Oracle data integrator project
- 1. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Oracle Data Integrator 11g (11.1.1) Oracle Data Integrator Project Document Part I This is one of our documents from ODI learning series. This document is created for new bees in ODI. The object of the document is to assist new bees with step by step approach to perform various tasks. History: Version Description Change Author Publish Date 0.1 Initial Draft Gourav Atalkar 30-June-2011 0.1 Review 1st Amit Sharma 01-Jul-2011 Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 1
- 2. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Table of Contents 1) Introduction 3 a. Objective b. Business-Rules Driven Approach c. Traditional ETL versus E-LT Approach d. Understanding Oracle Data Integrator Interfaces 2) Using ODI in your Data Warehouse Project 9 a. Introduction b. Organizing the Teams 3) Creating an ODI Project and Interface: Exporting a Flat File to a Flat File 11 a. Purpose b. Overview c. Creating a New Physical Schema for the Flat File Model d. Creating a New ODI Model for the Flat File Source e. Creating a New ODI Source Datastore for use with ODI Interface f. Creating a New ODI Target Datastore for use with ODI Interface g. Creating a New ODI Interface for Flat File to Flat File Transformations 4) Creating an ODI Project and Interface: Exporting a Relational Table to a Flat File 21 a. Purpose b. Creating Interface 5) Creating ODI Interface: Exporting a Flat File to a Relational Table 25 a. Create a new physical schema for the source flat-file model. b. Create the new project in ODI. c. Create a new model folder for the flat-file source data store d. Create a new ODI Interface to perform a flat-file-to-RDBMS-table transformation. 6) Create new Project and Procedure 46 a. Create new Project b. Create Procedure Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 2
- 3. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ 1) Introduction Objective • Introduce the key concepts of a business-rule driven architecture • Introduce the key concepts of E-LT • Understand what an Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) interface is • Through a business problem case study, understand and evaluate some different development approaches including: • Manual coding • Traditional ETL • ODI’s business-rule driven approach combined with E-LT Business-Rules Driven Approach Introduction to Business rules: - Business rules specify mappings, filters, joins and constraints. They often apply to metadata to transform data and are usually described in natural language by business users. In a typical data integration project (such as a Data Warehouse project), these rules are defined during the specification phase in documents written by business analysts in conjunction with project managers. Business Rules usually define “What” to do rather than “How” to do it. They can very often be implemented using SQL expressions, provided that the metadata they refer to is known and qualified in a metadata repository. Examples of business rules are given in the table below: Business Rule Type SQL Expression Sum of all amounts of items Mapping SUM(CASE WHEN SALES.YEARMONTH=2010/05 sold during May 2010 THEN SALES.AMOUNT * PRODUCT.ITEM_PRICE multiplied by the item price ELSE 0 END ) Products that start with Filter Upper(PRODUCT.PRODUCT_NAME) like ‘CPU%’ ‘CPU’ and that belong to the And PRODUCT.CATEGORY = ‘HARDWARE’ hardware category Customers with their orders Join CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_ID = ORDER.ORDER_ID and order lines And ORDER.ORDER_ID = ORDER_LINE.ORDER_ID Reject duplicate Customer Unique CONSTRAINT CUST_NAME_PK names Key PRIMARY KEY (CUSTOMER_NAME) Constraint Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 3
- 4. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Reject orders with a link to Reference CONSTRAINT CUSTOMER_FK an non-existent customer Constraint FOREIGN KEY (CUSTOMER_ID) REFERENCES CUSTOMER(CUSTOMER_ID) Mappings: A mapping is a business rule implemented as a SQL expression. It is a transformation rule that maps source columns (or fields) onto one of the target columns. It can be executed by a relational database server at run-time. This server can be the source server (when possible), a middle tier server or the target server. Joins: A join operation links records in several data sets, such as tables or files. Joins are used to link multiple sources. A join is implemented as a SQL expression linking the columns (fields) of two or more data sets. Joins can be defined regardless of the physical location of the source data sets involved. For example, a JMS queue can be joined to a relational table. Depending on the technology performing the join, it can be expressed as an inner