Nephrectomy : Operative Technique
- 1. Operative techniques: Nephrectomy Presenter: Dr Sangamesh S K Moderator: Col S Tripathy
- 2. Overview of presentation • Surgical anatomy • Indication of Nephrectomy • Types of Nephrectomy – Simple, Partial & Radical nephrectomy – Donor Nephrectomy • Different technique of Nephrectomy • Complications
- 3. Surgical anatomy • Bean shaped organ • Location: Retroperitoneal • Extend :- T12-L3 • Two surface (anterior & posterior) • Two pole (superior & inferior) • Two border (medial & lateral)
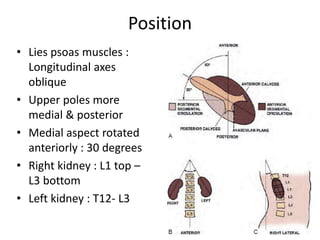
- 4. Position • Lies psoas muscles : Longitudinal axes oblique • Upper poles more medial & posterior • Medial aspect rotated anteriorly : 30 degrees • Right kidney : L1 top – L3 bottom • Left kidney : T12- L3
- 5. Anterior relation of kidney
- 6. Posterior relation of kidney
- 10. Arterial supply
- 11. Indication of Nephrectomy • Severe trauma • Renal infection – Xanthogranulomatous & Emphysematous Pyelonephritis • Malignancy • Non functioning kidney – Stones & obstruction • Renal fistula • Renal vascular Hypertension – All medical & surgical therapy have failed • Transplantation
- 12. Types of Nephrectomy • Simple Nephrectomy – Removal of kidney within Gerota fascia • Partial Nephrectomy – Small-sized renal cancer – Benign diseases- excised renal capsule (renorrhaphy) • Radical Nephrectomy – Complete removal of kidney outside Gerota fascia – Ipsilateral adrenal gland – Complete regional lymphadenectomy (crus of diaphragm - aortic bifurcation)
- 13. Different surgical approach 1. Open approach of Nephrectomy 2. Laparoscopic • Transperitoneal • Retroperitoneal • Hand assisted 3. Robotic assisted
- 14. Pre- op evaluation • Global assessment of pt’s renal function is done: – Urine analysis & culture – Serum Creatinine – GFR evaluation – Cardiac & pulmonary status: Positioning & bleeding – Cross sectional imaging (CT/MRI) :- Surgical planning – Locally advanced metastatic lesion : Screen hepatic status (stauffer syndrome) – Renal Artery Embolisation (RAE) : Large tumor
- 15. Instruments • General set • Abdominal drainage tube • Self-retaining retractors : omni tract, balfour • Long genitourinary surgical instruments • Bulldog &/or Satinsky vascular pedicle clamps • Mixters right angle forceps • Bulldog arterial clamp • Retractor- doyen’s and deiver’s • Kidney pedicle clamp
- 16. Positioning • Induction & ET tube placement • Catheterization done • Pt : Lateral decubitus • Table flexed b/w iliac crest & costal margin • Head supported: Avoid excessive flexion • Pt back supported by blanket • Dependent leg flexed & top leg straight • All pressure point : padded surface • Pt secured to table : tape
- 17. Surgical approach to kidney
- 18. Anterior approach of kidney INCISION INDICATION BENEFIT LIMITATION Midline Transperitoneal Trauma, IVC Thrombus , B/L Renal or Ureteral disease , Horseshoe Rapid ,Early vascular control , Access both kidney Limited exposure to kidney & bowel Subcostal Radical nephrectomy , UPJO Incision can extend to chevron , early vascular control Bowel complication Hilum access poor Chevron B/L renal tumor , IVC thrombus Excellent b/l exposure , Injury to Liver , Spleen , Transection of large muscle Transverse abdominal Wilms tumor Easy access to pedicle & retroperitoneal node Modified Thoracoabdominal Radical nephrectomy , lymphadenectomy versatile Bowel complication, Transection of large muscle
- 19. Flank incision INCISION INDICATION BENEFIT LIMITATION 11th or 12th rib supracostal Partial nephrectomy , & Simple nephrectomy Good renal & retroperitoneal exposure Pleural injury 11th rib Transcostal Partial and Simple nephrectomy Good renal & retroperitoneal exposure Pleural injury & Noticeable flank defect Thoracoabdominal Large renal mass , IVC thrombus , involvement of surrounding structure Excellent exposure , Can approach completely extraperitoneally Pleural injury , Transection of large muscles,
