Metaprogramming with JavaScript
- 1. Metaprogramming with JavaScript Timur Shemsedinov Research Institute of System Technologies
- 2. What is Metaprogramming? • Templates and macroses to generate source code in compile-time • Self-changing programs • Programs that generate other programs • other meanings ?
- 3. What is Metaprogramming? 1. This is not artificial intelligence. 2. Metaprogramming is not something new, you've always used it. 3. In programming languages of Von Neumann architecture nothing happens without metadata (architecture in which data and instructions are stored in shared memory and computer needs to recognize numbers, strings, addresses, executable instruction, etc.)
- 4. What is Metaprogramming? Programming paradigm that implies program structure and functionality modification programmatically
- 5. How Metaprogramming works? Programming paradigm that implies program structure and functionality modification programmatically 1. When changes occur? 2. What is changing? 3. Whereby changes occur?
- 6. How Metaprogramming works? When changes occurs? • Design-time • Compile-time • Run-time • Just-in-Time (immediate when executing/processing) • Lazy (between executing/processing) • On Timer • On Pull requests • On Push notifications
- 7. How Metaprogramming works? What is changing? • data types and data structures • identifiers (class names, type names, variable names) • calls (method/function names, dynamic binding) • algorithm parameters • formula syntax, regular expression syntax, etc. • dynamic code interpretation (eval) • data serialization/deserialization
- 8. How Metaprogramming works? Whereby changes occurs? • Parsing and translation of syntactic structures • Access to objects and functions by identification name • Full introspection • First-class objects individuation: • functions, using closures • classes, using inheritance (prototypes in js) • objects, using mixins
- 9. The problem definition Why do we need Metaprogramming? • To raise functionality, universality and abstraction level of software solutions • Dynamic domains when changing functionality and structure is a normal mode • Intersystem/inter-module integration, using introspection and dynamic binding
- 10. Example 1: data definition var names = [ "Marcus Aurelius Antoninus Augustus", "Darth Vader", "Victor Michailovich Glushkov", "Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz", "Mao Zedong", "Vladimir Sergeevich Soloviov", "Ibn Arabi", "Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy", "Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi", "Rene Descartes", "Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoyevsky", "Benedito de Espinosa" ];
- 11. Example 1: solution (without metaprogramming) function filter(names) { var result = [], name; for (var i=0; i<names.length; i++) { name = names[i]; if ( name.length >= 10 && name.length <= 200 && name.indexOf("Mich") > -1 && name.indexOf("V") === 0 && name.slice(-2) == "ov" && !( name.length >= 50 && name.length <= 65 && name.indexOf("Abu") > -1 && name.indexOf("Lev") === 0 && name.slice(-3) == "iov") ) result.push(name); } return result; }
- 12. Example 1: extracted metadata var conditions = { length: [10, 200], contains: "Mich", starts: "V", ends: "ov", not: { length: [50, 65], contains: "Abu", starts: "Lev", ends: "iov" } };
- 13. Example 1: metamodel function filter(names, conditions) { var operations = { length: function(s,v) { return s.length>=v[0] && s.length<=v[1] }, contains: function(s,v) { return s.indexOf(v) > -1 }, starts: function(s,v) { return s.indexOf(v) === 0 }, ends: function(s,v) { return s.slice(-v.length) == v }, not: function(s,v) { return !check(s,v) } }; function check(s, conditions) { var valid = true; for (var key in conditions) valid &= operations[key](s, conditions[key]); return valid; } return names.filter(function(s) { return check(s, conditions); }); }
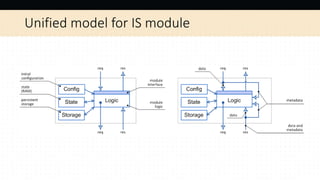
- 14. Unified model for IS module
