Python_presentation_data_science_lecture.pptx
- 1. Python for Beginners: Use GenAI to help you -Colab AI- Kai-Yuan, Hsiao
- 2. Python IDE Python shell Atom Visual Studio Code Sublime Jupyter Notepad++ Spyder PyCharm Google Colab Cursor
- 3. Colab • Prerequisites : We assume you are already have a google account • How to open google colab? • Just search “colab”
- 4. Colab Someone will see this screen Someone will see this screen Different from login the google account
- 5. • Where is this colab file? • In your google drive Colab
- 6. • Another way to open colab Colab
- 7. • Connect / Changing Runtime • Every time you open the colab file, you should connect the server first. Click! Getting Started
- 8. • Connect / Changing Runtime • If you want to use “GPU”, click on “Runtime” > “Change Runtime Type” and select “GPU”for “Hardware Accelerator” Getting Started
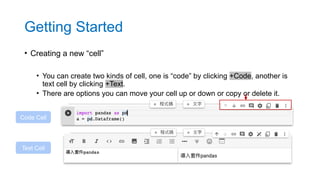
- 9. • Creating a new “cell” • You can create two kinds of cell, one is “code” by clicking +Code, another is text cell by clicking +Text. • There are options you can move your cell up or down or copy or delete it. Code Cell Text Cell Getting Started
- 10. • You can type python code in code cell, or use “!”to change the code cell to treating the input as a shell script to install python module or do something. Python shell script shell script Other magic commands are listed here Getting Started
- 11. • Click on the play button to execute a specific cell • Other options to run the code Executing Code Block
- 12. • File Folder • Click the folder icon on the screen- left to view your current files. • If the files are not immediately shown, click the refresh button. • Note!!! Files are temporarily stored, and it will be removed once you end your session. Folder icon refresh File Manipulation
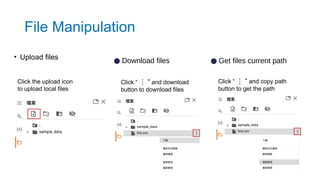
- 13. • Upload files Click the upload icon to upload local files ● Download files ● Get files current path Click “ ” ⋮ and download button to download files Click “ ” ⋮ and copy path button to get the path File Manipulation
- 14. • Mounting Google Drive • Click on the Google drive icon and allow the connect message File Manipulation
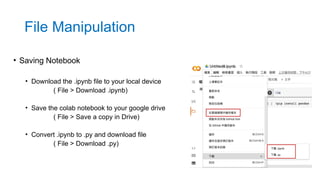
- 15. • Saving Notebook • Download the .ipynb file to your local device ( File > Download .ipynb) • Save the colab notebook to your google drive ( File > Save a copy in Drive) • Convert .ipynb to .py and download file ( File > Download .py) File Manipulation
- 16. • If user does not interact with his Google Colab notebook for more than 90 minutes, its instance is automatically terminated. • GPU usage is not unlimited. (the max gpu usage 12 hrs) Colab Limit
- 17. Colab AI
- 18. Colab AI
- 19. Python for Beginners: Use GenAI to help you -Basic Concept- Kai-Yuan, Hsiao
- 20. Your first program 使用 Colab AI 修改程式碼,使 python 對「你」打 招呼 Practice
- 21. Your first program 使用 Colab AI 修改程式碼,使 python 對「小白」打招 呼 Practice Colab AI 會讀取前 面 的 資 訊 , 包 括 Markdown 註解 # 後面的字是註解
- 22. Colab AI is a helper
- 23. Colab AI is a helper
- 24. Strings • Show the output – “print()” You need to use quotation(“ ”) for strings You can use + to connect strings You can use * to repeat strings
- 25. Python as a calculator • Just try it! Click play button or try shift+enter 運算子 功能 範例 + 加 a + b - 減 a - b * 乘 a * b ** 指數 a ** b / 除 a / b // 整數除法 a // b % 取餘數 a % b
- 26. Assign • a = b means b (object) has been assigned to a (variable) 運算子 功能 範例 = 指派 a = b += 相加同時指派 a += b -= 相減同時指派 a -= b *= 相乘同時指派 a *= b **= 取指數同時指派 a **= b /= 相除同時指派 a /= b /= 整數相除同時指派 a //= b %= 取餘數同時指派 a %= b You don’t need to use quotation(“ ”) for variable
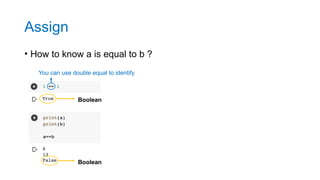
- 27. Assign • How to know a is equal to b ? You can use double equal to identify Boolean Boolean
- 28. Variable String Data Types -string Numeric Data Types -int -float -boolean Containers Data Types -list -tuple -set -dict
- 29. 整數 數字以十進位的 (decimal) 整數型態 (integral type) 的字面常數 1235 ; 99999 ; 33 (Slide Credit : Santy) Variable Type