join, right outer join, left outer join and full outer join. Filters: A filter is an expression applied to source data sets columns. Only the records matching this filter are processed by the data flow. Constraints: A constraint is an object that defines the rules enforced on data sets’ data. A constraint ensures the validity of the data in a given data set and the integrity of the data of a model. Constraints on the target are used to check the validity of the data before integration in the target. Traditional ETL versus E-LT Approach: Traditional ETL tools operate by first Extracting the data from various sources, Transforming the data on a proprietary, middle-tier ETL engine, and then Loading the transformed data onto the target data warehouse or integration server. Hence the term “ETL” represents both the names and the order of the operations performed, as shown in Figure below. Understanding Oracle Data Integrator Interfaces : An interface is an ODI object stored in the ODI Repository that enables the loading of one target datastore with data transformed from Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 4
- 5. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ one or more source datastores, based on business rules implemented as mappings, joins, filters and constraints. A data stores can be: • A table stored in a relational database • An ASCII or EBCDIC file (delimited, or fixed length) • A node from a XML file • A JMS topic or queue from a Message Oriented • A node from a LDAP directory • An API that returns data in the form of an array of records Figure shows a screenshot of an ODI interface that loads data into the FACT_SALES target table. Source Data is defined as a heterogeneous query on the CORRECTIONS file, the Store and Region tables. A Business Problem case study: Figure describes an example of a business problem to extract, transform and load data from a Microsoft SQL Server database and a file into a target Oracle table. Data is coming from two Microsoft SQL Server tables (Store joined to Region) and. The target SALES Oracle table must match some constraints such as the uniqueness of the ID column and valid reference to the SALES_REP table. Data must be transformed and aggregated according to some mappings as shown in Figure Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 5
- 6. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Translating these business rules from natural language to SQL expressions is usually straightforward. In our example, the rules that appear in the figure could be translated as follows: TYPE RULE SQLEXPRESSION/ CONSTRAINT Filter Only Store marked as Books STORE.store_type=’Books’ Join A row from LINES has a matching ORDERS.ORDER_ID= LINES.ORDER_ID ORDER_ID in ORDERS Mapping Target’s SALE is the sum of the order lines’ SUM(LINES.AMOUNT+ AMOUNT grouped by sales rep., with the CORRECTIONS.VALUE) corrections applied. Mapping Sales Rep = Sales Rep ID from ORDERS ORDERS.SALES_REP_ID Constraint ID must not be null ID is set to “not null” in the data model Constraint ID must be unique A Primary Key is added to the data model with (ID) as set of columns Constraint The Sales Rep. ID should exist in the Target A Reference (Foreign Key) is added in sales Rep table the data model on SALES.SALES_REP = SALES_REP.SALES_REP_ID We will be looking at an organization that wishes to track sales from various heterogeneous data sources issued from the production systems. The following data sources will be used: The Repository: The Repository contains all of the metadata required for the training examples. It is hosted, for these evaluation purposes, in a supplied database. Orders Application: An application for tracking customer orders, hosted in a supplied database (the "src_sales" sample database). Sales Administration: The administration or tracking of sales, hosted in another supplied database (the "trg_sales" sample database). We will populate this data warehouse with our transformations Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 6
- 7. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ The schema diagrams below define the supplied data models that we will be using throughout this guide: Orders Application 1) Store_table Region_table 2) Dim Reason Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 7
- 8. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Product_Table Period_Table Fact_table Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 8
