Php a dynamic web scripting language
- 2. P - PHP H - Hypertext P - Preprocessor
- 3. PHP is an acronym for “PHP Hypertext Preprocessor”. (Originally, „Personal Home Page’). It was created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1995 to maintain his personal home page PHP is a widely-used server scripting language, and is a powerful tool for making dynamic and interactive web pages quickly
- 4. PHP is an object-oriented programming language, which means that you can create objects, which can contain variables and functions PHP scripts are executed on the server PHP is an open source software PHP costs nothing, it is free to download and use
- 5. PHP files can contain text, HTML, CSS, JavaScript and PHP code PHP files are executed on the server and the result are returned to the browser as plain HTML PHP files have extension “.php”
- 6. To start using PHP, you can: Find a web host with PHP and MySQL Support Install a web server on your own PC, and then install PHP and MySQL Visit www.php.net for free download.
- 7. Download XAMPP installer XAMPP is an all-in-one installer package of local server, MySql and PHP * Take a look at this video on how to install XAMPP
- 9. 1. Go to XAMPP directory folder located in local disk C: & open it 2. Click the “htdocs” folder 3. Create your own folder inside that „htdocs’ 4. Put/save all your PHP Files inside your own folder *Remember: Never rename or delete any default folder/s inside XAMPP directory except that of your own folder
- 10. *Take the ff. steps every time you want to test/run your PHP files? 1. Open XAMPP Control Panel 2. Click the „Start‟ button of the Apache Server and of the MySQL if your PHP has a database 3. Open any web browser (Chrome, IE,Firefox, Safari etc) 4. Type in the address bar “localhost/yourfoldername” & press Enter button
- 11. <?php //php code goes here ?>
- 12. .php Example: myfirstproject.php File Name File Extension
- 13. <html> <body> <?php echo "Hello World"; print “Hello World”; ?> </body> </html> Example:
- 14. There are two basic statements to output or send text to the browser: echo or print Example: echo "Hello World"; print “Hello World”; Each code line in PHP must end with a semicolon (;). The semicolon is a separator and is used to distinguish one set of instructions from another.
- 15. <html> <body> <?php //This is a single line comment # This is also a single line comment /* This is a multiple lines comment block that spans over more than one line */ ?> </body> </html>
- 16. Variables are “containers” for storing information. It can store values like text strings, numbers or arrays. Rules for PHP variables: A variable starts with a $ (sigil) sign, followed by the name of the variable. A variable name must start with a letter or the underscore character A variable name cannot start with a number A variable name can only contain alpha-numeric characters and underscores (A-z, 0-9, and _) Variable names are case sensitive ($y and $Y are two different variables)
- 17. The correct way of declaring a variable in PHP: $var_name = value; Example: <?php $text="Hello Math!"; $x=5; $y=6; $z=$x+$y; echo $z; ?> Remember: (put quotes for text variable’s value) (no quotes needed for number variable’s value)
- 18. All user-defined functions, classes, and keywords (e.g. if, else, while, echo, etc.) are case- insensitive Example 1: <?php EcHo “Hello World!”; echo “Hello World!”; ECHO “Hello World!”; ?> all three echo statements are legal (and equal)
- 19. All variables are case-sensitive Example: <?php $color=”red”; echo “My car is “ . $color; echo “My car is “ . $COLOR; echo “My car is “ . $coLOR; ?> only the first statement will display the value of the $color variable
- 20. ( .) – Concatenator The concatenation operator (.) is used to put two string values together. Example: <?php $txt1="Hello World!"; $txt2="What a nice day!"; echo $txt1 . " " . $txt2; ?> The output of the code above will be: Hello World! What a nice day!
