Python Basics
- 1. BASICS ON PYTHON PROGRAMMING PROF. POOJA B S
- 2. About the Course Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics. Python is simple, easy to learn syntax emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. Python supports modules and packages, which encourages program modularity and code reuse Course Objectives Learn Syntax and Semantics and create Functions in Python. Handle Strings and Files in Python. Understand Lists, Dictionaries and Regular expressions in Python. Implement Object Oriented Programming concepts in Python Introduction to Network Programming in Python Course Outcomes Explain basic principles of Python programming language Interpret the fundamentals of Python and usage of various support libraries Problem Solving and Programming Capability To learn how to design and program Python applications
- 3. Introduction to Python: Basics of Python, Variables, Expressions, Statements Guido Van Rossum in 1991 Open Source General purpose programming language. Applications: GUI Applications Website Applications Mobile Applications Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Algorithms
- 4. Where Python is Used? Google Netflix Dropbox National Security Agency (USA) BitTorrent NASA Python Development Environments PyDev on Eclipse Notepad++ Komodo IDE PC (PyCharm) Bluefish Vim LiClipse IDLE (Integrated Development and Learning Environment)
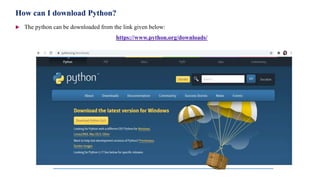
- 5. How can I download Python? The python can be downloaded from the link given below: https://www.python.org/downloads/
- 6. Basics of Python Programming >>> Chevron Comments in Python: # ‘’’……………..’’’ or “””……………””” Interactive Mode and Scripting Mode Keyboard Interrupt: Ctrl+c Quit the program: quit() Interpreter v/s Compiler Types of Errors in a Program: Syntax Errors Logical Errors Semantic Errors
- 7. Simple Programs 1. print(“Hello! Welcome to Python World”) # Hello! Welcome to Python World 2. print(Hello) #Error 3. print(‘Hello’) # Hello 4. print(‘’‘Hello’’’) # Hello 5. X=10 #30 Y=20 print(x+y) 6. num1 = 1.5 #The sum of 1.5 and 6.3 is 7.8 num2 = 6.3 sum = num1 + num2 print('The sum of {0} and {1} is {2}'.format(num1, num2, sum))
- 8. Variables Variable is a named literal to store a value. Need not be declared before usage in python Use “=” to assign value Rules for naming a variable: Variable name should not be a keyword Should not start with a number or special character Can only contain special characters “_” Eg: 1. 3a=5 #invalid 2. A$=10 #valid 3. if=15 #invalid
- 9. Values and Types The type of a value can be checked using “type” function Eg: 1. type(‘Hello’) 2. type(3) 3. type(100.4) 4. type(2/3) 5. type(325%6) 6. type(2==3) 7. type(‘500’) 8. type(“500”) 9. x=10 y=‘Hi’ print(x) print(y) type(x) type(y)
- 10. Operators and Operands Arithmetic Operators: Relational or Comparison Operators: + Addition [a+b] - Subtraction [a-b] * Multiplication [a*b] / Quotient [a/b] eg: 5/3=1.66667 % Remainder [a%b] eg: 5%3=2 // Floor Division [a//b] eg: 5//3=1 ** Exponent [a**b] is equal to a^b eg: 2**3=2^3=8 < Less Than [a<b] > Greater Than [a>b] == Comparison [a==b]
- 11. Bitwise Operators Assignment Operators Used to assign values to variables Compound Assignment Operator is: =+ Eg: x=3 y=5 x+=y #Same as x=x+y print(x) #8 & AND | OR ~ NOT ^ XOR >> Right Shift << Left Shift
- 12. Assign different types to variables in a single statement Eg: x, y, str = 3, 4.2, “Hello” print(“x=”,x, “y=”,y,”str=”,str) #x=3 y=4.2 str=Hello Expressions Combination of values, variables and operators is known as an expression. Eg: x=5 y=x+10 z=x+y-3
- 13. Order of Operations Evaluation of Expressions follows on PEMDAS rule P Parenthesis () E Exponent ** M Multiplication * D Division / and % A Addition + S Subtraction - Eg: print(2**3) #8 print(2**3**2) #512 print(5*2/4) #2.5 print(5/4*2) #2.5
- 14. String Operations Use + operator for string concatenation Eg: x=“32” y=“40” print(x+y) #3240 User Input Built in function: input() Eg: 1] str1= input() print(“Entered String is:”, str1) #Entered String is Hello Python! 2] x= input(“Enter a number”) type(x) #<class 'str'> 3] x= int(input(“Enter a number”)) type(x) #<class ‘int'>









![Operators and Operands
Arithmetic Operators:
Relational or Comparison Operators:
+ Addition [a+b]
- Subtraction [a-b]
* Multiplication [a*b]
/ Quotient [a/b] eg: 5/3=1.66667
% Remainder [a%b] eg: 5%3=2
// Floor Division [a//b] eg: 5//3=1
** Exponent [a**b] is equal to a^b eg: 2**3=2^3=8
< Less Than [a<b]
> Greater Than [a>b]
== Comparison [a==b]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbasics-200813063818/85/Python-Basics-10-320.jpg)



![ String Operations
Use + operator for string concatenation
Eg: x=“32”
y=“40”
print(x+y) #3240
User Input
Built in function: input()
Eg: 1] str1= input()
print(“Entered String is:”, str1) #Entered String is Hello Python!
2] x= input(“Enter a number”)
type(x) #<class 'str'>
3] x= int(input(“Enter a number”))
type(x) #<class ‘int'>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbasics-200813063818/85/Python-Basics-14-320.jpg)