- 9. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ 2) Using ODI in your Data Warehouse Project Introduction The main goal of a Data Warehouse is to consolidate and deliver accurate indicators to business users to help them make decisions regarding their everyday business. A typical project is composed of several steps and milestones. Some of these are: • Defining business needs (Key Indicators) • Identifying source data that concerns key indicators; specifying business rules to transform source information into key indicators • Modeling the data structure of the target warehouse to store the key indicators • Populating the indicators by implementing business rules • Measuring the overall accuracy of the data by setting up data quality rules • Developing reports on key indicators • Making key indicators and metadata available to business users through ad-hoc query tools or predefined reports • Measuring business users’ satisfaction and adding/modifying key indicators. Organizing the Teams: As Oracle Data Integrator relies on a centralized repository, different types of users may need to access it. The list below describes how ODI may be used by your teams. 1) PROFILE: Business User DESCRIPTION: Business users have access to the final calculated key indicators through reports or ad-hoc queries. In some cases, they need to understand what the definition of the indicators is, how they are calculated and when they were updated. Alternatively, they need to be aware of any data quality issue regarding the accuracy of their indicators. ODI MODULES USED: ODI Console 2) PROFILE: Business Analyst DESCRIPTION: Business Analysts define key indicators. They know the source applications and specify business rules to transform source data into meaningful target indicators. They are in charge of maintaining translation data from operational semantics to the unified data warehouse semantic. ODI MODULES USED: Designer Navigator (limited access) ,ODI Console Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 9
- 10. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ 3) PROFILE: Developer DESCRIPTION: Developers are in charge of implementing the business rules in respect to the specifications described by the Business Analysts. They release their work by providing executable scenarios to the production team. Developers must have both technical skills regarding the infrastructure and business knowledge of the source applications. ODI MODULES USED: Limited access to Models Full access to Projects Operator Navigator ODI Console 4) PROFILE: Metadata Administrator DESCRIPTION: Metadata Administrators are in charge of reverse-engineering source and target applications. They guarantee the overall consistency of Metadata in the ODI Repository. They have an excellent knowledge of the structure of the sources and targets and they have participated in the data modeling of key indicators. In conjunction with Business Analysts, they enrich the metadata by adding comments, descriptions and even integrity rules (such as constraints). Metadata Administrators are responsible for version management. ODI MODULES USED: Topology Navigator (limited access), Designer Navigator: Full access to Models Restore access to Projects, ODI Console 5) PROFILE: Database Administrator DESCRIPTION: Database Administrators are in charge of defining the technical database infrastructure that supports ODI. They create the database profiles to let ODI access the data. They create separate schemas and databases to store the Staging Areas. They make the environments accessible by describing them in the Topology ODI MODULES USED: Topology Navigator (full access), Designer Navigator (full access), Operator Navigator (full access), ODI Console 6) PROFILE: System Administrator DESCRIPTION: System Administrators are in charge of maintaining technical resources and infrastructure for the project. For example, they may install and monitor Scheduler Agents backup / restore Repositories install and monitor ODI Console Setup environments (development, test, maintenance etc.) ODI MODULES USED: Agents, Topology Navigator (limited access), ODI Console 7) PROFILE: Security Administrator Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 10
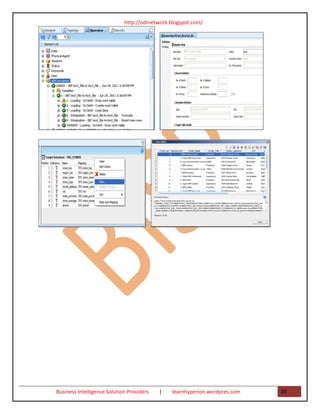
- 11. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ DESCRIPTION: The Security Administrator is in charge of defining the security policy for the ODI Repository. He or she creates ODI users and grants them rights on models, projects and contexts. ODI MODULES USED: Security Navigator (full access), Designer Navigator (read access), Topology Navigator (read access), ODI Console 8) PROFILE: Operator DESCRIPTION: Operators are in charge of importing released and tested scenarios into the production environment. They schedule the execution of these scenarios. They monitor execution logs and restart failed sessions when needed. ODI MODULES USED: Operator Navigator ODI Console Oracle Enterprise Manager Plug-in For ODI The ODI Master Repository contains built-in default profiles that can be