Project Manifold (Forwarding and Delegation)
- 1. Yann-Gaël Guéhéneuc (/jan/, he/il) Work licensed under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 International Project Manifold (Forwarding and Delegation) yann-gael.gueheneuc@concordia.ca Version 0.2 2024/10/09
- 2. 2/55 Fragile Base Class Problem Joshua Bloch ; Effective Java ; Prentice Hall, 2nd edition (May 28, 2008)
- 4. 4/55 Requirements – Need Implement a Set that counts the number of added elements, which is different from the current number of elements, e.g., for performance tuning
- 5. 5/55 Requirements – Client Code public class Main { public static void main(final String[] args) { final CountingHashSet<String> s = new CountingHashSet<String>(); s.addAll(Arrays.asList("Rick Deckard", "Roy Batty", "Pris Stratton", "Zhora Salome", "Leon Kowalski", "Rachael")); s.remove("Leon Kowalski"); s.remove("Zhora Salome"); s.remove("Pris Stratton"); s.remove("Roy Batty"); s.add("Tyrell"); System.out.print("Was expected 7, got "); System.out.println(s.getAddCount()); } }
- 6. 6/55 Requirements – Client Code 7? 13? public class Main { public static void main(final String[] args) { final CountingHashSet<String> s = new CountingHashSet<String>(); s.addAll(Arrays.asList("Rick Deckard", "Roy Batty", "Pris Stratton", "Zhora Salome", "Leon Kowalski", "Rachael")); s.remove("Leon Kowalski"); s.remove("Zhora Salome"); s.remove("Pris Stratton"); s.remove("Roy Batty"); s.add("Tyrell"); System.out.print("Was expected 7, got "); System.out.println(s.getAddCount()); } }
- 7. 7/55 Given – Set Interface public interface Set extends Collection { int size(); boolean isEmpty(); boolean contains(Object o); Iterator iterator(); Object[] toArray(); Object[] toArray(Object a[]); boolean add(Object o); boolean remove(Object o); boolean containsAll(Collection c); boolean addAll(Collection c); boolean retainAll(Collection c); boolean removeAll(Collection c); void clear(); boolean equals(Object o); int hashCode(); }
- 8. 8/55 Given – HashSet Implementation public class HashSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { private transient HashMap<E,Object> map; public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); } public Iterator<E> iterator() { return map.keySet().iterator(); } public int size() { return map.size(); } ...
- 9. 9/55 Solution Straightforward solution – Reuse of code – Subtyping
- 10. 10/55 Solution – First Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> extends HashSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { ? @Override public boolean add(final E e) { ? ? } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { ? ? } @Override public int getAddCount() { ? } }
- 11. 11/55 Solution – First Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> extends HashSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { private int addCount = 0; @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return super.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return super.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } }
- 12. 12/55 Solution – First Implementation Broken!
- 13. 13/55 Solution – First Implementation Broken! – Method addAll() calls add(), which implies that added elements will be counted twice!
- 14. 14/55 Solution – First Implementation Broken! – Method addAll() calls add(), which implies that added elements will be counted twice! – You could NOT know that, without either reading the source code of HashSet or testing your implementation of CountingHashSet
- 15. 15/55 Solution – First Implementation Broken! – Method addAll() calls add(), which implies that added elements will be counted twice! – You could NOT know that, without either reading the source code of HashSet or testing your implementation of CountingHashSet – What if you did NOT have access to the source code of HashSet?
