Pointers lesson 5 (double pointer, call by value, call_by_reference)
- 1. Double Pointer Call by Value and Call by reference Pointers taking Multiple References
- 2. Content to be covered • Double Pointer Concept • Call by value • Call by reference • Example program to understand
- 3. Double Pointer Concept • When a pointer start keeping address of another pointer. • This is called either Double Pointer or Pointer to Pointer. • To fetch value from a double pointer we have to use multiple reference by using ** or ***. • To obtain address of a pointer we can use & operator itself.
- 4. Now check the following declarations: int *a, **b, ***c; And normal integer variable int d=10; The assignments a=&d; b=&a; c=&b; In above statements a is pointing to d’s address, b is pointing to a’s address and c is pointing to b’s address. *a gives 10 **b gives 10 ***c gives 10 So a will be called single pointer, b, c is called Double Pointer. 10 1000 2000 3000 1000 2000 3000 4000 d a b c
- 5. Call by Value & Call by Reference • Call by value: This is normal calling mechanism which we have studied in functions in which the value of actual parameters gets copied into formal parameters. • Call by Reference: In this calling mechanism reference (address) of actual parameters are copied to formal parameters which are actually pointers of same data type so that they are capable to keep addresses.
- 6. Difference between Call by Value & Call by Reference • Difference between above two: The major difference between above two is; in call by value, values are copied to local variables therefore whatever changes you are making in them they are temporary till the execution of that function as you come out of function they disappears while in call by reference they remains permanent because addresses are copied to the formal parameters and changes are made to them by using pointers at actual memory location original data gets changed. • Let’s have a program to be clear about call by value and call by reference.
- 7. #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void change1 (int, int); void change2 (int *, int *); void change1 (int a, int b) { a=0; b=0; printf(“%d%d”,a,b); } void change2 ( int *a, int *b) { *a=0; *b=0; printf(“%d%d”,*a, *b); } Changes are performed in memory of a and b of change1() which are treated as local variables so changes are temporary which will disappear as execution of function definition will be over i.e. changes in a and b of this function will not affect the a and b inside main() function. Changes are performed in memory of a and b of change2() which are treated as local variables but they are pointers and changing the values on addresses of a and b of main() function so changes are permanent which will remain in memory even after execution of function definition i.e. changes in a and b of this function will affect the a and b inside main() function.
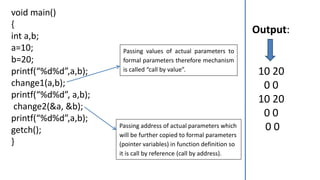
- 8. void main() { int a,b; a=10; b=20; printf(“%d%d”,a,b); change1(a,b); printf(“%d%d”, a,b); change2(&a, &b); printf(“%d%d”,a,b); getch(); } Output: 10 20 0 0 10 20 0 0 0 0 Passing values of actual parameters to formal parameters therefore mechanism is called “call by value”. Passing address of actual parameters which will be further copied to formal parameters (pointer variables) in function definition so it is call by reference (call by address).