RNAi interuption mechanism and application
- 1. 1 SUBMITTED BY: Milan Mailali and Sumeena Karki CDBT, Kirtipur, Nepal DATE:26th July,2015
- 2. RNAi is a mechanism that inhibits gene expression at the stage of translation or by hindering the transcription of specific genes. Also known as RNA silencing. RNAi targets include RNA from viruses and transposons. 2
- 3. 3
- 4. In 1990,Jorgensen and Nepoli. They were trying to make petunias more purple ( chalcone synthase) Entered homologous RNA. Over expression of petunia gene caused less pigmentation. Later similar mechanisms were found as cosupression in plants and quelling in fungi. After these initial observations in plants, laboratories searched for this phenomenon in other organisms. Craig C. Mello and Andrew Fire's 1998 paper reported a potent gene silencing effect after injecting double stranded RNA into C. elegans. In investigating the regulation of muscle protein production, they observed that neither mRNA nor antisense RNA injections had an effect on protein production, but double- stranded RNA successfully silenced the targeted gene. As a result of this work, they coined the term . 4
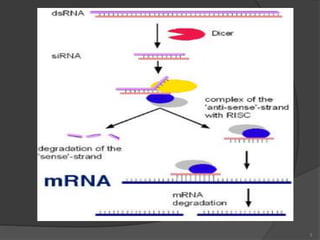
- 5. 1)RNA siRNA ; ds RNA (20-22 nt) miRNA : ss RNA ( 19-25 nt ) 2) RISC RNA induced silencing complex that cleaves m RNA 3) ENZYMES Dicer-produces 20-21 nt cleavages that initiate RNAi. Drosha -cleaves base hairpin in to form pre- miRNA ; which is later processed by Dicer. 5
- 6. Originates with dsRNA is most commonly a response to foreign RNA is often 100% complementary to target. A single base pair difference between siRNA template and the target m RNA is enough to block the process. 6
- 7. miRNA originates with ssRNA that forms a hairpin secondary structure. It regulates post transcriptional gene expression. The dsRNA portion of the pre-miRNA is bound and cleaved by Dicer to produce the mature miRNA molecule that can be integrated into the RISC complex; thus, miRNA and siRNA share the same downstream cellular machinery. 7
- 8. Drosha digests the Pri -miRNA to release a Pre-miRNA which is approximately 70nt with 25-30bp stem and a relatively small loop. 8
- 9. Conserved protein Enzyme involved in initiation of RNAi Dicer cleave the Pre-miRNA to form ~22 nt mature miRNA Able to digest dsRNA into uniformly small sized siRNA ATP dependent Acts as a dimer Dicer homologes exist in many organisms like C. elegans , Drosophila , yeast and humans 9
- 10. Large ( 500kDa) , RNA multiprotein complex which triggers m RNA degradation in response to siRNA Unwinding of double stranded siRNA by ATP independent helicase. The active components of as RISC are endonucleases called argonaute proteins which cleave the target m RNA strand. 10
- 11. Argonaute is a catalytic component of RISC Binds to non-coding RNA including miRNAs Members of Argonaute (Ago) protein family are central to RISC function. Argonaute are needed for miRNA-induced silencing and contain two conserved binding domains i.e. PAZ domain and Plwl domain(which structure resembles to Ribonuclease H) 11
- 12. Mechanism of gene silencing It is based on two steps Each involving Ribonuclease enzyme First step involves the slicing of dsRNA or miRNA primary transcript into siRNA(short interfering RNA) by Rnase II enzyme Dicer and Dorsa Second steps include loading of SiRNA to RISC complex(RNA induced silencing complex) and degradation of mRNA by Argonaute enzyme(slicer) 12
- 13. Lin-4 was first miRNA to be discovered(1993) Joint efforts of Victor Ambros on Lin-4(1987) and Gary Ruvkun on Lin-14(1988) Study of gene Lin-14 in Caenorhabditis elegans development by Victor Ambros, Rosalind Lee and Rhonda Fienbaum in 1993 40% of miRNA may lie in introns or even exons of long non-protein coding transcripts 13
- 14. 14 Victor Ambros and Rosalind Lee in their lab figure of C. elegans
- 15. 15
- 16. In the first step, the trigger RNA (either dsRNA or miRNA primary transcript) is processed into an short, interfering RNA (siRNA) by the RNase II enzymes Dicer and Drosha. During RNAi, long dsRNA is cut or "diced" into small fragments ~21 nucleotides long by the enzyme Dicer. These small fragments, referred to as small interfering RNAs (siRNA), bind to proteins from a special family: the Argonaute proteins. After binding to an Argonaute protein, one strand of the dsRNA is removed, leaving the remaining strand available to bind to messenger RNA target sequences 16
- 17. Contd… In the second step, siRNAs are loaded into the effector complex RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The RISC first mediates the unwinding of the siRNA duplex and the ss siRNA that is coupled to RISC then binds to a target mRNA in a sequence specific manner. Gene silencing is a result of nucleolytic degradation of the targeted mRNA by the RNase H enzyme Argonaute (Slicer). If the siRNA/mRNA duplex contains mismatches the mRNA is not cleaved. Rather, gene silencing is a result of translational inhibition. 17
- 18. RNAi are found in several eukaryotes and around 330 miRNAs are detected in humans Responsible for no. of cell responses like gene regulation(esp. controlling of plant shapes),formation of centromeric structure and heterochromatin formation(keeps heterochromatic region condensed and suppressed) Offers tools to repress gene specifically allowing them to be studied independently in almost every organism Secures genome stability( RNAi will be activate in presence of transposons) 18
- 19. Contd… In functional genomics like systematic analysis of loss of functional phenotypes induced by RNAi triggers Therapeutic invention for treatment of viral infection(destroys homologous section of viral dsRNA), dominant disorders, neurological disorders and many types of cancers(in vivo inactivation of gene products linked to human disease progression and pathology) In agriculture and other areas 19
- 20. Defense mechanism • Defense against infection by viruses. • As a defense mechanism to protect against transposons. Genome wide regulation • RNAi plays a role in regulating development and genome maintenance • 30% of human genome regulated. 20
- 21. 21
- 22. video2 22
- 23. 23 Any query?