Postgre sql 10 table partitioning
- 1. PostgreSQL 10 table partitioning by Marek Hudyma
- 2. Agenda ● What it table partitioning ● Benefits of partitioning ● How to implement it ● Limitations ● Postgres 11 features ● Scanning partitioned tables
- 3. Overview “Table partitioning refers to splitting what is logically one large table into smaller physical pieces.”
- 4. Methods ● Vertical partitioning ● Horizontal partitioning
- 5. Vertical partitioning Involves creating tables with fewer columns and using additional tables to store the remaining columns
- 6. Horizontal partitioning Involves putting different rows into different tables
- 7. Types of horizontal partitioning ● Range partitioning - The table is partitioned into “ranges” defined by a key column or set of columns, with no overlap between the ranges of values assigned to different partitions. For example, one might partition by date ranges or by ranges of identifiers for particular business objects. ● List Partitioning - The table is partitioned by explicitly listing which key values appear in each partition.
- 8. Benefits of partitioning ● Your SQL queries performance can be improved dramatically. ● Bulk loads and deletes can be accomplished by adding or removing partitions. ● Seldom-used data can be migrated to cheaper and slower storage media. ● For frequently-used data you can create sub-partitions.
- 9. PostgreSQL 9 partitioning CREATE FUNCTION transactions_with_partitioning_insert() RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$ DECLARE partition TEXT; BEGIN partition := 'transactions_with_partitioning_' || to_char(NEW.created, 'YYYY_MM'); EXECUTE 'INSERT INTO ' || partition || ' VALUES (($1).*)' USING NEW; RETURN NULL; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
- 10. Implementing partitions in PostgreSQL 10 - master table CREATE TABLE transactions ( sequence BIGINT DEFAULT nextval('global_sequence'::regclass) NOT NULL, created TIMESTAMP WITHOUT TIME ZONE NOT NULL DEFAULT clock_timestamp(), updated TIMESTAMP WITHOUT TIME ZONE NOT NULL DEFAULT clock_timestamp(), account_id UUID NOT NULL, amount NUMERIC NOT NULL ) PARTITION BY RANGE (created);
- 11. Implementing partition tables CREATE TABLE transactions_2015 PARTITION OF transactions FOR VALUES FROM ('2015-01-01 00:00:00') TO ('2016-01-01 00:00:00'); CREATE TABLE transactions_2016 PARTITION OF transactions FOR VALUES FROM ('2016-01-01 00:00:00') TO ('2017-01-01 00:00:00'); CREATE TABLE transactions_2017 PARTITION OF transactions FOR VALUES FROM ('2017-01-01 00:00:00') TO ('2018-01-01 00:00:00'); -- repeat for each partition table ..
- 12. Implementing partitioning Create an index on the key column(s) in each partition. CREATE INDEX ON transactions_2015 (account_id); … Create foreign keys on column(s) in each partition. ALTER TABLE ONLY transactions_2015 ADD CONSTRAINT transactions_2015_account_id_fkey FOREIGN KEY (account_id) REFERENCES accounts(id) ON UPDATE RESTRICT ON DELETE RESTRICT; …. Create triggers in each partition. CREATE TRIGGER set_updated_trigger BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE ON transactions_2015 FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE PROCEDURE public.set_updated();
- 13. Partition Limitation in PostgreSQL 10 ● No global unique constraint ● No global row triggers, indexes ● No global primary and foreign keys ● No auto creation of new partitions ● No update moves rows across partitions ● Not possible to turn a regular table into a partitioned table or vice versa.
- 14. Global Unique constraint problem ● you can create a table that contains only 1 column and unique constraint. (reverted partitioning). ● If there are no concurrency concerns let the application check beforehand for the existence of an entry with the same key before insertion. ● If there are concurrency concerns and there is a guarantee that uniqueness could only be violated within one account (or user), another table that contains all accounts could be used for locking this particular account with SELECT FOR UPDATE
- 15. Useful advices ● Do not go overboard with partitioning, only important tables ● Do it table by table ● Test partitions with integration tests (check if row is in proper partition) ● The popular idea for partitioning is DATETIME and having BIGINT as a primary key. From a theoretical point of view, it is possible that the last row in the older partition will have a higher primary key than the first row in the newer partition. It is a good idea to add an additional constraint on the partition on the primary key when you stop actively write to partition.
- 16. PostgreSQL 11 features PostgreSQL is planned for release in autumn 2018. ● Update Moves Rows Across Partitions ● Unique index on the master table ● Default Partition table ● Partition by Hash CREATE TABLE my_table (some_field text) PARTITION BY HASH (some_field); CREATE TABLE my_table_0 PARTITION OF my_table FOR VALUES WITH (MODULUS 3, REMAINDER 0);
- 17. Alternative solutions ● Sharding ● Sharding + partitioning ● NoSql
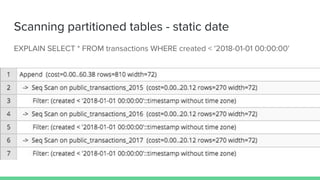
- 18. Scanning partitioned tables - static date EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM transactions WHERE created < '2018-01-01 00:00:00'
- 19. Scanning partitioned tables - now() EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM transactions WHERE created < now();
- 20. Immutable_now() CREATE FUNCTION immutable_now() RETURNS TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE AS $$ SELECT now(); $$ LANGUAGE sql IMMUTABLE;
- 22. immutable_now() with UUID CREATE FUNCTION immutable_now(ignored uuid) RETURNS TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE AS $$ SELECT now(); $$ LANGUAGE sql IMMUTABLE; EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM transactions WHERE created < immutable_now(uuid_generate_v4());
- 24. Summary ● Partitioning in PostgreSQL 10 is a big improvement. ● Partitioning is not trivial. ● PostgreSQL 11 will be another gamechanger.