracket positioning. Correct position. Band is seated more gingivally at the mesial when treating Class II molar relationship. It is common error to allow the band to seat too gingivally at the distal,causing excessive crown tip.www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 58. Lower first molar bracket positioning. Correct band positioning. A common error is to allow the band to seat too gingivally at the mesial . www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 59. Lower first molar bracket positioning Occlusal interferences can be a problem in some cases. A lower second molar tube can be used on lower first molars to avoid interferences in some cases. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 63. Arch form considerations for stability and esthetics. • Bonwill and Hawley in 1905,suggested the geometric method of constructing the ideal arch form. - The lower six anterior teeth lie along a circle whose radius equaled their combined widths. -From this circle an equilateral triangle is created,the base of which represented the condylar width. -Premolars and molars should lie along these extended lines. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 64. • In 1907 Angle- - The form of line from the premolars and molars should resemble a parabolic curve. -He proposed the need for natural curvature in molar region. • In 1934 Chuck- -Noted variation in arch form –square, oval, tapering. -The premolar region should be wider than canines to prevent excessive expansion of the canines. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 65. • In 1963 Boone – -Superimposed Bonwill-Hawley arch form on a millimeter grid and used Angles method for construction. -Thus Bonwill-Hawley arch form is used as a template in edgewise. • Braun et al,1998 -Reported that the human arch form could be represented by a complex mathematical formula,known as the Beta function. -This was calculated by entering measurements of dental landmarks on orthodontic models into a computer curve-fitting program. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 66. Traditional edgewise wire bending and Boone arch form. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 67. • The Catenary curve is formed by extending a chain from two fixed points. • Many of the tapered arch forms provided by orthodontic manufactures today are based on Catenary curve. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 69. Relapse tendency after changing arch form. • Riedel in 1969,postulated that arch form, in the mandibular arch,cannot be permanently altered during appliance therapy. • Similar research was done by Shapiro, Gardner, Felton,De La Cruz and Burke suggesting that changes in inter-molar width seem to be more stable than those of inter-canine width. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 70. The four components of archform i. ANTERIOR CURVATURE Based on inter-canine width. Its shape becomes more tapered when inter-canine width is narrow and more square when inter-canine width is wide. ii. INTER-CANINE WIDTH This appears to be the most critical aspect of arch form,because significant relapse occurs if this dimension is changed. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 71. • POSTERIOR CURVATURE In the posterior area a gradual curvature between canine and second molars are preferred. • INTER-MOLAR WIDTH Treatment changes in this dimension is more stable. Arch form in the inter-molar region can be widened or narrowed,depending on the needs of the case. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 72. MBT ARCH FORM • The three basic arch forms are tapered, square and ovoid. • When superimposed they vary mainly in inter-canine width,giving a range of approximately 6mm. • Inter-molar widths are similar ,but the molar areas can be widened or narrowed as needed,by easy wire bending. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 73. THE TAPERED ARCH FORM • Indicated for patients with narrow ,tapered arch form and gingival recession in canine and premolar regions. • Cases undergoing single arch treatment,in this way no expansion of treated arch occurs. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 74. THE SQUARE ARCH FORM • Indicated in cases with broad arch form. • Cases that require buccal uprighting of the lower posterior segments and expansion of the upper arch. • After over-expansion has been achieved ,it may be beneficial to change to the ovoid arch form in the later stages of treatment. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 75. THE OVOID ARCH FORM • It is the most preferred arch form. The ovoid arch form has proved to be good, reliable arch form for high percentage of cases treated with PAE • Treated cases have shown good stability, with minimal amounts of post-treatment relapse. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 76. ARCH FORMS - MBT www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 77. Selection of Archform i. Arch form template are placed on lower study models. -The inter-canine width is evaluated. ii.If buccal uprighting is needed in the lower arch, a wider arch form is selected. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 78. In 70% of cases buccal uprighting will result in lower anterior relapse. Cases in which buccal uprighting will be stable include- (a) Cases in which maxillary expansion is indicated. (b)Deep bite cases such as Class II /2 cases. iii.Contour and width in the lower posterior segment is estimated but this can be easily customized. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 79. Arch wire Sequencing EARLY IN TREATMENT - .015”/ .0175” multistranded /.014” SS OR .016” HANT. Less effect on arch form , so ovoid arch form indicated for all cases. MID TREATMENT – .014”/.016”/.018” SS OR .019x.025” Rec. HANT. Influence arch form –requires full inventory. LATE TREATMENT- .019x.025”SS – stocks of three arch forms.www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 80. Archwire Coordination • It is important throughout treatment. • Most critical with heavier round wires and . 019x.025 SS. • Arch form templates can be used for coordination. • The upper wire should superimpose approximately 3mm outside lower wire. • This is representative of overlap of the upper teeth relative to the lower teeth. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 81. SLIDING MECHANICS Passive tiebacks. Type 1 active tiebacks www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 82. SLIDING MECHANICS Type 2 active tieback. Type 3 active tieback. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 83. ARCH WIRE WITH SOLDERED HOOKS www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 84. Arch form during finishing and detailing • Phase of settling is preferred with lighter wires. -Lower arch- .014”SS or .016” NiTi - Upper arch- .014”SS sect.,with light triangular elastics. • Teeth adjacent to extraction sites lightly tied together. • An upper removable plate is required to maintain maxillary expansion. • In Class II/1 cases to prevent overjet relapse, a full .014”SS arch wire with bendbacks is advocated. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 85. EXCLUSIVE MBT APPLIANCE FEATURES. • Reduced anterior tip. • Upper bicuspid brackets with 00 tip. • Lower bicuspid brackets with 20 tip. • Additional palatal root torque for upper incisors and additional labial root torque for lower incisors. • Upper cuspid brackets with the normal –70 torque or 00 torque. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 86. • Upper molar brackets with additional 50 buccal root torque. • Progressive buccal crown torque in lower cuspids and lower buccal segments. • Optional upper second bicuspid brackets with an additional 0.5mm of in-out compensation. • Three bracket types,Clarity Aesthetic Brackets, Victory Series brackets, and Unitek Full Size Twin Brackets,all available with APC Adhesive Coating. www.indiandentalacademy.com