phytoplasma.ppt
- 2. Phytoplasma : An Introduction and Classification with Recent Molecular Tools by SUJATA DANDALE
- 3. Phytoplasmas: historical Pleomorphic cells observed in ultra-thin section of leaves of mulberry infected with dwarf disease (Doi et al.,1967) These bodies disappear after tetracycline treatment when seen in EM (Ishiie et al.,1967) Called as MLOs (Mycoplasma Like Organisms) Causal agents of yellow diseases in plants Trival name “Phytoplasma” adopted in 10th congress of International Organization of Mycoplasmology (1994) Lee et al. (2000) Annu. Rev. Microbiol.
- 4. Single celled, wall-less prokaryotes, resembling mycoplasmas in morphology (Doi et al.,1967) Obligate parasites, can’t be grown in in-vitro cell free culture (Lee et al., 1986) Transmitted by phloem feeding insects (leafhoppers, plant hoppers, psyllids) and Cuscuta (Tsai et al., 1979) Sensitive to tetracycline but resistant to penicillin (Ishii et al. 1967) Descended from low G+C gram positive bacterium (Woese et al., 1987) Lee et al. (2000) Annu. Rev. Microbiol
- 5. Round to filamentous (Kirkpatrick,1982) Size 200-800 nm Phytos- plant + plasma- thing moulded (Greek) In sieve elements of Plants Cont..
- 6. Symptoms due to Phytoplasmas: Virescence Phyllody Little leaf Sterility of flowers Witches’ broom Slender shoots Stunting, leaf curling Generalized decline, Bunchy growth etc. Virescence on horseradish Lee et al. (2000) Ann. Rev. Microbiol. Diseased control
- 7. lethal yellowingSesame phyllody Little leaf of brinjalCarrot yellow Witches’ broom lime Palm wilt Brassica phyllody Grape vine yellow
- 8. First reports of phytoplasma diseases: Clover phyllody (Merrett,1866) Peach yellow (Smith,1888) Aster yellow on China aster (1902) First Etiology : Mulberry dwarf (1967) Important plant diseases world wide: Aster yellows in Carrot & Onion Apple proliferation Coconut lethal yellowing Peach X disease Elm yellow More than 300 plant Diseases in hundreds of plant genera Lee et al. (2000) Ann. Rev. Microbiol.
- 9. Important diseases in India Disease Host Area First Report of etiology Little leaf Brinjal Periwinkle All India Lukhnow Varma et al. (1969) Rao et al. (1983) X disease Peach NE region Ahlawat & Chenulu (1979) Bushy Stunt Brinjal New Delhi Mitra & Chakraborty (1988) Phyllody Bottle gourd & other gourd Black pepper Sesame Banglore Banglore Karela All India Sastry & Singh (1981) Bhat et al. (2006) Sahambi (1970) Witches’ broom Acid Lime Winged bean Sunhemp MH, AP Ghosh et al. (1999) Singh (1991) Sharma et al. (1990) Rubbery wood Citrus Darjeeling Ahlawat & Chenula (1985) Root wilt Coconut Kerala Solomon et al. (1983) Sandal spike Sandal Kerala,Kr Varma et al. (1969) GSD Sugarcane All India Rishi et al. (1973) White leaf Bermuda grass UP Rishi (1978) Rao et al. (2007) Yellow dwarf Rice All India Raychaudhri et al. (1967)
- 10. “After a time the growth of and accumulation of specimens or phenomena forces people to try to classify” - Pirie (1995) Hurdles to definite description and classification: Obligately parasitic habit Structural fragility Presence in low numbers in infected plants Intimate association with host tissues Firraro et al. (2005) J. Pl. Pathol
