Midbrain And Cerebellum
- 2. Midbrain
- 3. GrossAppearanceGrossAppearance of Midbrain:of Midbrain: • connectstheponsand cerebellum with the forebrain. • Itslong axisascends through theopening in the tentorium cerebelli. • Themidbrain istraversed by anarrow channel, the cerebral aqueduct, which isfilled with cerebrospinal fluid
- 4. posterior surface 1. Four colliculi Thesearerounded eminencesthat are divided by avertical and atransversegrooveinto : • Superior colliculi : arecentersfor visual reflexes • Inferior colliculi : arelower auditory centers.
- 5. 2. Trochlear nerves: emergeIn the midlinebelow the inferior colliculi, (Theseareslender cranial nervesthat wind around thelateral aspect of the midbrain to enter the lateral wall of the cavernoussinus).
- 6. • On thelateral aspect of themidbrain, 3. Superior brachium passesfrom thesuperior colliculusto thelateral geniculatebody and the optic tract. 4. Inferior brachium connectstheinferior colliculusto themedial geniculatebody.
- 7. Anterior aspect 1. thereisadeep depression in themidline, called : Interpeduncular fossa, 2. Thisdepression is bounded on either sideby the: Cruscerebri. Many small blood vessels perforatethefloor of the interpeduncular fossa, and thisregion istermed the: Posterior perforated substance
- 8. 3. Theocculomotor nerve emergesfrom agroove on themedial sideof thecruscerebri and passesforward in the lateral wall of the cavernoussinus.
- 9. Arterial supply: issupplied by: 1. Posterior cerebral 2. Superior cerebellar 3. Basilar arteries. Venousdrainage: into thebasal or great cerebral veins
- 11. Level Inferior colliculi Cavity Cerebral aqueduct Nuclei Inferior colliculus, Substantianigra, Trochlear nucleus, Mesencephalic nuclei of cranial nerveV MotorTracts Corticospinal and corticonuclear tracts, Temporopontine, Frontopontine, Medial longitudinal fasciculus, Sensory Tracts Lateral, trigeminal, spinal, and medial lemnisci; decussation of superior cerebellar peduncles
- 12. Nuclie: 4. Mesencephalic nuclei of cranial nerveV 1. Inferior colliculus, 2. Trochlear nucleus, 3. Substantia nigra,
- 13. Motor Tracts: 1. Temporo- pontine 2. Corticospinal & corticonuclear 3. Frontopontine, 4. Medial longitudinal fasciculus
- 14. Sensory tracts 1. Lemnisci (Lmn.) Lateral Lmn. Trigeminal Lmn Spinal Lmn. Medial Lmn. 2. Decussation of2. Decussation of superior cerebellarsuperior cerebellar pedunclespeduncles Cerebral aqueduct
- 15. Level Superior colliculi Cavity Cerebral aqueduct Nuclei Superior colliculus, substantianigra, Oculomotor nucleus, Edinger-Westphal nucleus, red nucleus, Mesencephalic nucleusof cranial nerveV MotorTracts Corticospinal and corticonuclear tracts, temporopontine, frontopontine, medial longitudinal fasciculus, decussation of rubrospinal tract Sensory Tracts Trigeminal, spinal, and medial lemnisci
- 17. Nuclie: 1. Superior colliculus, 2. Mesencephalic nucleusof cranial nerveV 2. Oculomotor nucleus, 3. Edinger-Westphal nucleus, 4. Red nucleus 5. Substantianigra,
- 18. Motor Tracts: 1. Temporo- pontine 2. Corticospinal & corticonuclear 3. Frontopontine, 5. Medial longitudinal fasciculus 4. Decussation of rubrospinal tract
- 19. Sensory tracts Lemnisci (Lmn.) Trigeminal Lmn Spinal Lmn. Medial Lmn.