- 16. 16/55 Fragile Base Class Problem The provider cannot determine whether a change to a base class is safe for users by examining in isolation the methods of the base class The user cannot determine whether extending the base class is safe by reading the API of the base class – Must study its implementation
- 17. 17/55 Solution – Second Implementation Problem: fragile base class problem Solution: favour composition over inheritance
- 18. 18/55 Solution – Second Implementation Favour composition over inheritance – Allow changing implementation – Allow safe inheritance Problem: fragile base class problem Solution: favour composition over inheritance
- 19. 19/55 Solution – Second Implementation Favour composition over inheritance – Allow changing implementation – Allow safe inheritance Add one level of indirection – A ForwardingSet delegates to HashSet – Composite delegates to component – CountingHashSet extends ForwardingSet Problem: fragile base class problem Solution: favour composition over inheritance
- 20. 20/55 Add one level of indirection – ForwardingSet delegates to HashSet • Composite delegates to component – CountingHashSet extends ForwardingSet Solution – Second Implementation
- 21. 21/55 Solution – Second Implementation public class ForwardingSet<E> implements Set<E> { private final Set<E> s = new HashSet<E>(); public void clear() { s.clear(); } public boolean contains(final Object o) { return s.contains(o); } public boolean isEmpty() { return s.isEmpty(); } public int size() { return s.size(); } public Iterator<E> iterator() { return s.iterator(); } public boolean add(final E e) { return s.add(e); } public boolean remove(final Object o) { return s.remove(o); } public boolean containsAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.containsAll(c); } public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { return s.addAll(c); } public boolean removeAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.removeAll(c); } public boolean retainAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.retainAll(c); } public Object[] toArray() { return s.toArray(); } public <T> T[] toArray(final T[] a) { return s.toArray(a); } public boolean equals(final Object o) { return s.equals(o); } public int hashCode() { return s.hashCode(); } public String toString() { return s.toString(); } }
- 22. 22/55 Solution – Second Implementation Typical delegations public class ForwardingSet<E> implements Set<E> { private final Set<E> s = new HashSet<E>(); public void clear() { s.clear(); } public boolean contains(final Object o) { return s.contains(o); } public boolean isEmpty() { return s.isEmpty(); } public int size() { return s.size(); } public Iterator<E> iterator() { return s.iterator(); } public boolean add(final E e) { return s.add(e); } public boolean remove(final Object o) { return s.remove(o); } public boolean containsAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.containsAll(c); } public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { return s.addAll(c); } public boolean removeAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.removeAll(c); } public boolean retainAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.retainAll(c); } public Object[] toArray() { return s.toArray(); } public <T> T[] toArray(final T[] a) { return s.toArray(a); } public boolean equals(final Object o) { return s.equals(o); } public int hashCode() { return s.hashCode(); } public String toString() { return s.toString(); } }
- 23. 23/55 Solution – Second Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> extends ForwardingSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { private int addCount = 0; @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return super.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return super.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } }
- 24. 24/55 Solution – Second Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> extends ForwardingSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { private int addCount = 0; @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return super.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return super.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } } Same as first solution but for this
- 25. 25/55 Solution – Second Implementation Forwarding involves two distinct objects – Not one object and its superclass this refers alternatively – To the instance of CountingHashSet – To the (unrelated) instance of HashSet
- 26. 26/55 Solution – Third Implementation Project Manifold – “Manifold is a Java compiler plugin, its features include Metaprogramming, Properties, Extension Methods, Operator Overloading, Templates, a Preprocessor, and more.” – https://github.com/manifold-systems