assigned to users. The following table suggests how to use these built-in profiles: PROFILE BUILT-IN PROFILE IN ORACLE DATA INTEGRATOR Business User CONNECT, NG REPOSITORY EXPLORER Business Analyst CONNECT, NG REPOSITORY EXPLORER, NG DESIGNER Developer CONNECT, DESIGNER Metadata Administrator CONNECT, METDATA ADMIN, VERSION ADMIN Database Administrator CONNECT, DESIGNER, METADATA ADMIN, TOPOLOGY ADMIN System Administrator CONNECT, OPERATOR Security Administrator CONNECT, SECURITY ADMIN Operator CONNECT, OPERATOR 3) CREATING AN ODI PROJECT AND INTERFACE: EXPORTING A FLAT FILE TO A FLAT FILE PURPOSE This tutorial walks you through the steps that are needed to create a project and an interface in Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) to export a flat file to another flat file. OVERVIEW A common task that is performed using ODI is to export data from a flat file and load this data into another flat file. This tutorial walks you through the steps that are needed to create a project and an interface that will import a file to a staging area, perform some minor transformations, and then write the data to a file. You also execute the interface and verify the execution using ODI Operator. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 11
- 12. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ CREATING A NEW PHYSICAL SCHEMA FOR THE FLAT FILE MODEL Step: 1) Click Topology tab. In Topology navigator, click the Physical Architecture tab, select Technologies > File. Right-click FILE_GENERIC, and then select New Physical Schema. Step: 2) For the Directory (Schema) and Directory (Work Schema) fields, enter the path to the directory, where your input flat files are located ( C:Demonstration ). Select Default check box, and then click save button. Close editing window for your new physical schema. On the Information window that follows, click OK. Step: 3) Open Logical Architecture, navigate to Technologies > File, right-click File and select New Logical Schema. Enter the Logical Schema name: SRC_Text_file, select the recently created physical schema in Global context as shown below. Click Save and close the editing windows. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 12
- 13. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ CREATING A NEW ODI MODEL FOR THE FLAT FILE SOURCE Step: 1) Click the Models tab in the left panel of ODI Designer. Click the Insert Model Folder icon, and then select New Model Folder. On the screen that appears, set the Name to Files. Click Save icon Step: 2) Save. Right-click the Text model folder and select New Model. On the screen that appears, enter the values provided in the following image. Select Reverse Engineer tab. Step: 3) On the screen that appears, verify settings and click Save icon to save your model. CREATING A NEW ODI SOURCE DATASTORE FOR USE WITH ODI INTERFACE Step:1) Expand the Flat Files folder, right-click the newly created file data model, and then select New Datastore. On the screen that appears, set Name to SRC_STORE. Click the button next to the Resource Name field. Select the STORES.txt file and click Open. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 13
- 14. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 2) Click the Files tab. Set the File Format to Fixed, and then click the Columns tab. Step: 3) On the Columns tab, click the Reverse Engineer button. The following screen appears. Click Yes. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 14
- 15. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 4) In the FILE DATA MODEL, right-click Stores datastore, and then select View Data option. Close all tabs Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 15
- 16. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ CREATING A NEW ODI TARGET DATASTORE FOR USE WITH ODI INTERFACE Step:1) Browse to the H:Demonstration directory . Make a copy of the STORES.txt file and name the copy TRG_STORES.txt as shown in the example in the following screenshots. Step:2) In ODI Designer, right-click the newly created source datastore STORES and select Duplicate. On the screen that follows, click Yes. The new Copy of STORES.txt appears in the tree view. Step:3) Right-click the newly created duplicate Copy of STORES.txt and select Edit. On the screen that appears, set the Name to TRG_STORES. Click the button next to the Resource Name field. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 16
- 17. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 4) Select the TRG_STORES.txt file and click Open. Click Save icon. The data stores for the source and target files have now been successfully created in the same model and can be used in an ODI interface. Close editing tabs. CREATING A NEW ODI INTERFACE FOR FLAT FILE TO FLAT FILE TRANSFORMATIONS Step: 1) In ODI Designer, click the Projects tab. Expand your project, and then expand First Folder. Right-click Interfaces and select Insert Interface. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 17