- 21. Operators are used to operate on values. Arithmetic Operators Assignment Operators Comparison Operators Logical Operators + - * / % ++ -- = += -= *= /= .= %= == != <> > < >= <= && and II or ! not
- 22. Conditional Statements The if...else Statement Use the if....else statement to execute some code if a condition is true and another code if a condition is false. Syntax if (condition) code to be executed if condition is true; else code to be executed if condition is false;
- 23. The if...else Statement Example: <html> <body> <?php $d=date("D"); if ($d=="Fri") echo "Have a nice weekend!"; else echo "Have a nice day!"; ?> </body> </html>
- 24. Conditional Statements The if...elseif....else Statement Use the if....elseif...else statement to select one of several blocks of code to be executed. Syntax if (condition) code to be executed if condition is true; elseif (condition) code to be executed if condition is true; else code to be executed if condition is false;
- 25. The if...elseif....else Statement Example: <?php $d=date("D"); if ($d=="Fri") echo "Have a nice weekend!"; elseif ($d=="Sun") echo "Have a nice Sunday!"; else echo "Have a nice day!"; ?>
- 26. Conditional statements are used to perform different actions based on different conditions. Syntax switch (n) { case label1: code to be executed if n=label1; break; case label2: code to be executed if n=label2; break; default: code to be executed if n is different from both label1 and label2; }
- 27. Example: <?php switch ($x) { case 1: echo "Number 1"; break; case 2: echo "Number 2"; break; case 3: echo "Number 3"; break; default: echo "No number between 1 and 3"; } ?>
- 28. PHP $_POST Function The built-in „$_POST‟ function is used to collect values in a form with method="post".
- 29. PHP $_POST Function Example: <form action="welcome.php" method="post"> Name: <input type="text" name="fname" /> Age: <input type="text" name="age" /> <input type="submit" /> </form> When the user clicks the "Submit" button, the "welcome.php" file can now use the $_POST function to collect form data Welcome <?php echo $_POST["fname"]; ?>!<br /> You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old. Output could be something like this: Welcome John! You are 28 years old.
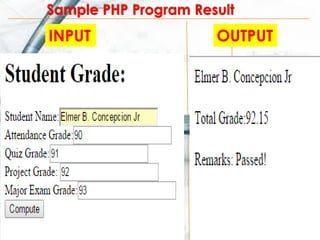
- 30. Problem: How to create a program that inputs „student name‟, „attendance grade‟, „quiz grade‟, „project grade‟, & „major exam grade‟ with an output of student name, total grade and remarks using PHP?
- 31. <html> <body> <h1> Student Grade:</h1> <form action="compute.php" method="post"> Student Name:<input type="text" name="sname" /> <br> Attendance Grade:<input type="text" name="agrade" /> <br> Quiz Grade:<input type="text" name="qgrade" /> <br> Project Grade: <input type="text" name="pgrade" /> <br> Major Exam Grade:<input type="text" name="egrade" /> <br> <input type="submit" value="Compute"/> </form> </body> Create this first file and Save this as studentgrade. php PHP file #1
- 32. <html> <body> <?php echo $_POST["sname"]; ?> <br> <?php $attgrade = $_POST['agrade']; $quizgrade = $_POST['qgrade']; $prograde = $_POST['pgrade']; $megrade = $_POST['egrade']; $total = ($attgrade * 0.10) + ($quizgrade * 0.15) + ($prograde * 0.25) + ($megrade * 0.50); ?> <br> PHP file #2
- 33. <?php echo 'Total Grade:' . $total; ?> <br> <?php if ($total >= 75) { echo "Remarks: Passed!"; } else { echo "Remarks: Failed!"; } ?> </body> </html> Create this second file and Save this as compute.php and run/test the two files
- 34. Save this file as compute.php INPUT OUTPUT
- 35. THANK YOU!




























![PHP $_POST Function
Example:
<form action="welcome.php" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="fname" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
When the user clicks the "Submit" button, the
"welcome.php" file can now use the $_POST function to
collect form data
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["fname"]; ?>!<br />
You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old.
Output could be something like this:
Welcome John!
You are 28 years old.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-adynamicwebscriptinglanguage-151217011420/85/Php-a-dynamic-web-scripting-language-29-320.jpg)


![<html>
<body>
<?php
echo $_POST["sname"];
?>
<br>
<?php
$attgrade = $_POST['agrade'];
$quizgrade = $_POST['qgrade'];
$prograde = $_POST['pgrade'];
$megrade = $_POST['egrade'];
$total = ($attgrade * 0.10) + ($quizgrade * 0.15) + ($prograde * 0.25)
+ ($megrade * 0.50);
?>
<br>
PHP file #2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-adynamicwebscriptinglanguage-151217011420/85/Php-a-dynamic-web-scripting-language-32-320.jpg)