- 27. 27/55 Solution – Third Implementation Manifold Delegation – “The manifold-delegation project is a compiler plugin that provides language support for call forwarding and true delegation. These features are an experimental effort toward interface composition as a practical alternative to implementation inheritance.” – https://github.com/manifold-systems/manifold/ tree/master/manifold-deps-parent/manifold- delegation
- 28. 28/55 Solution – Third Implementation Manifold Delegation – “The manifold-delegation project is a compiler plugin that provides language support for call forwarding and true delegation. These features are an experimental effort toward interface composition as a practical alternative to implementation inheritance.” – https://github.com/manifold-systems/manifold/ tree/master/manifold-deps-parent/manifold- delegation
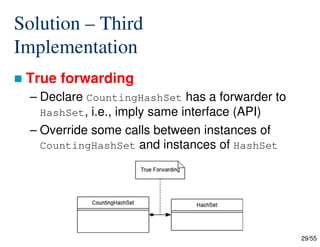
- 29. 29/55 Solution – Third Implementation True forwarding – Declare CountingHashSet has a forwarder to HashSet, i.e., imply same interface (API) – Override some calls between instances of CountingHashSet and instances of HashSet
- 30. 30/55 Solution – Third Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { @link HashSet<E> s; private int addCount = 0; public CountingHashSet() { this.s = new HashSet<E>(); } @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return this.s.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return this.s.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } }
- 31. 31/55 Solution – Third Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { @link HashSet<E> s; private int addCount = 0; public CountingHashSet() { this.s = new HashSet<E>(); } @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return this.s.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return this.s.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } } CountingHashSet is a Set through CountingSet
- 32. 32/55 Solution – Third Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { @link HashSet<E> s; private int addCount = 0; public CountingHashSet() { this.s = new HashSet<E>(); } @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return this.s.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return this.s.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } } CountingHashSet is a Set through CountingSet Forwards most calls on one HashSet
- 33. 33/55 Solution – Third Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { @link HashSet<E> s; private int addCount = 0; public CountingHashSet() { this.s = new HashSet<E>(); } @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return this.s.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return this.s.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } } CountingHashSet is a Set through CountingSet Forwards most calls on one HashSet Overrides safely some methods
- 34. 34/55 Solution – Third Implementation public class CountingHashSet<E> implements CountingSet<E> { @link HashSet<E> s; private int addCount = 0; public CountingHashSet() { this.s = new HashSet<E>(); } @Override public boolean add(final E e) { this.addCount++; return this.s.add(e); } @Override public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { this.addCount += c.size(); return this.s.addAll(c); } @Override public int getAddCount() { return this.addCount; } }
- 40. 40/55 Other Problem Constructor of inheritable class must never call overridable method, why? public class SuperClass { public SuperClass() { this.overrideMe(); } public void overrideMe() { // Some behaviour... } }
- 41. 41/55 Other Problem Constructor of inheritable class must never call overridable method, why? public class SuperClass { public SuperClass() { this.overrideMe(); } public void overrideMe() { // Some behaviour... } } The constructor calls an overridable method
- 42. 42/55 Other Problem – What Happens? public class SubClass extends SuperClass { private final Date date; public SubClass() { this.date = new Date(); } @Override public void overrideMe() { System.out.println(this.date.toString()); } }
- 43. 43/55 Other Problem – What Happens? NullPointerException public class SubClass extends SuperClass { private final Date date; public SubClass() { this.date = new Date(); } @Override public void overrideMe() { System.out.println(this.date.toString()); } }
- 44. 44/55 Other Problem – Second Implementation Constructor of inheritable class must never call overridable method! public class SafeSuperClass { public SafeSuperClass() { this.cannotOverrideMe(); } public final void cannotOverrideMe() { // Some behaviour... } }
