Object oriented programming 2
- 1. OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING FPL II Unit II SPPU-2017/18 Prof. Ansari Aadil Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 2. Object OBJECT is an identifiable entity with some characteristics and behavior. In OOP programming object represents a entity that can store data and has its interface through functions. CLASS is a template/blue-print representing a group of objects that share common properties and relationships. Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 3. Structure of an Object Oriented Program Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 4. Features of OOP • More emphasis on data rather than procedure. • Programs are divided into object. • Function and data are tied together in a data structure. • Objects communicate with each other through Functions. • Data is hidden or cannot be access by external function. Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 5. Principle of OOPS • Class: It is type or a category of things. It is similar to a structure with the difference that it can also have function. Ex. Class of Cars. There may be many cars with different names and brand but all of them will share some common properties like all of them will have 4 wheels, Speed Limit, Mileage range etc. Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 6. OBJECT : It is an instance of class. Ex. Class fruit can have apple as its object. ABSTRACTION refers to the act of representing essential features without including the background details or explanations. ENCAPSULATION :The wrapping up of data and operations / functions (that operate on the data ) into a single unit (called class) is known as ENCAPSULATION. INHERITANCE: Inheritance is the capability of one class of things to inherit capabilities or properties from other class POLYMORPHISM: Multiple form of the same thing. It is the ability for a message or data to be processed in more than one form. Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 7. Structure of Object Oriented Program in c++ #include<iostream.h> class class-name { access-specifiers… int i,j; float f; char ch; double b; access-specifiers… void function-name() { statement 1; statement 2; } } main() { class-name.obj-name; } Header File class Data Variables or fields Function or Method Object of class Class members Prof. Ansari Aadil S
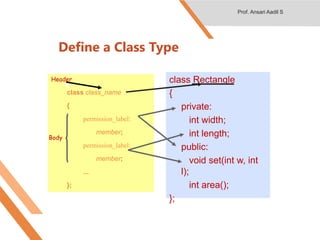
- 8. Define a Class Type class class_name { permission_label: member; permission_label: member; ... }; class Rectangle { private: int width; int length; public: void set(int w, int l); int area(); }; Body Header Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 9. class Rectangle { private: int width; int length; public: void set(int w, int l); int area(); }; Classes & Objects Rectangle r1; Rectangle r2; Rectangle r3; …… int a; Objects: Instance of a class Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 10. • Information hiding • To prevent the internal representation from direct access from outside the class • Access Specifiers • public • may be accessible from anywhere within a program • private • may be accessed only by the member functions, and friends of this class • protected • acts as public for derived classes • behaves as private for the rest of the program Class Definition - Access Control Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 11. Read and print details of a student using class program in C++ /*C++ program to create class for a student.*/ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class student { private: char name[30]; int rollNo; int total; float perc; public: //member function to get student's details void getDetails(void); //member function to print student's details void putDetails(void); }; //member function definition, outside of the class void student::getDetails(void){ cout << "Enter name: " ; cin >> name; cout << "Enter roll number: "; cin >> rollNo; cout << "Enter total marks outof 500: "; cin >> total; perc=(float)total/500*100; } //member function definition, outside of the class void student::putDetails(void){ cout << "Student details:n"; cout << "Name:"<< name << ",Roll Number:" << rollNo << ",Total:" << total << ",Percentage:" << perc; } int main() { student std; //object creation std.getDetails(); std.putDetails(); return 0; } Output: Enter name: mike Enter roll number: 112 Enter total marks outof 500: 456 Student details: Name:mike,Roll Number:112,Total:456,Percentage:91.2 Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 12. // Program to illustrate the working of objects and class in C++ Programming #include <iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class Test { private: int data1; float data2; public: void insertIntegerData(int d) { data1 = d; cout << "Number: " << data1; } float insertFloatData() { cout << "nEnter data: "; cin >> data2; return data2; } }; int main() { Test o1, o2; float secondDataOfObject2; o1.insertIntegerData(12); secondDataOfObject2 = o2.insertFloatData(); cout << "You entered " << secondDataOfObject2; getch(); } Output Number: 12 Enter data: 23.3 You entered 23.3 Prof. Ansari Aadil S
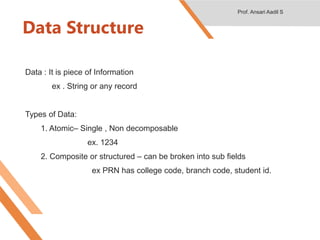