- 20. Clinical Notes
- 21. Clinical Significance of the Midbrain • Themidbrain formstheupper end of thenarrow stalk of the brain or brainstem. Asit ascendsout of theposterior cranial fossathrough therelatively small rigid opening in the tentorium cerebelli, it isvulnerableto traumatic injury. • It possessestwo important cranial nervenuclei (oculomotor and trochlear), reflex centers(thecolliculi), and thered nucleusand substantianigra, which greatly influencemotor function, and themidbrain servesasaconduit for many important ascending and descending tracts. • Asin other partsof thebrainstem, it isasitefor tumors, hemorrhage, or infarcts that will produceawidevariety of symptomsand signs.
- 22. 1. Trauma to the Midbrain • asudden lateral movement of thehead could result in thecerebral pedunclesimpinging against the sharp rigid freeedgeof thetentorium cerebelli. • Sudden movementsof thehead resulting from traumacausedifferent regionsof thebrain to move at different velocities relativeto oneanother. For example, thelargeanatomical unit, theforebrain, may moveat adifferent velocity from theremainder of thebrain, such asthecerebellum. Thiswill result in themidbrain being bent, stretched, twisted, or torn.
- 23. • Involvement of the oculomotornucleus will produceipsilateral paralysis of thelevator palpebraesuperioris; thesuperior, inferior, and medial recti muscles; and theinferior oblique muscle. • Malfunction of the parasympathetic nucleus of the oculomotornerve producesadilated pupil that isinsensitiveto light and doesnot constrict on accommodation. • Involvement of the trochlearnucleus will producecontralateral paralysis of thesuperior obliquemuscleof theeyeball.
- 24. 2. Blockage of the Cerebral Aqueduct Thecavity of themidbrain, thecerebral aqueduct, isoneof thenarrower partsof theventricular system. • In congenital hydrocephalus, thecerebral aqueduct may be blocked or replaced by numerous small tubular passagesthat are insufficient for thenormal flow of cerebrospinal fluid. • When thecerebral aqueduct isblocked, theaccumulating cerebrospinal fluid within thethird and lateral ventricles produceslesionsin themidbrain. • Thepresenceof theoculomotor and trochlear nervenuclei, together with theimportant descending corticospinal and corticonuclear tracts, will providesymptomsand signsthat arehelpful in accurately localizing alesion in thebrainstem.
- 25. 3. VascularLesions of the Midbrain A. Weber Syndrome • which iscommonly produced by occlusion of abranch of theposterior cerebral artery that suppliesthe midbrain, resultsin thenecrosis of brain tissueinvolving oculomotor nerveand thecruscerebri. • Thereisipsilateral ophthalmoplegiaand contralateral paralysisof thelower part of theface, thetongue, and the arm and leg. Theeyeball isdeviated laterally becauseof theparalysisof themedial rectusmuscle; thereisdrooping (ptosis) of theupper lid, and thepupil isdilated and fixed to light and accommodation.
- 26. B. Benedikt Syndrome • issimilar to Weber syndrome, but thenecrosis involvesthemedial lemniscusand red nucleus, • producing contralateral hemianesthesiaand involuntary movementsof thelimbsof theopposite side.
- 27. Cerebellum
- 28. DefinitionDefinition: • The trilobed structure of the brain, lying posterior to the pons and medulla oblongata and inferior to occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres, thusit liesin theposterior cranial fossa. • Responsible for the regulation and coordination of complex voluntary muscular movementsand the maintainenceof postureand balance
- 29. GrossAppearanceof theCerebellum • situated in theposterior cranial fossa • covered superiorly by the tentorium cerebelli • liesposterior to thefourth ventricle, thepons, and themedullaoblongata • issomewhat ovoid in shapeand constricted in its median part.
- 30. It consistsof: 1. two cerebellar hemi- spheres 2. Vermis: joining both hemi- spheres.
- 31. Connected to posterior aspect of thebrainstem by threesymmetrical bundles of nervefiberscalled the: 1.Superior cerebellar peduncle 2.Middlecerebellar peduncle 3.inferior cerebellar peduncle
- 32. Thecerebellum is divided into three main lobes: 1. Anteriorlobe : may beseen on the superior surfaceof thecerebellum and is separated from the middlelobeby awide V-shaped fissure called theprimary fissure.