- 46. 46/55 Forwarding and Delegation “Real-world” example – 12 interfaces – 5 abstract classes – 21 concrete classes – Max. depth of inheritance tree, 5
- 47. 47/55 Forwarding and Delegation @org.junit.jupiter.api.Test void testUnexpectedCallToOverridingMethod() { final IVertebrate nyx = new Cat(); Assertions.assertEquals(1, nyx.getNumberOfFightMechanisms()); nyx.addFightingMechanisms( Arrays.asList(new FightMechanismHissing(), new FightMechanismTeeth())); System.out.println( "nWARNING: All the tests should pass, but this test actually shows the erroneous behaviour!n"); Assertions.assertEquals(5, nyx.getNumberOfFightMechanisms(), "Received 5 but expected 3, because the method IVertebrate.addFightingMechanism() is called by IVertebrate.addFightingMechanisms()"); } @org.junit.jupiter.api.Test void testUnexpectedMissingCallToOverridingMethod() { final IBird echidna1 = new Echidna1(); Assertions.assertEquals(20, echidna1.layEgg()); final IBird echidna2 = new Echidna2(); System.out.println( "nWARNING: All the tests should pass, but this test actually shows the erroneous behaviour!n"); Assertions.assertEquals(50, echidna2.layEgg(), "Received 50 but expected 20, because the method Echidna2.getEggSize() is NOT called by AbstractBird.layEgg()"); }
- 48. 48/55 Forwarding and Delegation @org.junit.jupiter.api.Test void testUnexpectedCallToOverridingMethod() { final IVertebrate nyx = new Cat(); Assertions.assertEquals(1, nyx.getNumberOfFightMechanisms()); nyx.addFightingMechanisms( Arrays.asList(new FightMechanismHissing(), new FightMechanismTeeth())); System.out.println( "nWARNING: All the tests should pass, but this test actually shows the erroneous behaviour!n"); Assertions.assertEquals(5, nyx.getNumberOfFightMechanisms(), "Received 5 but expected 3, because the method IVertebrate.addFightingMechanism() is called by IVertebrate.addFightingMechanisms()"); } @org.junit.jupiter.api.Test void testUnexpectedMissingCallToOverridingMethod() { final IBird echidna1 = new Echidna1(); Assertions.assertEquals(20, echidna1.layEgg()); final IBird echidna2 = new Echidna2(); System.out.println( "nWARNING: All the tests should pass, but this test actually shows the erroneous behaviour!n"); Assertions.assertEquals(50, echidna2.layEgg(), "Received 50 but expected 20, because the method Echidna2.getEggSize() is NOT called by AbstractBird.layEgg()"); } Broken Forwarding
- 49. 49/55 Forwarding and Delegation @org.junit.jupiter.api.Test void testUnexpectedCallToOverridingMethod() { final IVertebrate nyx = new Cat(); Assertions.assertEquals(1, nyx.getNumberOfFightMechanisms()); nyx.addFightingMechanisms( Arrays.asList(new FightMechanismHissing(), new FightMechanismTeeth())); System.out.println( "nWARNING: All the tests should pass, but this test actually shows the erroneous behaviour!n"); Assertions.assertEquals(5, nyx.getNumberOfFightMechanisms(), "Received 5 but expected 3, because the method IVertebrate.addFightingMechanism() is called by IVertebrate.addFightingMechanisms()"); } @org.junit.jupiter.api.Test void testUnexpectedMissingCallToOverridingMethod() { final IBird echidna1 = new Echidna1(); Assertions.assertEquals(20, echidna1.layEgg()); final IBird echidna2 = new Echidna2(); System.out.println( "nWARNING: All the tests should pass, but this test actually shows the erroneous behaviour!n"); Assertions.assertEquals(50, echidna2.layEgg(), "Received 50 but expected 20, because the method Echidna2.getEggSize() is NOT called by AbstractBird.layEgg()"); } Broken Forwarding Broken Delegation
- 50. 50/55 Forwarding and Delegation As of 24/10/01, project Manifold comes with some constraints on declared types – Class AbstractBird must implement IBird – Must use AbstractBird instead of Mallard public class Echidna2 extends AbstractMammal implements IBird, IMammal { // For Manifold: must be "AbstractBird // birdTraits", not "Mallard birdTraits" @link AbstractBird birdTraits = new Mallard();
- 51. 51/55 CONCLUSION
- 52. 52/55 Conclusion Polymorphism is a fundamental concept of object-oriented programming, but it is not without problem Adding one level of indirection solves the problem – Encapsulation – Delegation Information hiding
- 53. 53/55 Conclusion Encapsulation and delegation Typing and reflection Can be used to prevent problem and make programs more flexible! Do not require unnecessary, boring, and error-prone boilerplate code ( Manifold)
- 54. 54/55 Food For Thoughts HashSet does not allow duplicate keys so it could be that super.addAll(c) add less elements because of some duplicated keys and, therefore, that this.addCount() reports more than the really added elements If we wanted this.addCount() to be also equal to size...