- 15. Example 2: task definition var tasks = [ { interval:5000, get:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method1.json", expect:"OK", save:"file1.json" }, { interval:"8s", get:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method2.json", put:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method4.json", save:"file2.json" }, { interval:"7s", get:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method3.json", expect:"Done", post:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method5.json" }, { interval:"4s", load:"file1.json", expect:"OK", put:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method6.json" }, { interval:"9s", load:"file2.json", save:"file1.json", post:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method7.json" }, { interval:"3s", load:"file1.json", save:"file3.json" }, ];
- 16. Example 2: metamodel function iterate(tasks) { function closureTask(task) { return function () { console.dir(task); var source; if (task.get) source = request.get(task.get); if (task.load) source = fs.createReadStream(task.load); if (task.save) source.pipe(fs.createWriteStream(task.save)); if (task.post) source.pipe(request.post(task.post)); if (task.put) source.pipe(request.put(task.put)); } }; for (var i=0; i<tasks.length; i++) setInterval(closureTask(tasks[i]), duration(tasks[i].interval)); }
- 17. Example 2: metamodel (with internal configuration) function iterate(tasks) { var sources = { get: request.get, load: fs.createReadStream }; var destinations = { save: fs.createWriteStream, post: request.post, put: request.put }; function closureTask(task) { return function () { console.dir(task); var verb, source, destination; for (key in sources) if (task[key]) source = sources[key](task[key]); for (key in destinations) if (task[key]) source.pipe(destinations[key](task[key])); } }; for (var i=0; i<tasks.length; i++) setInterval(closureTask(tasks[i]), duration(tasks[i].interval)); }
- 18. Example 3: interpretation // Parse duration to seconds, example: duration("1d 10h 7m 13s") function duration(s) { var result = 0; if (typeof(s) == 'string') { var days = s.match(/(d+)s*d/), hours = s.match(/(d+)s*h/), minutes = s.match(/(d+)s*m/), seconds = s.match(/(d+)s*s/); if (days) result += parseInt(days[1])*86400; if (hours) result += parseInt(hours[1])*3600; if (minutes) result += parseInt(minutes[1])*60; if (seconds) result += parseInt(seconds[1]); result = result*1000; } if (typeof(s) == 'number') result = s; return result; }
- 19. Example 3: interpretation (configurable) function duration(s) { if (typeof(s) == 'number') return s; var units = { days: { rx:/(d+)s*d/, mul:86400 }, hours: { rx:/(d+)s*h/, mul:3600 }, minutes: { rx:/(d+)s*m/, mul:60 }, seconds: { rx:/(d+)s*s/, mul:1 } }; var result = 0, unit, match; if (typeof(s) == 'string') for (var key in units) { unit = units[key]; match = s.match(unit.rx); if (match) result += parseInt(match[1])*unit.mul; } return result*1000; }
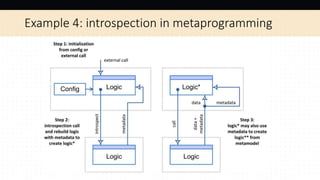
- 20. Example 4: introspection in metaprogramming
- 21. Example 4: introspection var ds = wcl.AjaxDataSource({ read: { get: "examples/person/read.json" }, insert: { post: "examples/person/insert.json" }, update: { post: "examples/person/update.json" }, delete: { post: "examples/person/delete.json" }, find: { post: "examples/person/find.json" }, metadata: { post: "examples/person/metadata.json" } }); ds.read({ id:5 }, function(err, data) { data.phone ="+0123456789"; ds.update(data, function(err) { console.log('Data saved'); }); });
- 22. Example 4: introspection in metaprogramming var ds = wcl.AjaxDataSource({ introspect: { post: "examples/person/introspect.json" } }); ds.read({ id:3 }, function(err, data) { data.phone ="+0123456789"; ds.update(data, function(err) { console.log('Data saved'); }); });
- 23. Example 4: introspection in metaprogramming var ds = wcl.MemoryDataSource({ data: [ { id:1, name:"Person 1", phone:"+380501002011", emails:[ "person1@domain.com" ], age: 25 }, { id:2, name:"Person 2", phone:"+380501002022", emails:[ "person2@domain.com", "person2@domain2.com" ], address: { city: "Kiev", street:"Khreschatit", building: "26" } }, { id:3, name:"Person 3", phone:"+380501002033", emails:[ "person3@domain.com" ], tags: [ {tag:"tag1", color:"red"}, {tag:"tag2", color:"green"} ] }, ]}); ds.read({ id:3 }, function(err, data) { data.phone ="+0123456789"; ds.update(data, function(err) { console.log('Data saved'); }); });