- 33. 2. Middlelobe: (sometimescalled the posterior lobe), which is thelargest part of the cerebellum, issituated between theprimary and posterolateral fissures. • Flocculonodular lobe: • issituated posterior to theposterolateral fissure. • Formed by two flocculi and thenodule Inferior veiw Superior veiw
- 34. Tonsils • Are roughly spherical lobuleson theinferior aspect of posterior lobe. • Thetonsil may bedisplaced down through theforamen magnum in conditionsof severeraised intracranial pressureor in congenital malformations
- 35. • horizontal fissure: that isfound along the margin of thecerebellum separatesthesuperior from theinferior surfaces.
- 36. The vermis • consistsof ; A. Superior part B. Inferior part • SuperiorVermis liesbetween superior medullary velum & primary fissure • Iscomposed of: 1. Lingula 2. Central lobule 3. Culmuen
- 37. • InferiorVermis liesbetween primary fissureand postero- lateral fissure, and consistsof : 1. Declive 2. Folium 3. Tuber 4. Pyramid 5. Uvula 6. Nodule
- 38. longitudinal division: 1. Vermis(medial zone) 2. Paravermal Region ( Intermediatezone) 3. Cerebellar Hemisphere: (Lateral zone)
- 39. Anatomically Transverseplane Longitudinal plane Anterior lobe Vermis Posterior lobe Paravermis Flocculonodular Hemisphere Functionally Spino- cerebellum Cerebro- cerebellum Vestibulo- cerebellum Phylogenetic Paleo- cerebellum Neo- cerebellum Archi- cerebellum
- 40. Functionally: • Thevestibulocerebellum (correspondsbest with theflocculonodular lobe) has reciprocal connectionswith vestibular and reticular nuclei and playsarolein control of body equilibrium and eye movement. • Thespinocerebellum (correspondsbest to theanterior lobe) hasreciprocal connectionswith thespinal cord and playsarolein control of muscletoneaswell asaxial and limb movements, such asthoseused in walking and swimming. • Thecerebrocerebellum or pontocerebellum (correspondsbest to theposterior lobe) hasreciprocal connectionswith thecerebral cortex and playsarolein planning and initiation of movements, aswell asthe regulation of discretelimb movements.
- 41. Phylogenetically: 1. Thearchicerebellum: theoldest zone, correspondsto theflocculonodular lobe. 2. Thepaleocerebellum,: of morerecent phylogenetic development than the archicerebellum, correspondsto theanterior lobe and asmall part of theposterior lobe. 3. Theneocerebellum: themost recent phylogenetically, correspondsto theposterior lobe.
- 42. Functional Areas of the CerebellarCortex • cerebellar cortex isdivided into threefunctional areas. • Thecortex of thevermis: influencesthemovementsof thelong axisof thebody, namely, theneck, theshoulders, thethorax, theabdomen, and thehips. • Intermediatezoneof thecerebellar hemisphere: This areahasbeen shown to control themusclesof the limbs, especially thehandsand feet. • Lateral zoneof each cerebellar hemisphere: Appears to beconcerned with theplanning of sequential movements of theentirebody and isinvolved with theconscious assessment of movement errors.
- 43. Arterial supply of The cerebellum is by: 1. Superior cerebellar 2. Anterior inferior cerebellar, 3. Posterior inferior cerebellar Venous drainage by veinsthat empty into the • Great cerebral vein • Venoussinuses.
- 44. IntracerebellarNuclei • Four massesof gray matter areembedded in thewhitematter of thecerebellum on each sideof themidline. From lateral to medial, thesenuclei are: 1. Dentatenucleus, 2. Emboliform nucleus, 3. Globosenucleus, 4. Fastigial nucleus.