- 18. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 2) On the screen that follows, enter the interface name as INT_text_file to text_file. Select In-Memory Engine: SUNOPSIS_MEMORY_ENGINE from drop-down list. Click the Mapping tab. Step: 3) Click the Models tab to drag the source and target to Designer. Expand Text File model > Flat File Model and drag the Stores datastore from the Text File model folder into the Sources container. Drag the TRG_Stores.txt datastore from Text File model into the Target Datastore container. When Designer asks "Do you want to perform an Automatic Mapping?" click Yes. Step: 4) Go to the Flow Tab Click the Srs_Set0(FILE_GENERIC) source datastore. This makes the properties for the source appear below. In the LKM Selector section, select LKM File to SQL from the LKM drop-down list if not already selected. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 18
- 19. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 5) Click Target (FILE_GENERIC). This makes the properties for the target appear below. For IKM, select IKM SQL to File Append from the IKM drop-down list if not already selected. Set the IKM options TRUNCATE to True and GENERATE_HEADER to False as shown below. Click Save icon to save your interface. Step: 6) To test your interface, click Execute icon. The following screen appears. Retain the defaults and click OK. On the screen that follows, click OK. Step: 7) To verify that your interface was executed successfully; you need to open ODI Operator. Click the ODI Operator tab. In ODI Operator, click Hierarchical Sessions. Expand All Execution > INT_text_file to text_file > Steps > INT_text_file to text_file, and view the execution results for each step. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 19
- 20. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 20
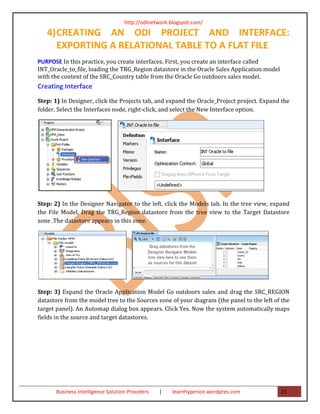
- 21. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ 4) CREATING AN ODI PROJECT AND INTERFACE: EXPORTING A RELATIONAL TABLE TO A FLAT FILE PURPOSE In this practice, you create interfaces. First, you create an interface called INT_Oracle_to_file, loading the TRG_Region datastore in the Oracle Sales Application model with the content of the SRC_Country table from the Oracle Go outdoors sales model. Creating Interface Step: 1) In Designer, click the Projects tab, and expand the Oracle_Project project. Expand the folder. Select the Interfaces node, right-click, and select the New Interface option. Step: 2) In the Designer Navigator to the left, click the Models tab. In the tree view, expand the File Model. Drag the TRG_Region datastore from the tree view to the Target Datastore zone .The datastore appears in this zone. Step: 3) Expand the Oracle Application Model Go outdoors sales and drag the SRC_REGION datastore from the model tree to the Sources zone of your diagram (the panel to the left of the target panel). An Automap dialog box appears. Click Yes. Now the system automatically maps fields in the source and target datastores. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 21
- 22. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 4) Click the Flow tab. Select the Distinct Rows check box. Step: 5) Click the Save button to save your interface. If the Locking Object window appears, select “Don’t show this window next time,” and click Yes. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 22
- 23. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 6) Run this interface, and check the content of the TRG_Region table. Step: 7) Click OK in the Execution window, and then click OK when the Session Started message appears. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 23
- 24. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 8) Click the Operator tab to open the ODI Operator Navigator. The Operator window appears. In the Session List tab, expand the All Executions node. The session called “INT_Oracle_to_file” should appear complete. Expand this session in the tree view as shown: Step: 9) Go to the model tab select file model expand it and select TRG_Region data store Right click select View Data. Verify your data and close this window. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 24
- 25. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ 5) CREATING ODI INTERFACE: EXPORTING A FLAT FILE TO A RELATIONAL TABLE Create a new physical schema for the source flat-file model. Step: 1) If not connected, connect to the Work repository. Step: 2) Click Topology navigator. In Topology navigator, click the Physical Architecture tab, select Technologies > File. Right-click and then select New Data Server. In Definition tab specify the Name for the Data Server and go to JDBC tab. specify the JDBC Driver and JDBC Url by selecting browse button. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 25