- 24. Metaprogramming techniques • Task definition style: declarative, using metadata, imperative and functional elements • Hashes (associative arrays) beforehand unknown key: var a = {}; a[key] = value; • String interpretation, inventing domain-specific syntactic structures or using universal ones (json, js, regexp ...) • Mixins: beforehand unknown targer object/class function mixin(a) { a.fn=function(){ ... } } • Closures: function individuations fn = (function(a) { return function() { return a*2 } })(value)
- 25. The findings • Code size: generally decrease a lot but may increases code size in rare cases (compensated by code readability) • Speed: slightly decreases but good implementation may remain approximately the same speed • Flexibility: solution becomes more abstract/universal software application scope expands • Integration: usually much simplified integration and requires less code changes • Working pleasure: metaprogramming is interesting so we have more pleasure and motivation • Working speed: increasing development time but modification and support tasks take less time, so total time is less
- 26. Metaprogramming with JavaScript Github: https://github.com/tshemsedinov/metaprogramming Article: http://habrahabr.ru/post/227753/
- 27. Metaprogramming with JavaScript Thank you! Questions please Timur Shemsedinov Research Institute of System Technologies










![Example 1: data definition
var names = [
"Marcus Aurelius Antoninus Augustus",
"Darth Vader",
"Victor Michailovich Glushkov",
"Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz",
"Mao Zedong",
"Vladimir Sergeevich Soloviov",
"Ibn Arabi",
"Lev Nikolayevich Tolstoy",
"Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi",
"Rene Descartes",
"Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoyevsky",
"Benedito de Espinosa"
];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-10-320.jpg)
![Example 1: solution (without metaprogramming)
function filter(names) {
var result = [], name;
for (var i=0; i<names.length; i++) {
name = names[i];
if ( name.length >= 10 && name.length <= 200 &&
name.indexOf("Mich") > -1 &&
name.indexOf("V") === 0 &&
name.slice(-2) == "ov" &&
!( name.length >= 50 && name.length <= 65 &&
name.indexOf("Abu") > -1 &&
name.indexOf("Lev") === 0 &&
name.slice(-3) == "iov")
) result.push(name);
}
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-11-320.jpg)
![Example 1: extracted metadata
var conditions = {
length: [10, 200],
contains: "Mich",
starts: "V",
ends: "ov",
not: {
length: [50, 65],
contains: "Abu",
starts: "Lev",
ends: "iov"
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-12-320.jpg)
![Example 1: metamodel
function filter(names, conditions) {
var operations = {
length: function(s,v) { return s.length>=v[0] && s.length<=v[1] },
contains: function(s,v) { return s.indexOf(v) > -1 },
starts: function(s,v) { return s.indexOf(v) === 0 },
ends: function(s,v) { return s.slice(-v.length) == v },
not: function(s,v) { return !check(s,v) }
};
function check(s, conditions) {
var valid = true;
for (var key in conditions)
valid &= operations[key](s, conditions[key]);
return valid;
}
return names.filter(function(s) { return check(s, conditions); });
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-13-320.jpg)
![Example 2: task definition
var tasks = [
{ interval:5000, get:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method1.json",
expect:"OK", save:"file1.json" },
{ interval:"8s", get:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method2.json",
put:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method4.json", save:"file2.json" },
{ interval:"7s", get:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method3.json",
expect:"Done", post:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method5.json" },