- 11. Based on biological properties (1970s) Based on serological properties (1980s) Based on molecular properties (1990s onward) Working Team on Phytoplasmas of International Research Program of Comparative Mycoplasmology (IRPCM) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology (ICSB)- Subcommittee on the Taxonomy of Mollicutes Development of classification systems in Phytoplasmas Bergeys’ manual of systematic bacteriology: Vol. III , class- Mollicutes
- 12. First attempts: Symptomatology Host Range (eg. Aster yellow, Clover phyllody) Transmission by insect vectors (vector species) Groups based on Symptoms Kirkpatrick et al. (1992) Decline agents Proliferation agents Virescence agents Kirkpatrick et al. (1992) Aster yellows Stolbur Witches’ broom Decline Phyllody Grunewald et al. (1977)
- 13. Chyokowski & Sinha (1989) Phytoplasmas Mutually exclusive floral symptoms Reduced flower size and colour with other symptoms On experimental host Periwinkle Catharanthus roseus Classification based on symptoms is not reliable
- 14. Serology mostly used for detection/identification Phytoplasma enriched extract used for production of : Monoclonal antibodies (Chen et al., 1988) Polyclonal antibodies (Kirkpatrick et al., 1992) Monoclonal antibodies suited for differentiation of closely related strains (Lee et al., 1993a ) Limitations: Difficult to obtain pure phytoplasmas Low concentration Non-specific reaction Lee et al. (1993a)
- 15. Molecular Era Year Work Scientists 1987 Improvement in phytoplasma extraction from infected hosts Kirkpatrick et al. 1989 First estimate of phytoplasma DNA composition - Reported low G+C value: 23-26 mol% Kollar et al. 1989 Plant pathogenic MLOs different from Mycoplasmas by 16S rDNA sequence analysis Lims & Sears 1991 Suggested primer pair for 16S rRNA gene amplification for wider array of MLO identification Deng & Hiruki 1992 Cloned DNA fragments as probes in dot blot hybridization to identify phytoplasma Lee et al. 1992 Suggested RFLP analysis of amplified 16S rDNA Ahrens & Seemuller 1993 by pulse field gel electrophoresis showed genome size of phytoplasma Neimark et al. 1993 Used oligo-nuceotide primers that amplify 16S DNA of AY-MLO Cluster Davis & Lee
- 16. Table Cont.. Year Work Scientists 1994 Cloned DNA fragments used in southern hybridization to identify phytoplasmas from hosts Schneider et al. 1994 combined RFLP (16S rDNA) & ribosomal protein gene sequence for classification Gundersen et al. 1997 characterization & classification by using enzymes and sequence analysis Schneider et al. 1998 Based on RFLP of 16S rRNA gene & rp gene classified phytoplasmas to 14 groups Lee et al. 2004,2006 Expanded phytoplasma classification to 18 16Sr groups Lee et al. 2005 Gave description of 21 Candidatus phytoplasma sp. Firrao et al. 2007 Expanded RFLP based 16Sr classification through in silico analysis Wei w. et al.
- 17. Classification based on DNA hybridization assays SNo. Strain Cluster Ref. 1 Little leaf disease of periwinkle-MLO Davis et al. (1990) 2 Ash yellows-MLO Davis et al. (1991) 3 Clover proliferation-MLO Lee et al. (1992) 4 Aster yellows-MLO Lee et al. (1992) 5 Canadian peach X disease , Western X disease, Clover yellow edge Lee et al. (1992) 6 Italian periwinkle virescence Davis et al. (1992) •Cloned DNA fragments from known phytoplasma were used for hybridization • Each Strain Cluster consists of strains with extensive sequence homology Lee & Davis et al. (1992)