- 13. Data Structure Data : It is piece of Information ex . String or any record Types of Data: 1. Atomic– Single , Non decomposable ex. 1234 2. Composite or structured – can be broken into sub fields ex PRN has college code, branch code, student id. Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 14. A data structure is a particular way of organizing data in a computer so that it can be used effectively. Data structure is linear or non Linear in nature 1.Linear- every item is attach to previous and next item ex. Array , Linked list, Stack ,Queue 2. Non linear – every item is attached to many other items. Multidimensional array, Tree , Graph. Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 15. Stack Queue Linked List Graph Tree Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 16. Defining member function 1. Internally defined function- when member function of a class are defined inside the class itself #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class circle { float r,a; public: void read() { cout<<“Enter radius:”; cin>>r; } void compute() { a= 3.14 *r * r; } void display() { cout<<“Area”=<<a; } }; void main() { clrscr(); circle c; c.read(); c.compute(); c.display(); getch(); } Output: Enter radius: 5 Area= 78.5 Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 17. 2. Externally defined function When the member function of a class are defined outside the class. :: () scope resolution operator is used. #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class circle { float r,a; public: void read(); void compute(); void display(); }; void circle :: read() { cout<<“Enter radius:”; cin>>r; } void circle :: compute() { a= 3.14 *r * r; } void circle :: display() { cout<<“Area”=<<a; } }; void main() { clrscr(); circle c; c.read(); c.compute(); c.display(); getch(); } Output: Enter radius: 5 Area= 78.5 Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 18. 3. Inline Member function If a function is defined outside the class but still to be treated as internally defined function then such function has to be made “inline” function #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class circle { float r,a; public: void read(); void compute(); void display(); }; inline void circle :: read() { cout<<“Enter radius:”; cin>>r; } inline void circle :: compute() { a= 3.14 *r * r; } inline void circle :: display() { cout<<“Area”=<<a; } }; void main() { clrscr(); circle c; c.read(); c.compute(); c.display(); getch(); } Output: Enter radius: 5 Area= 78.5 Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 19. Constructor A constructor is a member function of a class which initializes objects of a class. • Constructor has same name as the class itself • Constructors don’t have return type • A constructor is automatically called when an object is created. • If we do not specify a constructor, C++ compiler generates a default constructor for us (expects no parameters and has an empty body). Prof. Ansari Aadil S
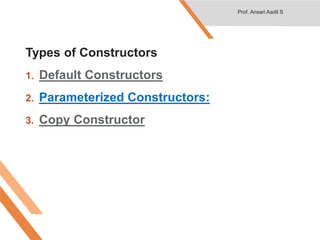
- 20. Types of Constructors 1. Default Constructors 2. Parameterized Constructors: 3. Copy Constructor Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 21. Default Constructors: Default constructor is the constructor which doesn’t take any argument. It has no parameters. #include <iostream.h> #include<conio.h> using namespace std; class construct { public: int a, b; // Default Constructor construct() { a = 10; b = 20; } }; void main() { // Default constructor called automatically // when the object is created construct c; cout << "a: "<< c.a << endl << "b: "<< c.b; getch(); } Output: a: 10 b: 20 Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 22. Parameterized Constructors To create a parameterized constructor, simply add parameters to it the way you would to any other function. When you define the constructor’s body, use the parameters to initialize the object. #include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> class Point { private: int x, y; public: // Parameterized Constructor Point(int x1, int y1) { x = x1; y = y1; } int getX() { return x; } int getY() { return y; } }; int main() { // Constructor called Point p1(10, 15); // Access values assigned by constructor cout << "p1.x = " << p1.getX() << ", p1.y = " << p1.getY(); return 0; } Output: p1.x = 10, p1.y = 15 Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 23. Copy Constructor A copy constructor is a member function which initializes an object using another object of the same class. ClassName (const ClassName &old_obj); Prof. Ansari Aadil S
- 24. Destructors Destructor is a member function which destructs or deletes an object. Destructors have same name as the class preceded by a tilde (~) class test { int *p; public: test() { p=new int; } void read() { cout<< “ Enter a number: ”; cin>> *p; } void display() { cout<< “ Value= “<<*p<< endl; } ~ test() { delete p; cout<<“Destroyed”; } }; void main() { clrscr(); test t; t.read(); t.display(); getch(); } Output: Enter a number: 5 Value=5; Destroyed Prof. Ansari Aadil S










![Read and print details of a student using class
program in C++
/*C++ program to create class for a student.*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class student
{
private:
char name[30];
int rollNo;
int total;
float perc;
public:
//member function to get
student's details
void getDetails(void);
//member function to print
student's details
void putDetails(void);
};
//member function definition, outside of the class
void student::getDetails(void){
cout << "Enter name: " ;
cin >> name;
cout << "Enter roll number: ";
cin >> rollNo;
cout << "Enter total marks outof 500: ";
cin >> total;
perc=(float)total/500*100;
}
//member function definition, outside of the class
void student::putDetails(void){
cout << "Student details:n";
cout << "Name:"<< name << ",Roll
Number:" << rollNo << ",Total:" << total <<
",Percentage:" << perc;
}
int main()
{
student std; //object
creation
std.getDetails();
std.putDetails();
return 0;
}
Output: Enter name: mike
Enter roll number: 112
Enter total marks outof 500: 456
Student details:
Name:mike,Roll
Number:112,Total:456,Percentage:91.2
Prof. Ansari Aadil S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogramming2-180128175130/85/Object-oriented-programming-2-11-320.jpg)