- 30. (Slide Credit : Santy) 浮點數 帶小數點的數字都為浮點數型態 (floating-point type) 的字面常數 12.35 ; 99.999 ; 3.3 ; 1.125e-1 ; 3.521e4 Variable Type
- 31. (Slide Credit : Santy) 布林值 表達正確( True )或是錯誤( False )以及空變數 null Variable Type
- 32. • Numeric Data Types You can use type to check variable type Variable Type
- 33. (Slide Credit : Santy) 字串 以單引號或雙引號為起來的 Unicode 字元都是字串字面常 數 例如:” 1235” ; ”Hello World” Variable Type
- 34. • String Data Types Variable Type
- 35. (Slide Credit : Santy) 串列 串列( List )可變資料型態,有順序的資料集合 Variable Type
- 36. (Slide Credit : Santy) 序對 Tuple 不可變資料型態,有順序的資料集合 序列型態 (sequence type) 的索引符號,或用作定義串列 (list) Variable Type
- 37. (Slide Credit : Santy) 集合 Set 無順序的資料集合 Variable Type
- 38. (Slide Credit : Santy) 字典 鍵值對( Key-Value Pair )的集合 Variable Type
- 39. • Container Data Types You can use [ ] to define list You can use ( ) to define tuple You can use { } to define set You can use { } and call the key to define dict Variable Type
- 40. • Another story to explain variable and data types CUP_A = 30 (整數) CUP_B = 30.5 (浮點 數) CUP_C = " 杯子 " (字串) (Slide Credit : Santy) Variable Type
- 41. 補充資料 (Slide Credit : Santy) 識別字: Python 識別符號是函式、變數、類等的名稱 1.識別符號可以包含字母(大寫或小寫),數字( 0-9 )或下劃線( _ ) 例如: last_name1 , my_first_name 和 CapName 是合法識別符號。 2.識別符號不能以數字來開頭 例如, 1last_name 是非法識別符號。 3.關鍵字不允許作為為識別符號的名稱。 4.識別符號中不允許使用諸如 $, !, @, #, % 等特殊符號。 5.Python 識別符號沒有長度限制 6.Python 識別符號中不允許出現空格 命名規則
- 42. 補充資料 (Slide Credit : Santy) 1.由於 Python 區分大小寫,所以大寫和小寫的變數是不同的。 例如: last_name 和 LAST_name 是兩個不同的變數。 2.使用有意義的變數名稱,提高程式的可讀性。 3.如果變數中包含多個單詞,它們應該用下劃線分開。 4.駝峰式大小寫,大寫駝峰型 (upper camel case) 或是小寫駝峰型 (lower camel case) 1. 大寫駝峰型 SimpleGame 2. 小寫駝峰型 simpleGame 識別符號要點
- 43. • import package (as name) • 導入 套件 A ( 且縮寫為 name) 導入 pandas 套件,並縮寫為 pd 導入 numpy 套件,並縮寫為 np Package
- 44. • package(/name).function() • 套件名稱 ( 或縮寫 ). 功能名稱 () pd 套件裡的 DataFrame 功能 pd 套件裡 read_csv 功能 Package
- 45. • from package import module • 從 套件 A 導入 特定功能,以此方式宣告時,在使用上就不需要 package. 從 random 套件中導入 randint 功能 使用 randint 隨機從 1 到 100 抽一個數字 Package
- 46. Python for Beginners: Use GenAI to help you -Case Study (TVL)- Kai-Yuan, Hsiao
- 49. VOLLEBALL
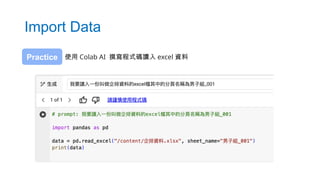
- 50. Import Data 使用 Colab AI 撰寫程式碼讀入 excel 資料 Practice
- 51. • pd.read_csv() • 讀取 csv 檔 • pd.read_excel() • 讀取 excel(.xlsx) 檔 Import Data
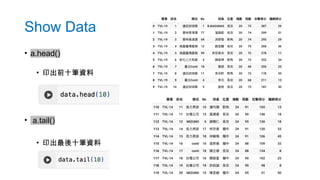
- 52. Show Data 使用 Colab AI 撰寫程式碼印出前 10 筆資料 Practice
- 53. • a.head() • 印出前十筆資料 • a.tail() • 印出最後十筆資料 Show Data
- 58. • 表 [“ 欄位名稱” ] • 選擇一個欄位 ( 隊伍 ) • 表 [[“ 欄位名稱 1”,” 欄位名稱 2”]] • 選擇多個欄位 ( 隊伍 , 球員 ) Select Columns
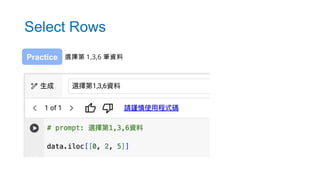
- 60. • 表 [ 起始 index( 含 ) : 終點 index( 不含 )] • 選擇多列資料 • 表 [:] • 冒號的多重用法 Select Rows
- 61. Select Rows 選擇第 1,3,6 筆資料 Practice
- 62. Select Rows and Columns 找出前三筆資料的球員姓名 Practice
- 63. • 表 [“ 欄位名稱” ] [ 起始 index( 含 ) : 終點 index( 不含 )] • 選擇特定欄位多列資料 • 表 [[“ 欄位名稱 1”,” 欄位名稱 2”]] [ 起始 index( 含 ) : 終點 index( 不含 )] • 選擇多欄位多列資料 Select Rows and Columns
- 64. Select Rows and Columns 攻擊得分大於 350 的資料 Practice
- 65. • 表 [ 條件 ] • 篩選符合單一條件的資料 • 表 [( 條件 1)&( 條件 2)] • 篩選符合複合條件的資料 Select Rows and Columns
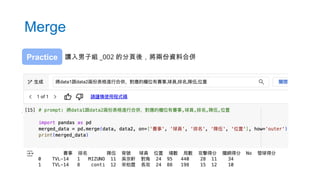
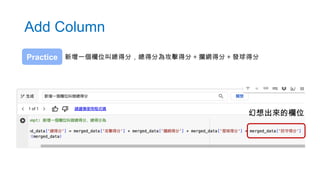
- 70. Add Column 新增一個欄位叫總得分,總得分為攻擊得分 + 攔網得分 + 發球得分 Practice 幻想出來的欄位
- 71. Add Column 新增一個欄位叫「每局平均總得分 / 局數」 Practice 新增一個欄位叫「性別」 Practice
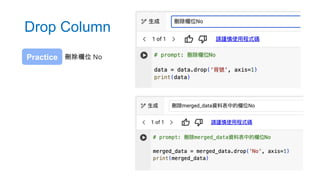
- 73. • 表 .drop( 欄位名稱 ,axis=1) • 刪除資料欄位 Drop Column
- 74. Descriptive Statistics 對 merged_data 做敘述統計 Practice
- 76. • 表 .describe() • 連續型欄位敘述統計 • 表 .describe(include=[”object”]) • 類別型欄位敘述統計 • 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].value_counts() • 類別型欄位值分佈情形 Descriptive Statistics
- 77. • 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].min() • 取最小值 • 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].max() • 取最大值 Descriptive Statistics • 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].mean() • 取平均數 • 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].mode() • 取眾數 • 表 [ 欄位名 稱 ].median() • 取中位數 • 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].std () • 取標準差


