- 26. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 3) Save the Data Server Step: 4) Now in Topology navigator, click the Physical Architecture tab, select Technologies > File. Right-click, Demonstration and then select New Physical Schema. Step: 5) For the Directory (Schema) and Directory (Work Schema) fields, enter the path to the directory where your input flat files are located Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 26
- 27. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ (C:oracleMiddlewareOracle_ODI1oraclediDemoDemonstration). Select the Default check box and click Yes in the Confirmation window, and then click the Save button. Close the editing window for your new physical schema. On the Information window that follows, click OK. Close the editing tab. Step: 6) Verify that your new Physical schema was added under the Demonstration data server in the Technologies tree view. Step: 7) Open Logical Architecture, navigate to Technologies > File, right-click File, and select New Logical Schema. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 27
- 28. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 8) Enter the Logical Schema name: Demonstration Integration, and select the Physical schema Demonstration in all three contexts as shown here. Click Save and close the editing Window. Step: 9) Verify that your new Logical schema was added under the File node in the Technologies tree view. Create the new project in ODI. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 28
- 29. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 11) On the screen that appears, set the Name of the project to Flat file to Relation Table in the Name field. The Code field is filled in automatically. Click Save, and then close the tab. The newly created Flat file to Relation Table project now appears in the Projects pane. Create a new model folder for the flat-file source data store. Step: 13) In ODI Designer, click the Models tab, and then click the New Model. Then select the New Model option to insert a new model. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 29
- 30. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 14) Create a new ODI source data store. On the screen that appears, set the Name to Sales Region. Click the button next to the Resource Name field. Navigate to the C:oracleMiddlewareOracle_ODI1oraclediDemoDemonstration folder, and then select the SRC Sales Region.txt file. Click Open. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 30
- 31. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 15) Click the Files tab. Set the File Format to Fixed, and then click the Columns tab. Step: 16) On the Columns tab, click the Reverse Engineer button. The following Confirmation screen appears. Click Yes. The Column Setup Wizard appears. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 31
- 32. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 17) Place the cursor, and then click the ruler at the beginning of each column as shown next. The wizard marks each column as shown in the following screens. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 32
- 33. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 33
- 34. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 18) After the columns are marked, click each column data to select a column, and then set the name and data type for each column in the Definition panel to the right, as shown in the following screens. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 34
- 35. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 19) The columns should look as follows. Click Save to save the model. If the Unlocking Object window appears, select the check box and click OK. Expand Flat file Model > Sales Region > Columns and view the newly created columns. Step: 20) You must create a schema to host the ODI target datastore. To create a new RDBMS schema for the ODI datastore, perform the following steps: Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 35
