Parallel Algorithms- Sorting and Graph
- 1. PARALLELALGORITHMS SORTING AND GRAPH Prof. Shashikant V. Athawale Assistant Professor | Computer Engineering Department | AISSMS College of Engineering, Kennedy Road, Pune , MH, India - 411001
- 2. Contents ❖ Issues in Sorting on Parallel Computers ❖ Bubble Sort and its Variants ❖ Parallelizing Quicksort ❖ All-Pairs Shortest Paths ❖ Algorithm for sparse graph ❖ Parallel Depth-First Search ❖ Parallel Best-First Search.
- 3. Parallel Depth First Search ❖ Depth-first search can be performed in parallel by partitioning the search space into many small, disjunct parts (subtrees) that can be explored concurrently.
- 4. Sorting ❖ Sorting can be comparison-based or non comparison- based ❖ The fundamental operation of comparison-based sorting is compare-exchange.
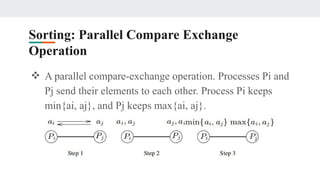
- 5. Sorting: Parallel Compare Exchange Operation ❖ A parallel compare-exchange operation. Processes Pi and Pj send their elements to each other. Process Pi keeps min{ai, aj}, and Pj keeps max{ai, aj}.
- 6. Sorting: Parallel Compare Split Operation ❖ A compare-split operation. Each process sends its block of size n/p to the other process. ❖ Each process merges the received block with its own block and retains only the appropriate half of the merged block. ❖ In the example, process Pi retains the smaller elements and process Pj retains the larger elements.
- 7. Sorting: Parallel Compare Split Operation
- 8. Bubble Sort and its Variants ❖ The sequential bubble sort algorithm compares and exchanges adjacent elements in the sequence to be sorted. ❖ The complexity of bubble sort is Θ(n2 ). ❖ Bubble sort is difficult to parallelize since the algorithm has no concurrency. ❖ A simple variant, though, uncovers the concurrency.
- 9. Parallelizing Quicksort ❖ Quicksort is one of the most common sorting algorithms for sequential computers because of its simplicity, low overhead, and optimal average complexity. ❖ Quicksort selects one of the entries in the sequence to be the pivot and divides the sequence into two – one with all elements less than the pivot and other greater. ❖ The process is recursively applied to each of the sublists. ❖ In parallel quicksort,choose a pivot from one of the processes and broadcast it to every process.
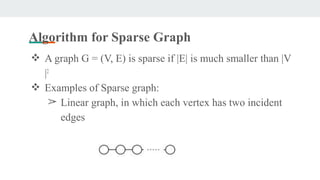
- 11. Algorithm for Sparse Graph ❖ A graph G = (V, E) is sparse if |E| is much smaller than |V |2 ❖ Examples of Sparse graph: ➢ Linear graph, in which each vertex has two incident edges
- 12. Algorithm for Sparse Graph ❖ Grid graph,in which each vertex has four incident vertices ❖ Random sparse graph.
- 13. Parallel Depth First Search ❖ Depth-first search can be performed in parallel by partitioning the search space into many small, disjunct parts (subtrees) that can be explored concurrently. ❖ Depth-first search algorithm uses idea of backtraching.
- 14. Parallel Breadth First Search