Programming 8051 with C and using Keil uVision5.pptx
- 1. Embedded C Programming Tutorial with Keil Language M. L. N. Rao, Asst. Prof. in Electronics, St. Joseph’s Degree & PG College and https://www.elprocus.com/embedded-system- programming-using-keil-c-language/
- 2. Embedded System - Definition • An embedded system is an application that contains at least one programmable computer (typically in the form of a microcontroller, a microprocessor or digital signal processor chip) and which is used by individuals who are, in the main, unaware that the system is computer-based.
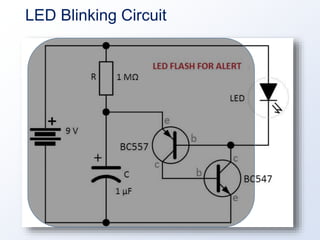
- 4. LED Blinking – Embedded System
- 5. Introduction to Embedded C • Looking around, we find ourselves to be surrounded by various types of embedded systems. Be it a digital camera or a mobile phone or a washing machine, • All of them has some kind of processor functioning inside it. • Associated with each processor is the embedded software. • If hardware forms the body of an embedded system, embedded processor acts as the brain, and embedded software forms its soul. It is the embedded software which primarily governs the functioning of embedded systems.
- 6. Introduction to Embedded C • During infancy years of microprocessor based systems, programs were developed using assemblers and fused into the EPROMs. • There used to be no mechanism to find what the program was doing. LEDs, switches, etc. were used to check correct execution of the program. • Some ‘very fortunate’ developers had In-circuit Simulators (ICEs), but they were too costly and were not quite reliable as well.
- 7. Introduction to Embedded C • As time progressed, use of microprocessor- specific assembly-only as the programming language reduced and embedded systems moved onto C as the embedded programming language of choice. • C is the most widely used programming language for embedded processors/controllers. • Assembly is also used but mainly to implement those portions of the code where very high timing accuracy, code size efficiency, etc. are prime requirements.
- 8. Advantages of C • Use of C in embedded systems is driven by following advantages. • It is small and reasonably simpler to learn, understand, program and debug. C Compilers are available for almost all embedded devices in use today, and there is a large pool of experienced C programmers. • Unlike assembly, C has advantage of processor- independence and is not specific to any particular microprocessor/ microcontroller or any system. This makes it convenient for a user to develop programs that can run on most of the systems.
- 9. Advantages of C • As C combines functionality of assembly language and features of high level languages, C is treated as a ‘middle-level computer language’ or ‘high level assembly language’. C language is fairly efficient and supports access to I/O and provides ease of management of large embedded projects. • Well proven compilers are available for every embedded processor (8-bit to 32-bit). • C x 51 Cross Compiler supports all of the ANSI Standard C directives.
- 10. C Versus Embedded ‘C’
- 11. Compilers Vs Cross Compiler • Compiler is a software tool that converts a source code written in a high level language to machine code. Generally compilers are used for desktop applications. • A cross compiler is a compiler capable of creating executable code for a platform other than the one on which the compiler is run. Cross compiler tools are generally found in use to generate compiles for embedded system
- 12. Embedded C Data Types • There are various type of Data types in C : • • unsigned char • • signed char • • unsigned int • • signed int • • sbit (single bit) • • bit and sfr
- 13. unsigned char • The character data type is the most natural choice. 8051 is an 8-bit microcontroller and unsigned char is also an 8-bit data type in the range of 0 –255 (00 –FFH).C compilers use the signed char as the default data types if we do not put the keyword unsigned char. We always use unsigned char in program until and unless we don’t need to represent signed numbers for example Temperature.
- 14. signed char • The signed char is an 8-bit data type. signed char use the MSB D7 to represent – or +. signed char give us values from –128 to +127.
- 15. unsigned int • • The unsigned int is a 16-bit data type. • • Takes a value in the range of 0 to 65535 (0000 –FFFFH) • • Define 16-bit variables such as memory addresses • • Set counter values of more than 256 • • Since registers and memory accesses are in 8-bit chunks, the misuse of int variables will result in a larger hex file.
- 16. signed int • • Signed int is a 16-bit data type. • • use the MSB D15 to represent –or +. • • We have 15 bits for the magnitude of the number from –32768 to +32767.
- 17. sbit (single bit) • Represents individual bits in SFR for example • User définie sbit x = P1^4 • Defline in header file • sbit RD = P3^7; • sbit WR = P3^6; • sbit T1 = P3^5; • sbit T0 = P3^4;
- 18. bit • The bit data type allows access to single bits of bit-addressable memory spaces 20 –2FH
- 19. sfr • Defined in header file reg51.h • /* BYTE Registers */ • sfr P0 = 0x80; • sfr P1 = 0x90; • sfr P2 = 0xA0; • sfr P3 = 0xB0; • sfr PSW = 0xD0; • sfr ACC = 0xE0; • sfr B = 0xF0; • sfr SP = 0x81; • sfr DPL = 0x82; • sfr DPH = 0x83; • sfr PCON = 0x87;
- 20. Using Keil uVision 4 • 1. Download and Install Keil uVision4 • 2. Open Keil uVision • 3. Create a new Project : Project >> Create µVision Project • 4. Browse for the location • 5. Select the microcontroller Atmel>>AT89C51/Generic 8051 • 6. Don’t Add The 8051 start up code • 7. File>>New • 8. Adding Hex file to the output • Right click on Target1>>options for target “target 1” • In the Output Tab check the “Create HEX file” • To change the operating frequency go to Target tab on the window obtained by right clicking on Target1>>options for target “target 1”
- 21. Write an 8051 C program to send values 00 – FF to port P1. #include <reg51.h> void main( ) { unsigned char z; for (z = 0; z <= 255; z++) P1=z; }
- 22. Write an 8051 C program to send max number out of 5 to P1. #include<reg51.h> void main() { char a1 = 0x51; char a2 = 0x34; char a3 = 0xa7; char a4 = 0x7f; char a5 = 0x65; char max = 0; if (max < a1) max = a1; if (max < a2) max = a2; if (max < a3) max = a3; if (max < a4) max = a4; if (max < a5) max = a5; P1 = max; }