- 20. Steps of flank approach
- 21. • After Gerota fascia incised & kidney is dissected free from surrounding perinephric fat. • Renal artery identified & ligated before vein • Renal vein ligated
- 22. Simple nephrectomy Indications • Poor functionaing kidney – Obstruction, infection, trauma, stones, nephrosclerosis, vesicoureteral reflux, polycystic kidney, or congenital dysplasia • Functional kidney – Relieve intractable symptoms : bleeding, pain, hypertension, or persistent infection
- 23. Simple nephrectomy • Flank incision : retroperitoneal access • Renal fascia incised , perirenal fat is separated from kidney • Aberrant vessels : near the poles • Large hydronephrotic : puncture and aspirate • Adrenal dissectd in upper pole • Lower pole mobilised and ureter isolated • Division of ureter : access to hilar structures
- 26. Radical nephrectomy : Right • Additional mobilization of liver, avascular Rt triangular ligament is incised • White line of Toldt : pelvis to hepatic flexure • 2nd part of duodenum : Kocher maneuver • Dissection anterior to IVC : Identification of renal vein & gonadal vein • Ligature of ureter below : kidney lifted , artery more exposed • Difficult hilar dissections : Dissect in the interaortocaval region • Lumbar veins close approximation
- 27. Radical nephrectomy : left • White line of Toldt : splenic flexure to descending colon is reflected medially. • Renocolic ligament is divided and extreme care is taken to avoid injury to the tail of the pancreas • Left renal vein is identified using the anterior surface of the aorta as a guide • Left renal artery is usually located cranial and posterior to the left renal vein • Further mobilization of the lower pole of the kidney, the left ureter and the left gonadal vein
- 28. PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY:- INDICATION 1) Absolute:- i) Single kidney ii) Bilateral renal tumor iii) Severe renal failure 2) Relative:- i) Abnormal contralateral ii) Metabolic disease associated with renal failure iii) Genetic syndrome with tumor multifocality (e.g VHL syndrome) 3) Elective:- i) Tumor < 4cm in young & healthy pt ii) Peripheral tumor
- 29. Partial Nephrectomy : Relative Contraindication Technical issue – Cold ischemia time >45min (consider extracorporeal approach) – Less than 20% of global nephron mass retained Cancer related issue – Diffuse encasement of renal pedicle by tumor – Diffuse invasion of central collecting system – Tumor thrombus involving major renal veins – Adjacent organ invasion (stage cT4) – Regional lymphadenopathy (stage cTxN1)
- 30. Partial nephrectomy • Avascular plane : Segmental artery clamping – 5ml Indigo carmine : clamped artey – Cooled down to 20o • Hyperfiltration injury : – Over decades, FSGS : proteinuria and progressive renal failure (nephron mass reduced by 80%) • Vascular clamping: Ischemia & hypothermia
- 31. Partial Nephrectomy :- Wedge Resection
- 32. Partial Nephrectomy: Segmental Polar Resection
- 33. Complication of partial nephrectomy • Urinary fistula • Post operative bleeding • Renal insufficiency
- 34. Wound closure • Hemostasis and evaluate adjacent organs for any signs of injury • Pleural injury, – retroperitoneum is filled to level of the flank incision with saline. – anesthesiologist then inflates lungs with high inspiratory volumes – Bubbling of saline irrigation in the retroperitoneum with deep inspiration would suggest a pneumothorax • Fascial layers approximated : two layers – Transversus abdominis & internal oblique fasciae are approximated together – External oblique fascia is approximated as a separate layer
- 35. Donor Nephrectomy • Kidney is mobilized, only remaining attachments are the ureter, renal vein, and renal artery • 12.5 g of mannitol and 20 mg of furosemide are rapidly infused intravenously • Immediately after dividing renal vessels, placed on workbench : Pan of ice slush covered with a towel. • Flushed intra-arterially by gravity flow with renal preservation solution at 6°C • Flushing should continue until it is cooled & renal effluent is clear (~500 to 1000 mL) • Kept in ice slush basin during procedure : Hypothermia