- 18. DNA fragments were cloned only from limited numbers of Phytoplasmas Difficulty in obtaining desired concentration of phytoplasma strains from infected hosts Standardized DNA probes for general detection & identification were not available PCR based Molecular tools became more popular Lee & Davis et al. (1992) Classification based on DNA hybridization assays: Difficulties
- 19. Classification systems based on recent molecular tools Tools for classification: Most conserved Less conserved regions 16S rRNA ( primers- P1/P7, R16F2n/R16R2) 23S rRNA Rp gene operon (rpl22,rps3) (primers-rpF1, rpR1) 16S-23S spacer Tuf elongation factor Gene Phytoplasma Phytoplasma & Acholeplasma 16S rRNA 88-99% 87.0-88.5% Ribosomal protein 60-79% 50-57% 16S rRNA Spacer 23S rRNA 1.5 Kb 0.3 Kb 0.4 Kb Lee et al. (1998, 2000) Sequence similarity:
- 20. DNA extracted from 52 isolates and digested with BclI 30 PCR amplification Cycles (primers- fD1, rp1) Amplification product (1500bp) digested with BclI and then with AlulI, RsaI, EcoRI Amplified DNA cloned and sequenced Schneider et al. (1992) J. Gen. Microbiol. Seven Groups determined
- 21. OAY I(AAY) II(ACLR) III(ASHY) IV(EY) V(AT) VI(WX) VII(SCWL) a b c d e f g h i j Fig: AluI restriction map of 16S rDNA depicting the seven (I-VII) Restriction profile Schneider et al. (1992)
- 22. 16S rRNA gene sequence homology: 52 isolates from 4 symptom groups (Aster yellows, Clover phyllody, Periwinkle virescence and stolbur) were divided to 7 groups Isolates from Same group Different gp Schneider et al. (1992) V IV II III I VI Fig: AluI Restriction profile Phytoplasma 16S rDNA Inference 97.8 to 99.5% 89.6 to 92%
- 23. Total nucleic acid extracted from 40 strains 35 PCR amplification cycles with primer pair R16F2/R2 PCR product digested separately with 15 Restriction enzymes Gel electrophoresis Similarity coefficient (F)= 2Nxy Nx+Ny Nei & Li (1979) Lee et al. (1993) Phytopathol. F > 0.9 for members of same group
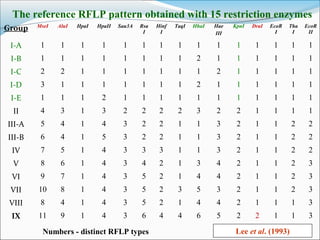
- 24. The reference RFLP pattern obtained with 15 restriction enzymes Lee et al. (1993) Group MseI AluI HpaI HpaII Sau3A Rsa I Hinf I TaqI HhaI Hae III KpnI DraI EcoR I Tha I EcoR II I-A 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 I-B 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 I-C 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 I-D 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 I-E 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 II 4 3 1 3 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 1 1 1 1 III-A 5 4 1 4 3 2 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 2 2 III-B 6 4 1 5 3 2 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 2 2 IV 7 5 1 4 3 3 3 1 1 3 2 1 1 2 2 V 8 6 1 4 3 4 2 1 3 4 2 1 1 2 3 VI 9 7 1 4 3 5 2 1 4 4 2 1 1 2 3 VII 10 8 1 4 3 5 2 3 5 3 2 1 1 2 3 VIII 8 4 1 4 3 5 2 1 4 4 2 1 1 1 3 IX 11 9 1 4 3 6 4 4 6 5 2 2 1 1 3 Numbers - distinct RFLP types
- 25. Key enzymes for Group and subgroup classification: MseI & AluI – sufficient to classify in 16Sr-I MseI, AluI, HpaII & HhaI – Further differentiation RFLP from 2 Strains (BBSI, HyphI) 16SrI-B, 16SrI-E (newly classified) Lee et al. (1993) AB B C
