Migraine and stroke what’s the link
- 1. Migraine and Stroke: What’s the link?
- 2. Disclosures Objectives • Assess the risk of stroke in migraine with & without aura • Describe the association of migraine & other risk factors for stroke • Be aware of the management of migraineurs at risk for stroke
- 3. Possible Relationships Between Stroke and Migraine • Migraine is extremely common – WHO deemed 3rd most prevalent • Migraine symptoms mimicking stroke • Headache may be coincidental with/due to stroke • Stroke may be due to migraine • migrainous infarction • ? PFO • Migraine therapy may complicate stroke • Migraine and stroke may share common cause – OCP, CADASIL
- 4. A. At least 2 attacks B. Fully reversible symptoms: often positive (may be negative) • visual • sensory • speech symptoms • no motor weakness C. At least 2 of the following: • Unilateral symptoms (sensory) • Develops gradually over > 5 mins • Duration: > 5 minutes and < 60 minutes D.Headache meets criteria for migraine and begins during the aura or follows within 60 mins Migraine Mimicking Stroke: What is an aura? Cephalalgia 2013
- 5. Migraine Mimicking Stroke Stroke Migraine Aura Symptom onset sudden gradual, prodrome Symptom characteristics negative, one eye, fixed positive & expanding, moving, both eyes/field/cover‐uncover march of sensory symptoms Age older younger (or older) Uncommon types Hemiplegic Migraine HaNDL Past History CVD, DM, lipids, HTN migraine 42 yr old, “trouble seeing” in right eye, lasting 15 minutes
- 6. Headache coincidental to/caused by stroke Lee 2016 Zhang 2017 Stroke Type % with Headache ischemic 8.4% hemorrhagic 21.3% CVST 50% Acta Neurologica Scan 2016
- 7. Stroke in Migraineur Zhang BMJ 2017 Kurth 2012 • first described in late 1800s by Charcot • numerous studies suggest link between migraine and stroke • conclusions are varied due: • inconsistencies in research methodology • varied patient populations • methods used to diagnose migraine ‐ neurologist vs self report • Consensus: • stroke is more common in women <45 yr migraine with aura
- 8. Studies of Stroke in Migraine Stang 2005, Kurth 2005 • Athersclerosis Risk in Communities study (ARIC) • Approx 12, 400 women and men >55yr • Women’s Health Study • Approx 39, 800 women >age 45 without cardiovascular ds Risk of stroke increased in migraine with aura
- 9. Migraine and Stroke Mawet 2016, Kurth 2012, Sacco 2013 • Migraine with aura affects 25% of migraine sufferers • Women under age 45 with aura seem to be at highest risk • Women with aura are more likely to have stroke than men with aura • Migraineurs have increased risk of CVD but do not have enhanced atherosclerosis • Inflammation? • Vasospasm? • Younger migraineurs have increased risk of cervical artery dissection • Is there endothelial dysfunction? • Childhood Adversity? • Migraineurs with aura are 2x more likely to have hypercoaguability
- 10. Stroke and Migraine Studies Zhang 2017 Lee 2016 • Ischemic stroke due to clot/reduced blood flow (> 80% of all strokes) • Stronger association of MwA and ischemic vs hemorrhagic stroke • Migraine with aura increased risk 2.4x • Estrogen HRT 30% more likely to have stroke b/c increased risk of clot • If HRT worsens migraine, 30% more likely to have stroke but risk very small to start (2.5%) • Multiple risk factors highly problematic • must manage other RF: smoking, HTN, DM, cholesterol, sedentary lifestyle • screen migraineurs for CVD risks – even if young
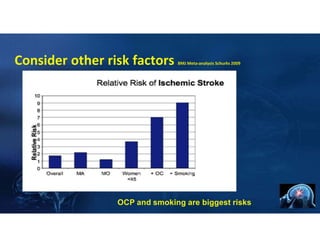
- 11. Consider other risk factors BMJ Meta‐analysis Schurks 2009 OCP and smoking are biggest risks
- 12. Migrainous Infarction Lee 2016 Zhang 2017 • Rare • Stroke occurs in immediate proximity to migraine attack • Symptoms/location of stroke must be consistent with known aura & >60 min • More in younger women and more in posterior circulation • Etiology • duration and degree of Cortical Spreading Depression • ? vasospam/vascular, inflammatory, endothelial structure • underlying hypercoaguable state • medications used to treat migraine attack ‐ vasoconstrictive • Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy w subcortical infarcts & leukoencephalopathy CADASIL • PFO • OCP
- 13. PFO – Migraine ‐ Stroke AAN Guidelines 2016, Tariq 2016 Tobis 2‐17 • PFO is common occurring in about 1 in 4 people (about same as ♀ migraine) • it is impossible to determine with certainty whether PFOs caused stroke/TIA • the effectiveness of PFO closure to reduce stroke risk remains uncertain • procedure associated with uncommon, yet potentially serious, complications • Clinicians should not routinely offer PFO closure for patients with cryptogenic ischemic stroke outside of a research study • Antiplatelet therapy is sufficient over anticoagulation in most circumstances
- 14. OCP and Migraine • Over 3 million Canadian women with migraine • Afflicted in peak productive years • Issue of OCP will arise • adolescent through post‐menopausal woman • OCP is one of most commonly prescribed drugs • Both OCP and migraine independently increase risk of stroke
- 15. Case – Oral Contraceptive Pill • 26 year old woman • OCP concerns • Severe migraines 6x/month • Can she go on/stay on pill? • What if she has aura?
- 16. Migraine and Estrogen International Headache Society Task Force on Combined Oral Contraceptives and HRT ⦿ estrogen use in a migraineur is safe provided: ⚫ no other risk factors for arterial/vascular disease ⚫ migraine is without aura or simple, predictable aura ⚫ use lowest effective dose ⚫ if symptoms change while on estrogen, d/c therapy Cephalalgia 2000, Contraception 2016
- 17. OCP and Migraine • generally migraine remains stable • use lowest effective dose (10ug or less) • use monophasic pills • ask about risk factors -? miscarriage • cautious use in migraine with simple aura • avoid OCP in migraine with >simple aura or new onset aura, or change in aura • not if smoker!
- 18. OCP Case • 24 year old ‐ hx migraine without aura • started on OCP for birth control • developed new onset aura with anomic aphasia and tingling right arm and leg, lasting 30‐40 min • referred to neurology • what now? • exam normal; MRI and bloodwork ordered • neurologist recommended stopping OCP to evaluate • patient felt safe to continue • left MCA infarct • found to have ACLA
- 19. Managing Migraine in Patient with Stroke Roberto 2015 Zhang 2017 • Migraine patients may experience a stroke • General principles in migraineur without a stroke • Detailed past history – risk factors • Hypercoaguability in family? Childhood adversity? • Limit triptans >age 50, use with caution over age 55 • New drugs in 2018 lasmitidan and CGRP blockers – no CVD risk • Migraineur with stroke • Strict management of RF • No triptans, ergotamines • Consider prevention agents at lower frequency to limit migraine attacks • ACE inhibitors; case studies with statin and vitamin D
- 20. Key Points in Migraineurs • Migraine with aura carries increased risk of stroke in women <45 yr • Encourage healthy lifestyle • Monitor risk factors • Explore childhood trauma as risk factor • Absolutely no smoking/help patient quit if she desires OCP • Avoid OCP except M w/o aura or M with SIMPLE aura • No chiropractic neck manipulation • Migraine prevention should be offered if 4 or > HA/month • Consider RF when choosing therapy