{ interval:"4s", load:"file1.json",
expect:"OK", put:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method6.json" },
{ interval:"9s", load:"file2.json", save:"file1.json",
post:"http://127.0.0.1/api/method7.json" },
{ interval:"3s", load:"file1.json", save:"file3.json" },
];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-15-320.jpg)
![Example 2: metamodel
function iterate(tasks) {
function closureTask(task) { return function () {
console.dir(task);
var source;
if (task.get) source = request.get(task.get);
if (task.load) source = fs.createReadStream(task.load);
if (task.save) source.pipe(fs.createWriteStream(task.save));
if (task.post) source.pipe(request.post(task.post));
if (task.put) source.pipe(request.put(task.put));
} };
for (var i=0; i<tasks.length; i++)
setInterval(closureTask(tasks[i]), duration(tasks[i].interval));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-16-320.jpg)
![Example 2: metamodel (with internal configuration)
function iterate(tasks) {
var sources = { get: request.get,
load: fs.createReadStream };
var destinations = { save: fs.createWriteStream,
post: request.post,
put: request.put };
function closureTask(task) { return function () {
console.dir(task);
var verb, source, destination;
for (key in sources)
if (task[key]) source = sources[key](task[key]);
for (key in destinations)
if (task[key]) source.pipe(destinations[key](task[key]));
} };
for (var i=0; i<tasks.length; i++)
setInterval(closureTask(tasks[i]), duration(tasks[i].interval));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-17-320.jpg)
![Example 3: interpretation
// Parse duration to seconds, example: duration("1d 10h 7m 13s")
function duration(s) {
var result = 0;
if (typeof(s) == 'string') {
var days = s.match(/(d+)s*d/),
hours = s.match(/(d+)s*h/),
minutes = s.match(/(d+)s*m/),
seconds = s.match(/(d+)s*s/);
if (days) result += parseInt(days[1])*86400;
if (hours) result += parseInt(hours[1])*3600;
if (minutes) result += parseInt(minutes[1])*60;
if (seconds) result += parseInt(seconds[1]);
result = result*1000;
} if (typeof(s) == 'number') result = s;
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-18-320.jpg)
![Example 3: interpretation (configurable)
function duration(s) {
if (typeof(s) == 'number') return s;
var units = {
days: { rx:/(d+)s*d/, mul:86400 },
hours: { rx:/(d+)s*h/, mul:3600 },
minutes: { rx:/(d+)s*m/, mul:60 },
seconds: { rx:/(d+)s*s/, mul:1 }
};
var result = 0, unit, match;
if (typeof(s) == 'string') for (var key in units) {
unit = units[key];
match = s.match(unit.rx);
if (match) result += parseInt(match[1])*unit.mul;
}
return result*1000;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-19-320.jpg)


![Example 4: introspection in metaprogramming
var ds = wcl.MemoryDataSource({ data: [
{ id:1, name:"Person 1", phone:"+380501002011",
emails:[ "person1@domain.com" ], age: 25 },
{ id:2, name:"Person 2", phone:"+380501002022",
emails:[ "person2@domain.com", "person2@domain2.com" ],
address: { city: "Kiev", street:"Khreschatit", building: "26" } },
{ id:3, name:"Person 3", phone:"+380501002033",
emails:[ "person3@domain.com" ],
tags: [ {tag:"tag1", color:"red"}, {tag:"tag2", color:"green"} ] },
]});
ds.read({ id:3 }, function(err, data) {
data.phone ="+0123456789";
ds.update(data, function(err) {
console.log('Data saved');
});
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-23-320.jpg)
![Metaprogramming techniques
• Task definition style: declarative, using metadata,
imperative and functional elements
• Hashes (associative arrays)
beforehand unknown key: var a = {}; a[key] = value;
• String interpretation, inventing domain-specific syntactic
structures or using universal ones (json, js, regexp ...)
• Mixins: beforehand unknown targer object/class
function mixin(a) { a.fn=function(){ ... } }
• Closures: function individuations
fn = (function(a) { return function() { return a*2 } })(value)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shemsedinov-metaprogramming-en-140710155630-phpapp02/85/Metaprogramming-with-JavaScript-24-320.jpg)