- 26. Resulted nine major 16Sr groups and 14 subgroups based on F Comparison of 16Sr groups with previous strain clusters Lee et al. (1993)-16Sr groups Lee & Davis (1992)-Strain Clusters 16SrI (5 subgroups) AY-MLO 16SrII Peach X disease -MLO 16SrV EY-MLO 16SrVI CP-MLO 16SrVII Ash Y-MLO Lee et al. (1993) 16SrI: 5 subgroups (largest) 16SrIII: 2 subgroups Inference
- 27. Nested PCR of 34 representative phytoplasma strains (16SrRNA) RFLP with 17 restriction enzymes and similarity coefficient Based on 16S rRNA similarity coefficient --14 groups -- 41 subgroups By combined RFLP 16S rDNA & rp gene sequence --46 subgroups Similarity coefficient between distinct Groups < 90% Lee et al.(1998) IJSB
- 28. 16S DNA Lee et al. (1998)
- 29. 16Sr RNA groups based on phylogeny Lee et al. (1998) Fig: RFLP analysis Fig: Phylogenetic Tree
- 30. Finer subgroup classification Strain 16S r-rp subgp. Strain 16S r-rp subgp Tomato big bud BB 16SrI-A (rp-A) Maize bushy stunt MBS 16SrI-B (rp-L) New Jersey AY NJAY 16SrI-A (rp-A) Clover phyllody CPh 16SrI-C (rp-C) Periwinkle little leaf CNI 16SrI-A (rp-A) Strawberry green petal SGP 16SrI-C (rp-C) Oklahoma AY OKAYI 16SrI-A (rp-A) Annulus phyllody RPh 16SrI-C (rp-C) Maryland aster yellow AYI 16SrI-B (rp-B) Paulownia WB PaWB 16SrI-D (rp-D) Dwarf aster yellow DAY 16SrI-B(rp-B) Blueberry stunt BBSI 16SrI-E (rp-E) Hydrangea phyllody HyPH 16SrI-B (rp-K) Grey dogwood WB GDI 16SrI (rp-M) Ipomoea WB IOB 16SrI-B (rp-F) Fig: RFLP of rp gene Lee et al. (1998)
- 31. Approach based on 16S r Groups: 16S rRNA gene sequence Subgroups: 16S r RNA gene & rp gene cluster 16S rRNA sequence homologies 88-94% : Two distinct 16S rRNA Groups 95-98%: Two subgroups with in a Group Grouping consistent with strain clusters (identified based on DNA- DNA homology and serological data) Lee et al. (1998) Inference So valid classification system
- 32. Case Study 4. Candidatus phytoplasma approach Taxonomic Notes Reference Major part of gene to be sequenced (1000bp from 16S rRNA) for taxonomy Murray et al. (1990) Candidatus (L. Candidatus, a candidate to indicate that assignment is provisional) and must include: Sequence (16S rRNA) Identification of morphotype with probes from characteristic sequence Murray & Schleifer (1994) Organisms with less than 97% sequence homology of 16S rRNA will not have more than 60-70% reassociation Stackebrandt & Goebel (1994) Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. (1994)
- 33. Candidatus phytoplasma description Character Description Refrence Morphology Single unit membrane, pleomorphic Doi et al. (1967) Habitat Phloem sieve, gut, haemolymph of sapsucking insects Tsai et al. (1979) Antibiotic sensitivity Tetracycline Ishii et al. (1967) DNA base composition G+C : 23-29% Kollar & Seemuller (1989) Chromosomal Size 530-1350 bp Neimark & Kirkpatrick (1993) Codon usage UGA- stop codon, not for tryptophan Lims & Sears (1991) Sterol in membrane Non sterol requiring Lim et al. (1992) Ribosomal RNA Two rRNA operons & a spacer 16s -23s rRNA genes Kuske & Kirkpatrick (1992) Phytoplasma/Spiroplasma Working Team IRPCM (2000) IJSEM
- 34. Rules: 1. Single, unique 16S rRNA gene sequence (>1200bp) from the ‘reference strain’ 2. A strain- novel Ca. Phytoplasma sp if sequence <97.5% similarity to previously defined Ca. Phytoplasma 3. Even if >97.5% similarity but ecologically separated population: Transmitted by different vectors Have different natural plant host/ different response on same host Significant molecular diversity ( DNA probe hybridization, serology, PCR assay) Phytoplasma/Spiroplasma working team IRPCM (2000)
