Oligonucleotide
- 1. OLIGONUCLEOTIDE Himal Barakoti Roll no: 171709 M.pharm, 2nd sem Department of Pharmacy Assam Down Town University
- 2. CONTENTS Oligonucleotides: Introduction DNA & RNA Nucleotides Oligonucleotide Drug Delivery Drug Delivery strategies Modes of Action Advantages and limitations Summary References Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 2
- 3. INTRODUCTION: OLIGONUCLEOTIDE Greek “oligo” – Few or small “Polynucleotide whose molecules contain relatively small number of nucleotides.” “Short nucleic acid chain usually consisting of approximately 25 nucleotides.” “Short nucleic acid polymers used in research, genetic testing and forensics.” Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 3
- 4. DNA & RNA In 1869, Friedrich Miescher, young Swiss physician discovered DNA. He termed the name “nuclein” as it came from nuclei. Later it was found to be strongly acidic, thus the name was changed to nucleic acid. In 1880, Emil Fisher identified purine and pyrimidine bases. Albrecht Kossel identified nitrogenous bases of nuclein as well as 5 carbon sugar and phosphoric acid group for which He was awarded nobel prize in 1910. In 1950, inter nucleotide bond was identified. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 4
- 5. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 5
- 6. DIFFERENCES IN STRUCTURE Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 6
- 7. 3 COMPONENTS OF NUCLEIC ACID 1. Pentose Sugar: 5’ and 3’ carbon of pentose sugar participate in phosphodiester bond and 1’ is occupied by organic base. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 7
- 8. 3 COMPONENTS OF NUCLEIC ACID 2. Organic Base: Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen in their rings; hence also called nitrogenous base. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 8
- 9. 3 COMPONENTS OF NUCLEIC ACID 3. Phosphoric acid: H3PO4 has three reactive hydroxyl group in which two are involved in forming sugar phosphate backbone of DNA. Phosphate moiety joins 5’C of one & 3’C of neighbouring pentose molecule to produce phosphodiester linkage. (5’C—O—P—O—C3’) Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 9
- 10. NUCLEOSIDES AND NUCLEOTIDES Linkage between Ribose sugar and organic base yields ribonucleosides and between deoxyribose and organic base produce deoxyribosides. Both are termed as nucleosides. Nucleotides are phosphorylated derivatives of nucleosides. A nucleotide is formed when a phosphate group is attached either 3’C or 5’C of pentose residue of nucleoside. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 10
- 11. SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE STRUCTURE Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 11
- 12. Nucleosides and Nucleotides Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 12
- 13. Mainframe of DNA and RNA strands Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 13
- 14. INTRODUCTION: OLIGONUCLEOTIDE Greek “oligo” – Few or small “Polynucleotide whose molecules contain relatively small number of nucleotides.” “Short nucleic acid chain usually consisting of approximately 25 nucleotides.” “Short nucleic acid polymers used in research, genetic testing and forensics.” Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 14
- 15. Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. The length of the oligonucleotide is usually denoted by "-mer" (from Greek meros, "part"). For example, an oligonucleotide of six nucleotides is a hexamer, while one of 25 nucleotides would usually be called a "25-mer". In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression (e.g. microRNA), or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 15
- 16. Oligonucleotides are commonly prepared in laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis method. Large number of DNA probes, each one with different sequence are immobilized at defined position on solid surface, made up of either nylon or glass. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5’ to 3’ direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is, most often, carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 16
- 17. Traditional small-molecule antiviral agents inhibit enzymes that are important to viral replication or reverse transcription. The synthesis and design of nucleoside-based antiviral agents is well- established and many clinically important drugs have been developed (e.g. acyclovir). However, it has proved difficult to develop compounds with the ability to eliminate viruses entirely or to prevent their integration into the host genome. For this reason a number of oligonucleotide-based approaches are now being developed. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 17
- 18. OLIGONUCLEOTIDE DRUG DELIVERY Strategy of therapeutic oligonucleotides is divided into four categories, as follows: A) Single piece of oligonucleotide B) Oligonucleotide-ligand conjugate C) Oligonucleotide-polymer conjugate D) Nanoparticle Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 18
- 19. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 19