- 36. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Open the Oracle 10g SQL Plus window .You will create the schema by executing the following SQL commands: create user <MY_SCHEMA> identified by <MY_PASS> ; To create a user, enter the following command. Verify that user odi_demo is created successfully. create user odi_demo identified by odi_demo; Grant connects privileges to the newly created user by executing the following SQL command: grant connect, resource, create trigger, create view to odi_demo; Step: 21) Now you need to create a new ODI datastore for the target model. This datastore will be used within the ODI Interface. To create a new ODI target datastore, perform the following steps: Enter the username as odi_demo with the password odi_demo. For SID enter ORCL. Create your target table by executing the following SQL commands. CREATE table "trg_sales_region"( "Region_Key" NUMBER(8,0) NOT NULL, "Region" VARCHAR2(80), "Territory" VARCHAR2(80), "Country" VARCHAR2(80), primary key("Region_Key") ) ; Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 36
- 37. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 22) After you have created the new database target datastore, you need to create a new ODI target data server and the physical schema. To create the ODI target data server and physical schema, perform the following steps: In ODI, open ODI Topology Navigator and then select the Physical Architecture tab. Expand Technologies, right-click Oracle, and select New Data Server. In the Data Server: New window, enter the values provided in the following image. Click the JDBC tab. Step: 23) Click for JDBC Driver. Select Oracle JDBC Driver. Click OK. Click for JDBC Url, select jdbc:oracle:thin:@<host>:<port>:<sid>, and then click OK. Edit the Url to read: jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL for Oracle Database. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 37
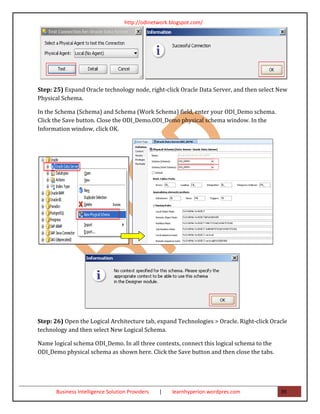
- 38. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 24) Click Test Connection. In the window that opens, click Yes to save your data. In the Information window, click OK. Click Test to verify a successful connection. Click OK. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 38
- 39. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 25) Expand Oracle technology node, right-click Oracle Data Server, and then select New Physical Schema. In the Schema (Schema) and Schema (Work Schema) field, enter your ODI_Demo schema. Click the Save button. Close the ODI_Demo.ODI_Demo physical schema window. In the Information window, click OK. Step: 26) Open the Logical Architecture tab, expand Technologies > Oracle. Right-click Oracle technology and then select New Logical Schema. Name logical schema ODI_Demo. In all three contexts, connect this logical schema to the ODI_Demo physical schema as shown here. Click the Save button and then close the tabs. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 39
- 40. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 27) Create a new ODI target model that will be used within your ODI Interface. To create a new ODI target model, perform the following steps: Open ODI Designer. Click the Models tab and select New Model. On the screen that appears, enter the values provided in the following image. Click the Reverse Engineer tab. Step: 28) On the Reverse Engineer tab, set the Context to Development. Click the Save button and then close the RDBMS tab. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 40
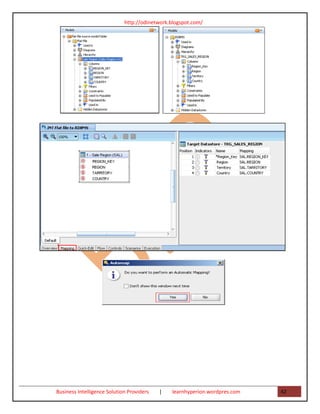
- 41. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 29) In the Models tab, right-click the RDBMS model. Select Reverse Engineer. To verify that the TRG_SALES_PERSON data store is successfully reversed, expand the model as shown here. Create a new ODI Interface to perform a flat-file-to-RDBMS-table transformation: In ODI Designer, click the Projects tab. Expand your project Flat file to Relation Table, and then expand First Folder. Right-click Interface and select New Interface. In the Optimization Context field, select Development. On the screen that follows, enter the interface name as INT Flat file to RDBMS. If selected, deselect the Staging Area Different From Target check box. Click the Mapping tab. Step: 31) Click the Models tab to drag the source and target to the diagram. Drag the Sales Region.txt datastore from the Flat_File model into the Sources container. Drag the TRG_Sales_Region datastore from the RDBMS model into the Target Datastore container. When Designer asks “Do you want to perform an Automatic Mapping?” click Yes. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 41
- 42. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 42
- 43. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 32) Click the Flow tab. Click the SrcSet_0 (Demonstration) datastore. The properties for the source appear in the following screen. For LKM, select LKM File to SQL from the LKM drop-down list if not selected. Now you need to ensure that the temporary objects created during the transformation are deleted. Set the LKM option DELETE_TEMPORARY_OBJECTS to <Default>:true as shown here. Step: 33) Click the Target datastore. Select IKM SQL Incremental Update. Set the IKM option Flow_Control to False. Set the IKM option DELETE_ALL to True. Click Save Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 43
