Python Modules, executing modules as script.pptx
- 1. OUTLINE Module More on Modules Executing Modules as script dir() function
- 2. Module • A module is a file containing Python definitions and statements. • The file name is the module name with the suffix .py appended. • Within a module, the module’s name (as a string) is available as the value of the global variable __name__. • For instance, use your favorite text editor to create a file called fibo.py in the current directory with the following contents:
- 3. Module
- 4. Module Now enter the Python interpreter and import this module with the following command: >>>import fibo • This does not add the names of the functions defined in fibo directly to the current namespace (see Python Scopes and Namespaces for more details); • it only adds the module name fibo there. Using the module name you can access the functions:
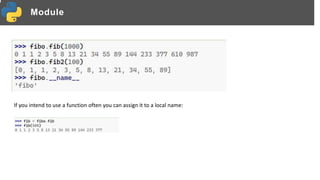
- 5. Module If you intend to use a function often you can assign it to a local name:
- 6. More on Module • A module can contain executable statements as well as function definitions. • These statements are intended to initialize the module. • They are executed only the first time the module name is encountered in an import statement. • Each module has its own private namespace, which is used as the global namespace by all function s defined in the module. • Thus, the author of a module can use global variables in the module without worrying about accidental clashes with a user’s global variables.
- 7. Module Modules can import other modules. It is customary but not required to place all import statements at the beginning of a module (or script, for that matter). The imported module names, if placed at the top level of a module (outside any functions or classes), are added to the module’s global namespace.
- 8. Module
- 9. Module This imports all names except those beginning with an underscore (_). In most cases Python programmers do not use this facility since it introduces an unknown set of names into the interpreter, possibly hiding some things you have already defined. Note that in general the practice of importing * from a module or package is frowned upon, since it often causes poorly readable code. However, it is okay to use it to save typing in interactive sessions.
- 11. Executing modules as scripts This is often used either to provide a convenient user interface to a module, or for testing purposes (running the module as a script executes a test suite).
- 12. The Module Search Path
- 14. Standard Modules Python comes with a library of standard modules, described in a separate document, the Python Library Reference (“Library Reference” hereafter). Some modules are built into the interpreter; these provide access to operations that are not part of the core of the language but are nevertheless built in, either for efficiency or to provide access to operating system primitives such as system calls.
- 15. The dir() Function The built-in function dir() is used to find out which names a module defines. It returns a sorted list of strings:
- 18. Examples # importing sqrt() and factorial from the # module math from math import * # if we simply do "import math", then # math.sqrt(16) and math.factorial() # are required. print(sqrt(16)) print(factorial(6))
- 19. Examples # importing built-in module math import math # using square root(sqrt) function contained # in math module print(math.sqrt(25)) # using pi function contained in math module print(math.pi) # 2 radians = 114.59 degrees print(math.degrees(2)) # 60 degrees = 1.04 radians print(math.radians(60)) # Sine of 2 radians print(math.sin(2))
- 20. Examples # Cosine of 0.5 radians print(math.cos(0.5)) # Tangent of 0.23 radians print(math.tan(0.23)) # 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 = 24 print(math.factorial(4)) # importing built in module random import random # printing random integer between 0 and 5 print(random.randint(0, 5)) # print random floating point number between 0 and 1 print(random.random())
- 21. Examples # random number between 0 and 100 print(random.random() * 100) List = [1, 4, True, 800, "python", 27, "hello"] # using choice function in random module for choosing # a random element from a set such as a list print(random.choice(List)) # importing built in module datetime import datetime from datetime import date import time # Returns the number of seconds since the # Unix Epoch, January 1st 1970 print(time.time())
- 22. Examples # Converts a number of seconds to a date object print(date.fromtimestamp(454554)) Output: 5.0 3.14159265359 114.591559026 1.0471975512 0.909297426826 0.87758256189 0.234143362351 24 3 0.401533172951 88.4917616788 True 1461425771.87
- 23. Problems 1. Write a Python program to select a random element from a list, set, dictionary-value, and file from a directory. Use random.choice() 2. Write a Python program to shuffle the elements of a given list. Use random.shuffle()



















![Examples
# random number between 0 and 100
print(random.random() * 100)
List = [1, 4, True, 800, "python", 27, "hello"]
# using choice function in random module for choosing
# a random element from a set such as a list
print(random.choice(List))
# importing built in module datetime
import datetime
from datetime import date
import time
# Returns the number of seconds since the
# Unix Epoch, January 1st 1970
print(time.time())](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4modules-240302152011-3bd12a42/85/Python-Modules-executing-modules-as-script-pptx-21-320.jpg)