- 20. OLIGONUCLEOTIDE DRUG DELIVERY Therapeutic oligonucleotides, on the basic of mechanism of action is divided into 2 categories, as follows: A) Antisense Oligonucleotides B) Modulator of protein activity (Aptamers) Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 20
- 21. A) ANTISENSE OLIGONUCLEOTIDES Many pharmacological approach involve creating compounds that binds and disable protein. Eg. Proponolol, Cimitidine A new way to block protein function is to prevent translation of mRNA into protein. An Antisense oligonucleotide therapy is one such approach which blocks protein formation by inhibiting translation step. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 21
- 22. Antisense oligonucleotides are the molecules made of synthetic genetic material, which interacts with the natural genetic material that codes the information for production of proteins. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 22
- 23. MOA : Antisense technology Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 23
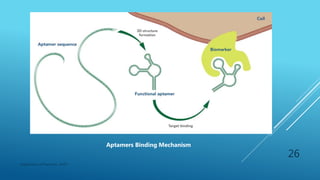
- 24. B) Modulator of protein activity (APTAMERS) Aptamers (Aptus- to fit, mer- smallest unit of repeating structures) Based on their 3-dimensional structure, Aptamers can well fittingly bind to a wide variety of targets from single molecules to complex target mixtures or whole organisms. Single stranded folded oligonucleotides and peptide that bind to molecular (protein) targets with high affinity and specificity. Range in size from 20 to 80 bases (6-26 kDa) Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 24
- 25. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 25
- 26. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 26 Aptamers Binding Mechanism
- 27. Advantages: Oligonucleotides can be manufactured quickly i.e. within a week Sensitivity of therapy can be easily measured. Potential of producing longer lasting responses. Potential for enhanced binding affinity to target. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 27
- 28. Limitations: Antisense agents have to be protected against nucleolytic attack. The pharmacokinetic characteristics of oligonucleotide drugs is similar to that of naturally occurring nucleic acids, makes them poor therapeutic candidates, as they are immediately degraded in vivo by nucleases and do not have adequate pharmacokinetic properties. Larger dose are required for therapeutic response. The difficulty in directing to a particular cells. The half-life in plasma is short. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 28
- 29. Applications: Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 29 Antisense oligonucleotide therapy As antiviral and antibacterial agents CVS & CNS Therapeutics Inflammation therapeutics Oncology Diabetes, Muscular Dystrophy, Asthma, Hair loss
- 30. Oligonucleotides also plays important role in: DNA sequencing: Determination of nucleotide sequence in DNA molecule. PCR: In-vitro technique of generating large quantity of specified target DNA. Artificial gene synthesis (DNA printing) Library construction of DNA Molecular Cloning: introducing recombinant DNA molecule and direct their replication within host organism. Genetic testing, research and forensics. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 30
- 31. Examples: Fomiversin for the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Mipomersen for High cholesterol. Affnitak and Genasense against cancer. AV 1-6002 & AV 1-6003 in treatment of hemorrhagic fever. AP 1-2009 for the treatment of high grade gliomas. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 31
- 32. Some oligonucleotides therapeutics Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 32
- 33. SUMMARY Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. Oligonucleotide-based therapeutics on the mode of their action are categorized as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), which are inhibitors of RNA activity, or modulators of protein activity (aptamers). Numerous development programs for oligonucleotide therapeutics are generating growing amount of data, contributing to better understanding of the pharmaceutical characteristics of oligonucleotides. Advances on oligonucleotide delivery systems play a game-changing role in turning the field of oligonucleotide therapeutics into a therapeutic reality… Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 33
- 34. REFERENCES: U. Satyanarayana, U. Chakrapani, “Biochemistry” 5th Ed. (2017), Elsevier P.S. Verma, V.K. Agarwal, “Cell Biology: Cytology, Biomolecules and Molecular Biology” 1st Ed. (2016), S. Chand and Company Pvt. Ltd B.D. Singh, “Genetics” 2nd revised Ed. (2009), Kalyani Publishers Yutaro Asami, Kotaro Yoshioka, Kazutaka Nishina, Tetsuya Nagata, Takanori Yokota* “Drug delivery system of therapeutic oligonucleotides” Drug Discoveries & Therapeutics. 2016; 10(5):256-262. Rudolph L. Juliano* “The delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides” Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, Vol. 44, No. 14 Wissenschaftliche Prüfungsarbeit, “Oligonucleotide-based Therapeutics, Development and Regulatory Challenges” 2016; 1-62 Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 34
- 35. Department of Pharmacy, ADTU 35