- 45. Fistugial nucleus Globosenucleus Emboliform nucleus Dentatenucleus 4th Ventricle Pons
- 47. Information regarding theinitiation of movement in thecerebral cortex isprobably transmitted to thecerebellum so that the movement can bemonitored and appropriate adjustmentsin thevoluntary muscleactivity can bemade. 1. CerebellarAfferent Fibers From the Cerebral Cortex
- 48. Pathway Function Origin Destination 1.1. CortiCo-CortiCo- pontoponto CerebellarCerebellar Conveyscontrol signalsfrom cerebral cortex Frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes Viapontine nuclei to cerebellar cortex 2.2. Cerebro-Cerebro- olivo-olivo- CerebellarCerebellar Conveyscontrol signalsfrom cerebral cortex Frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes Viainferior olivary nuclei to cerebellar cortex 3.3. Cerebro-Cerebro- retiCulo-retiCulo- CerebellarCerebellar Conveyscontrol signalsfrom cerebral cortex Sensorimotor areas Viareticular formation to cerebellar cortex
- 49. Corticopontocerebellar pathway Corticoreticulocerebellar pathway Cortico-olivocerebellar pathway Reticular formation Pontine nuclie Inferior olivary nucleus
- 50. • Thespinal cord sendsinformation to thecerebellum from somatosensory receptorsby threepathways: (1) theanterior spinocerebellar tract: isfound at all segmentsof thespinal cord, and itsfibers convey musclejoint information from theupper and lower limbs (2) theposterior spinocerebellar tract: receivesmusclejoint information from thetrunk and lower limbs. (3) thecuneocerebellar tract: receivesmusclejoint information from theupper limb and upper part of thethorax 2. CerebellarAfferent Fibers From Spinal Cord
- 51. 3. CerebellarAfferent Fibers From the VestibularNerve • Thevestibular nervereceives information from theinner ear concerning: A. Motion from thesemicircular canals B. position relativeto gravity from: Utricle Saccule.
- 52. 4. OtherAfferent Fibers • In addition, thecerebellum receivessmall bundlesof afferent fibersfrom: 1. thered nucleus 2. thetectum.
- 53. Superior cerebellar peduncle Inferior cerebellar peduncle Cerebellum Inferior cerebellar peduncle Medulla Anterior spinocerebellar tract (minority of fibers) Vestibular nuclie Dentatenucleus Nucleuscunatus Vestibular nucleus Posterior spinocerebellar tract Anterior spinocerebellar tract (majority of fibers)
- 55. Pathway Function Origin Destination Globose-Globose- emboliformemboliform -rubral-rubral Influences ipsilateral motor activity Globoseand emboliform nuclei contralateral red nucleus, then via crossed rubrospinal tract to ipsilateral motor neuronsin spinal cord
- 56. Pathway Function Origin Destination Dento-Dento- thalamicthalamic Influences ipsilateral motor activity Dentate nucleus contralateral ventro- lateral nucleusof thalamus, contralateral motor cerebral cortex; corticospinal tract crossesmidlineand controlsipsilateral motor neuronsin spinal cord
- 57. Pathway Function Origin Destination fastiGialfastiGial vestibularvestibular Influences ipsilateral extensor muscle tone Fastigial nucleus Mainly to ipsilateral and to contralateral lateral vestibular nuclei; vestibulo- spinal tract to ipsilateral motor neuronsin spinal cord
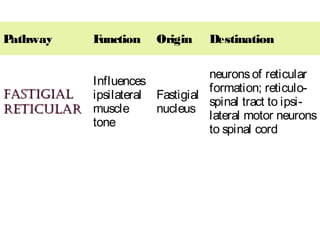
- 58. Pathway Function Origin Destination fastiGialfastiGial reticularreticular Influences ipsilateral muscle tone Fastigial nucleus neuronsof reticular formation; reticulo- spinal tract to ipsi- lateral motor neurons to spinal cord
- 59. CLINICAL NOTES
- 60. General Considerations: • Each cerebellar hemisphereisconnected by nervous pathwaysprincipally with thesamesideof thebody; thus, a lesion in onecerebellar hemispheregivesriseto signsand symptomsthat arelimited to thesamesideof thebody. • Theessential function of thecerebellum isto coordinate, by synergistic action, all reflex and voluntary muscular activity. Thus, it graduatesand harmonizesmuscletoneand maintainsnormal body posture. It permitsvoluntary movements, such aswalking, to takeplacesmoothly with precision and economy of effort. • It must beunderstood that although thecerebellum playsan important rolein skeletal muscleactivity, it is not ableto initiatemusclemovement.