- 36. Donor nephrectomy • Renal artery & vein are flushed independently with preservation solution : Bleeding • Retrograde flushing of ureter : Collecting system leaks • Transplanted into either lower quadrant, transferred to iliac fossa • Renal vein anastomosed : External iliac vein. • Renal artery anastomosis – End-to-end anastomosis to hypogastric artery – End-to-side anastomosis with external iliac artery
- 37. Donor nephrectomy • During anastomosis, vessels should be irrigated : Heparin solution (10,000 U Heparin in 100 mL NS) • Surgeon should consider injecting – 10 mg Verapamil into renal artery following anastomosis : Vasodilation. • Ureter is implanted into dome of bladder with a tension-free anastomosis • Prior to completion ureteral anastomosis: Ureteral stent is placed
- 38. Complication of Open Nephrectomy • Hemorrhage • Small bowel obstruction • Pneumothorax • Pneumonia • DVT • Superficial wound infection • Bowel injury
- 39. LAPROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY SURGICAL APPROACHES:- 1) Transperitoneal 2) Retroperitoneal 3) Hand-Assisted
- 40. TRANSPERITONEAL RETROPERITONEAL HAND-ASSISTED Small incision & gives advantage for trocar placement Limited working space ,result in difficulty in orientation , trocar spacing , & organ entrapment Bridge b/w lap & open surgery Affords optimal working space Preferred in pt with h/o multiple abdominal procedure or pt with peritonitis Permits tactile feedback Also preferred in pt with abnormality of posterior surface (exophytic cyst or mass) Allow the hand to assist with dissection , retraction , extraction & rapid control of bleeding
- 41. PATIENT EVALUATION & PREPARATION • Prior abdominal surgery – Transperitoneal & retroperitoneal – Pt positioning , – Placement of trocars • Pre-op abdominal CT :- useful in surgical planning • Rest of evaluation similar to open nephrectomy
- 42. Patient positioning & trocar sites
- 43. OPERATING ROOM
- 44. Procedure of transperitoneal approach • Reflection of colon • Dissection of ureter • Identification of renal hilum • Securing of renal blood vessel • Isolation of upper pole • Organ entrapment
- 46. Retroperitoneal Approach • Retroperitoneal approach used for posterior or lower pole lesion • Pt in full flank position ,10mm trocar is placed in posterior axillary line , halfway b/w iliac crest & 12th rib • Pneumo-peritonium is established & anterior wall is identified with gentle dissection of retroperitoneal fat
- 48. Retroperitoneal Approach • Second 12mm port is placed under direct vision in anterior axillary line • A third port 5mm is placed superior to 2nd port below rib cage • Using the perinephric fat to elevate kidney , surgeon readily sees the lower pole & posterior surface
- 49. Complication of laparoscopic renal surgery 1. Access related problems:- i. Solid organ injury ii. Bowel injury iii. Abdominal wall hematoma iv. Epigastric vessel injury 2. Hemorrhage 3. Pneumonia 4. Pulmonary embolus 5. Unrecognized bowel injury 6. Incisional hernia :- after intact specimen removal
- 50. Nephrectomy: Robotic Port Placement
- 51. Robotic Nephrectomy : Operating room
- 52. Advantage of robotic over laparoscopic • Minimal invasive approach • 3D visual & depth perception
- 53. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- #9: Level of IV disk between LV1 and LV2. Longer right renal artery passes posterior to IVC. Rt vein: 2-4cm, Left vein : 6-10cm
- #10: A small Apical segmental branch : post br, but MC : Ant div. Posterior segmental artery : the posterior division passes posterior to the renal pelvis, while others pass anterior to the renal pelvis. Accessory renal arteries are seen in 25% to 28%
- #34: renal artery is clamped with a vascular bulldo