![• Container Data Types
You can use [ ] to define list
You can use ( ) to define tuple
You can use { } to define set
You can use { } and call the key to define dict
Variable Type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-250202092238-519b591a/85/Python_presentation_data_science_lecture-pptx-39-320.jpg)
















![• 表 [“ 欄位名稱” ]
• 選擇一個欄位 ( 隊伍 )
• 表 [[“ 欄位名稱 1”,” 欄位名稱 2”]]
• 選擇多個欄位 ( 隊伍 , 球員 )
Select Columns](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-250202092238-519b591a/85/Python_presentation_data_science_lecture-pptx-58-320.jpg)

![• 表 [ 起始 index( 含 ) : 終點 index( 不含 )]
• 選擇多列資料
• 表 [:]
• 冒號的多重用法
Select Rows](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-250202092238-519b591a/85/Python_presentation_data_science_lecture-pptx-60-320.jpg)

![• 表 [“ 欄位名稱” ] [ 起始 index( 含 ) : 終點 index( 不含 )]
• 選擇特定欄位多列資料
• 表 [[“ 欄位名稱 1”,” 欄位名稱 2”]] [ 起始 index( 含 ) : 終點 index( 不含 )]
• 選擇多欄位多列資料
Select Rows and Columns](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-250202092238-519b591a/85/Python_presentation_data_science_lecture-pptx-63-320.jpg)

![• 表 [ 條件 ]
• 篩選符合單一條件的資料
• 表 [( 條件 1)&( 條件 2)]
• 篩選符合複合條件的資料
Select Rows and Columns](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-250202092238-519b591a/85/Python_presentation_data_science_lecture-pptx-65-320.jpg)







![• 表 .describe()
• 連續型欄位敘述統計
• 表 .describe(include=[”object”])
• 類別型欄位敘述統計
• 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].value_counts()
• 類別型欄位值分佈情形
Descriptive Statistics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-250202092238-519b591a/85/Python_presentation_data_science_lecture-pptx-76-320.jpg)
![• 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].min()
• 取最小值
• 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].max()
• 取最大值
Descriptive Statistics
• 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].mean()
• 取平均數
• 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].mode()
• 取眾數
• 表 [ 欄位名
稱 ].median()
• 取中位數
• 表 [ 欄位名稱 ].std ()
• 取標準差](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonppt-250202092238-519b591a/85/Python_presentation_data_science_lecture-pptx-77-320.jpg)