- 61. Characteristic symptoms and signs of cerebellardysfunction: 1.hypotonia: Themusclesloseresilienceto palpation. Thereis diminished resistanceto passivemovementsof joints. Shaking thelimb producesexcessive movementsat theterminal joints. Thecondition is attributableto lossof cerebellar influenceon the simplestretch reflex.
- 62. 2. Postural Changes and Alteration of Gait • Thehead isoften rotated and flexed, and the shoulder on thesideof thelesion islower than on thenormal side. • Thepatient assumesawidebasewhen heor she standsand isoften stiff legged to compensatefor lossof muscletone. • When theindividual walks, staggerstoward the affected side.
- 63. 3. Disturbancesof Voluntary Movement (Ataxia) Themusclescontract irregularly and weakly. • Tremoroccurswhen finemovements, such as buttoning clothes, writing, and shaving, are attempted. Musclegroupsfail to work harmon- iously, and thereisdecomposition of movement. • Testsfor tremor : 1. Asking thepatient to touch thetip of thenosewith theindex finger, thefinger either passesthenose (past-pointing) or hitsthenose. 2. asking thepatient to placetheheel of onefoot on theshin of theoppositeleg, it will either hit the shin or not.
- 64. 4. Dysdiadochokinesia: inability to perform alternating movementsregularly and rapidly. Ask thepatient to pronateand supinate theforearmsrapidly. On thesideof thecerebellar lesion, themovementsareslow, jerky, and incomplete.
- 65. 5. Disturbances of Reflexes • Movement produced by tendon reflexestendsto continuefor alonger period of timethan normal, e.g. pendular kneejerk, for example, occurs following tapping of thepatellar tendon.
- 66. 6. Disturbancesof Ocular Movement: • Nystagmus, which isan ataxia(incoordination) of theocular muscles, isarhythmical oscillation of the eyes. It ismoreeasily demonstrated when theeyes aredeviated in ahorizontal direction. 7. Disordersof Speech: Dysarthriaoccursin cerebellar diseasebecauseof ataxia(incoordination) of themusclesof thelarynx. Articulation isjerky, and thesyllablesoften are separated from oneanother. Speech tendsto be explosive, and thesyllablesoften areslurred.
- 67. CerebellarSyndromes 1. Vermis Syndrome: • Themost common causeof vermissyndromeisa medulloblastomaof thevermisin children. • Involvement of theflocculonodular lobe resultsin signsand symptomsrelated to thevestibular system. • Sincethevermisisunpaired and influencesmidline structures, muscleincoordination involvesthehead and trunk and not thelimbs. • Thereisatendency to fall forward or backward. Thereisdifficulty in holding thehead steady and in an upright position. Therealso may be difficulty in holding thetrunk erect.
- 68. 2. CerebellarHemisphere Syndrome: • Tumorsof onecerebellar hemispheremay bethecause of cerebellar hemispheresyndrome. • Thesymptomsand signsareusually unilateral and involvemuscleson thesideof thediseased cerebellar hemisphere. • Movementsof thelimbs, especially thearms, are disturbed. Swaying and falling to thesideof thelesion often occur. • Dysarthriaand nystagmusarealso common findings. • Disordersof thelateral part of thecerebellar hemispheresproducedelaysin initiating movements and inability to moveall limb segmentstogether in a coordinated manner but show atendency to moveone joint at atime.
- 69. Thanks