- 35. 4. No rank of subspecies 5. Description of new species submitted to IJSEM 6. Reference strain should be made available to scientists 7. Abbreviation of Candidatus is Ca. Reference sequence alignment available from TreeBase (accession no. S1048-1788) Phytoplasma/Spiroplasma working team, IRPCM (2000)
- 36. 16S rRNA groups and Ca. Phytoplamas (IRPCM Phytoplasma/spiroplasma Working Team, 2004) Phylogenetic Group Candidatus Phytoplasma sp. Reference Aster yellows (16SrI) Ca. Phytoplasma asteris Lee et al. (2004a) Peanut witches’-broom (16SrII) Ca. Phytoplasma aurantifolia Zreik et al. (1995) X-disease(16SrIII) Ca. Phytoplasma pruni Coconut lethal yellowing (16SrIV) Ca. Phytoplasma palmae Ca. Phytoplasma cocostanzaniae Ca. Phytoplasma castaneae Elm yellows (16SrV) Ca. Phytoplasma ziziphi Ca. Phytoplasma vitis Ca. Phytoplasma ulmi Jung et al. (2003a) Lee et al. (2004b) Clover proliferation (16SrVI) Ca. Phytoplasma trifolii Hiruki & Wang (2004) Ash yellows(16SrVII) Ca. Phytoplasma fraxini Griffith et al. (1999) Firraro et al. (2005) J. Plant pathol.
- 37. Table cont… Phylogenetic Group Candidatus Phytoplasma sp Reference Loofah witches’-broom (16SrVIII) Ca. Phytoplasma luffae Pigeon pea witches’-broom (16SrIX) Ca. Phytoplasma phoenicum Verdin et al. (2003) Apple proliferation (16SrX) Ca. Phytoplasma mali Ca. Phytoplasma pyri Ca. Phytoplasma prunorum Seemuller & Schneider (2004) Rice yellow dwarf (16SrXI) Ca. Phytoplasma oryzae Jung et al. (2003b) Stolbur (16SrXII) Ca. Phytoplasma australiense Ca. Phytoplasma japonicum Davis et al. (1997) Sawayanagi et al. (1999) BGWL (16SrXIV) Ca. Phytoplasma cynodontis Marcone et al. (2004) Hibiscus witches’- broom (XV) Ca. Phytoplasma brabilience Mexican periwinkle virescence (16SrXIII) No name suggested Firraro et al. (2005)Firraro et al. (2005) J. Plant pathol.
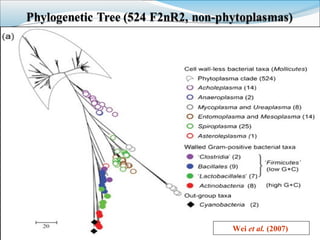
- 38. Phytoplasma 16S rRNA gene sequences retrieved (NCBI) Aligned and trimmed to 1.25 Kb (F2nR2) fragment bounded by two Conserved Nucleotide blocks In-silico restriction enzyme digestion (17 enzymes) Virtual gel plotting (3.0% agrose) Comparison of RFLP pattern and Similarity coefficient Calculation (51 patterns) Wei et al. (2007) IJSEM
- 39. Wei et al. (2007)
- 40. New 16Sr Groups Arabic no - subclades Roman no - Groups Wei et al. (2007)
- 41. Wei et al. (2007)Fig: In silico RFLP
- 42. New 16Sr groups based on 90% threshold of similarity Each strain in new groups F< 0.85 with other Group strains A total of 28 groups and more than 100 subgroups given New groups contains 3 previously defined Ca. Phytoplasma Sp. and 7 Potential sp. to be described Provided feasible method for future extension of classifation Wei et al. (2007)
- 43. Conclusion Phytoplasma are important plant pathogens causing economic losses in number of crop plants and tree species RFLP analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene with restriction enzymes remains a valuable tool for studying phytoplasma diversity and classification Till now the most accepted and stable classification is to describe phytoplasmas in ‘Candidatus phytoplasma species’ rank which combines both molecular (16S rRNA gene sequence) as well as biological, phytopathological properties.