- 44. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 34) To test your interface, click the Execute button. The following screen appears. Retain the defaults and click OK. On the next screen, click OK. Open ODI Operator and verify that your interface was executed successfully Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 44
- 45. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Double-click Step 12 and click the Execution tab. View the number of rows inserted into the target table Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 45
- 46. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ 6) CREATE NEW PROJECT AND PROCEDURE IN ODI DESIGNER Create New Project Step: 1) Switch to the Designer Navigator. Click the Designer tab. Select the Projects tab, click the New Project icon, and select New Project. Step: 2) Enter the name of the project: Procedure-demo. Click the Save button to create the project and close the tab. The project appears in the tree view. Expand the Procedure-demo project node. Create Procedure Step: 3) Open ODI Designer. In the Projects tab, select Procedure-Demo --> First Folder. Right-click Procedures and select New Procedure. Step: 4) Enter the procedure name as Procedure-Create-populate. Set Target Technology to Oracle. Click the Details tab. Click the icon to add a step in the procedure. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 46
- 47. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Step: 5) In the Command: New window, enter the parameters of the procedure and the command on the target provided in the following details shown in the image. You need this command to drop the table in case a table with this name exists. Select the Ignore Errors check box. Step: 6) Select the Details tab, and then click the icon to add another step in the procedure. In the Command: New screen, if not selected, click the Command on Target tab. Enter the parameters of the procedure and the command provided below. CREATE TABLE "ODI_DEMO"."TRG_SALES_REGION" ( "Region_Key" NUMBER(8,0) NOT NULL ENABLE, "Region" VARCHAR2(80 BYTE), Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 47
- 48. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ "Territory" VARCHAR2(80 BYTE), "Country" VARCHAR2(80 BYTE), primary key("Region_Key") ) Step: 7) Click the Details tab. Click the icon to enter the step to populate the TRG_SALES_REGION table. Step: 8) In the Command: New screen, click the Command on Target tab. Enter the parameters and the command shown below in the image. Click the Details tab to view your steps. begin Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (1,'Americas','North America','USA'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (2,'Americas','North America','Canada'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (3,'Americas','South America','Brazil'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (4,'Americas','South America','Argentina'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (5,'Europe','British Isles','United Kingdom'); Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 48
- 49. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (6,'Europe','British Isles','Ireland'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (7,'Europe','Scandinavia','Sweden'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (8,'Europe','Scandinavia','Norway'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (9,'Europe','Western','France'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (10,'Europe','Western','Germany'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values (11,'Asia Pacific','Pacific Rim','Australia'); Insert into TRG_SALES_REGION ("Region_Key","Region","Territory","Country") values(12,'Asia Pacific','Asia','Japan') end; Step: 9) Click Save and close the tab. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 49
- 50. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Execute your newly created procedure and verify the results. Step: 10) Open ODI Operator. In ODI Operator, click the All Executions node, click the Refresh icon, find your session, and verify that your procedure executed successfully. Step: 11) Open the Oracle SQL developer and expand the ODI_Demo connection. Select Tables node and click the Refresh button. Double–click the newly created table TRG_SALES_REGION, click the Data tab, and verify that your table TRG_SALES_REGION was successfully created and populated with records as shown in the following screen. Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 50
- 51. http://odinetwork.blogspot.com/ Business Intelligence Solution Providers | learnhyperion.wordpres.com 51