![5/55
Requirements – Client Code
public class Main {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final CountingHashSet<String> s = new CountingHashSet<String>();
s.addAll(Arrays.asList("Rick Deckard", "Roy Batty", "Pris Stratton",
"Zhora Salome", "Leon Kowalski", "Rachael"));
s.remove("Leon Kowalski");
s.remove("Zhora Salome");
s.remove("Pris Stratton");
s.remove("Roy Batty");
s.add("Tyrell");
System.out.print("Was expected 7, got ");
System.out.println(s.getAddCount());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanifoldforwardinganddelegationsplitted-241011022123-7fdf199b/85/Project-Manifold-Forwarding-and-Delegation-5-320.jpg)
![6/55
Requirements – Client Code
7? 13?
public class Main {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final CountingHashSet<String> s = new CountingHashSet<String>();
s.addAll(Arrays.asList("Rick Deckard", "Roy Batty", "Pris Stratton",
"Zhora Salome", "Leon Kowalski", "Rachael"));
s.remove("Leon Kowalski");
s.remove("Zhora Salome");
s.remove("Pris Stratton");
s.remove("Roy Batty");
s.add("Tyrell");
System.out.print("Was expected 7, got ");
System.out.println(s.getAddCount());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanifoldforwardinganddelegationsplitted-241011022123-7fdf199b/85/Project-Manifold-Forwarding-and-Delegation-6-320.jpg)
![7/55
Given – Set Interface
public interface Set extends Collection {
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator iterator();
Object[] toArray();
Object[] toArray(Object a[]);
boolean add(Object o);
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean containsAll(Collection c);
boolean addAll(Collection c);
boolean retainAll(Collection c);
boolean removeAll(Collection c);
void clear();
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanifoldforwardinganddelegationsplitted-241011022123-7fdf199b/85/Project-Manifold-Forwarding-and-Delegation-7-320.jpg)













![21/55
Solution – Second
Implementation
public class ForwardingSet<E> implements Set<E> {
private final Set<E> s = new HashSet<E>();
public void clear() { s.clear(); }
public boolean contains(final Object o) { return s.contains(o); }
public boolean isEmpty() { return s.isEmpty(); }
public int size() { return s.size(); }
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return s.iterator(); }
public boolean add(final E e) { return s.add(e); }
public boolean remove(final Object o) { return s.remove(o); }
public boolean containsAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.containsAll(c); }
public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { return s.addAll(c); }
public boolean removeAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.removeAll(c); }
public boolean retainAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.retainAll(c); }
public Object[] toArray() { return s.toArray(); }
public <T> T[] toArray(final T[] a) { return s.toArray(a); }
public boolean equals(final Object o) { return s.equals(o); }
public int hashCode() { return s.hashCode(); }
public String toString() { return s.toString(); }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanifoldforwardinganddelegationsplitted-241011022123-7fdf199b/85/Project-Manifold-Forwarding-and-Delegation-21-320.jpg)
![22/55
Solution – Second
Implementation
Typical delegations
public class ForwardingSet<E> implements Set<E> {
private final Set<E> s = new HashSet<E>();
public void clear() { s.clear(); }
public boolean contains(final Object o) { return s.contains(o); }
public boolean isEmpty() { return s.isEmpty(); }
public int size() { return s.size(); }
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return s.iterator(); }
public boolean add(final E e) { return s.add(e); }
public boolean remove(final Object o) { return s.remove(o); }
public boolean containsAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.containsAll(c); }
public boolean addAll(final Collection<? extends E> c) { return s.addAll(c); }
public boolean removeAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.removeAll(c); }
public boolean retainAll(final Collection<?> c) { return s.retainAll(c); }
public Object[] toArray() { return s.toArray(); }
public <T> T[] toArray(final T[] a) { return s.toArray(a); }
public boolean equals(final Object o) { return s.equals(o); }
public int hashCode() { return s.hashCode(); }
public String toString() { return s.toString(); }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanifoldforwardinganddelegationsplitted-241011022123-7fdf199b/85/Project-Manifold-Forwarding-and-Delegation-22-320.jpg)