Sacrum ppt 2
- 1. SACRUM S M BADAR HAYAT Tutor Department of Anatomy NMCH, Bihar
- 2. CONTENTS Introduction Anatomical position Features Sacral canal Attachments Sex differences Ossification Applied anatomy
- 3. INTRODUCTION The sacrum (vertebra magnum) iis a large, flattened, triangular/ wedge shaped bone formed by the fusion of 5 sacral vertebrae. It lies obliquely at the upper and posterior part of pelvic cavity between two hip bones at the sacroiliac joint.
- 4. FUNCTIONS Forms posterior part of the bony pelvis. Supports the vertebral column. Transmits the weight of the body to the pelvic girdle through the sacroiliac joints.
- 5. ANATOMICAL POSITION Its smooth pelvic surface faces downward and forward. Its rough dorsal surface faces forward and backward. Upper surface of the body of the 1st sacral vertebra slopes forward at an angle of about 300. Upper end of the sacral canal is directed almost upward and slightly backward.
- 7. FEATURES Base Apex Four surfaces 1. Pelvic 2. Dorsal 3. Right lateral 4. Left lateral Sacral canal
- 8. BASE( UPPER END) The base of the sacrum is directed upward and forward. It is formed by the superior surface of the 1st sacral vertebra. Its articulates with fifth lumbar vertebra to form sacro- vertebral angle. It is divided into three parts: median part and right and left lateral parts.
- 9. It presents features of a typical vertebra in a modified form. Body : 1. transverse measurement is more than antero-posterior measurement 2.sacral promontory- the anterior projecting edge of the body. 3. upper surface of the body of the 1st sacral vertebra articulates with the L-5 vertebra. Vertebral foramen: It is lying behind the body is large and triangular and leads into the sacral canal.
- 11. Pedicles: 1. short and widely separated 2. projects backwards and laterally. Laminae: very oblique and project downwards, backwards and medially. Spinous process : represented by a spinous tubercle Superior articular process : bear concave articular facets which face backward and medially to articulate with inferior articular facets of 5th lumbar vertebra.
- 12. Transverse process : is modified a. represented by a broad sloping mass of bone on the lateral side of the body, pedicle and superior articular process. It is known as ala of sacrum It is formed by fusion of the transverse process and costal element. This features is not present in any other vertebra. b. It forms upper surface of lateral part of sacrum. c. It is subdivided into a smooth medial part and a rough lateral part.
- 13. APEX Narrow blunt end lying at thr lower part and is formed by inferior surface of the body of 5th sacral vertebra. Bears an oval facet which articulates with body of 1st coccygeal vertebra to form the sacrococcygeal joint.
- 14. PELVIC SURFACE Concave all over ; broader at its upper part, directed downwards and forwards. It has 4 pairs of pelvic sacral foramina which communicate through intervertebral foramina with sacral canal . They transmits ventral rami of upper 4 sacral nerves and a branch from lateral sacral artery. Median area between foramina of right and left sides is formed by the flat pelvic surfaces of bodies of sacral vertebrae. The line of fusion of sacral vertebrae are seen as 4 raised transverse ridges.
- 16. Bars of bone which separate the foramina from one another on each side represent the costal element. Surface lateral to sacral foramina, on each side is formed by fusion of the costal elements to one another.
- 17. DORSAL SURFACE Rough, irregular and convex Faces backwards and forwards Median sacral crest: raised interruped crest in the median plane which bears 4 spinous tubercles. It represents the fused spines of sacral vertebrae. Sacral hiatus : an inverted U- shaped gap below the 4th spinous tubercle in the posterior wall of sacral canal. It is due to failure of laminae of 5th sacral vertebra to meet in the median plane.
- 19. Dorsal sacral foramina : 4 in number , laying on each side of the median sacral crest. They communicate with sacral canal through intervertebral foramina and transmit- dorsal rami of sacral nerves. Intermediate sacral crest : it is a row of 4 small articular tubercles lying just medial to dorsal sacral foramina. It represents the articular processes fused together. Lateral sacral crest : lies on the lateral side of dorsal sacral foramina. It is formed by fusion of transverse processes, tips of which appear as a row of tubercles. Sacral cornua : the free and projecting part at inferior part of 5th sacral vertebra on the sides of sacral hiatus. It is connected to cornua of coccyx by inter-cornual ligament. It represents the inferior articular processes of 5th sacral vertebra
- 20. LATERAL SURFACE Formed by fused transverse processes and costal elements . It is broader above and narrow below. Auricular surface : an ear-shaped surface at the upper part which articulates with ilium of hip bone to form sacro-iliac joint. It is entirely by costal element. It shows elevations and depressions. The area behind the surface is rough for ligamentous attachments. This surface is covered by cartilage in the recent state.
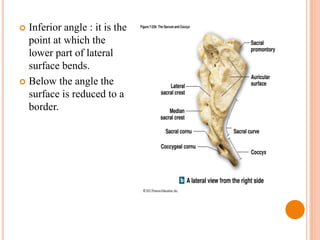
- 22. Inferior angle : it is the point at which the lower part of lateral surface bends. Below the angle the surface is reduced to a border.
- 23. SACRAL CANAL Formed by vertebral foramina of sacral vertebrae. Triangular in shape. It is bounded by a) In front by bodies of sacral vertebrae. b) Behind and on the sides by fused laminae and spinous processes Lateral wall of the canal presents 4 intervertebral foramina through which the canal is connected to pelvic and dorsal sacral foramina.
- 24. Its contents are- a) Cauda equina ( including filum terminale). b) Spinal meninges. c) Sacral and coccygeal nerve roots. d) Lateral sacral vessels. Sacral hiatus transmits: a) 5th pair of sacral nerves. b) Coccygeal nerves c) Filum terminale
- 25. ATTACHMENTS AND RELATIONS Base : 1. The smooth medial part of the ala of sacrum is related to the following four structures from medial to lateral side : a) sympathetic chain b) Lumbosacral trunk c) Iliolumbar artery d) Obturator nerve 2. The rough lateral part of ala gives origin to iliacus muscle anteriorly and attachment to the lumbosacral ligaments posteriorly.
- 26. PELVIC SURFACE The median sacral vessels are related to the pelvic surface in the median plane. The sympathetic trunks are related to the pelvic surface along the medial margins of pelvic sacral foramina. The upper two-and-half sacral vertebrae are related to the parietal peritoneum except for the site of attachment of the medial part of sigmoid mesocolon. The lower two-and-half vertebrae are related to the rectum, but separated from S3 vertebra by bifurcation of the superior rectal artery. The piriformis muscle arises from the bodies of middle 3 sacral vertenrae in an E-shaped fashion.
- 28. DORSAL SURFACE The erector spinae muscle arises from an elongated U-shaped linear area involving the continuous rows of the spinous and transverse tubercles. The multifidus muscles arises from the area enclosed by U-shaped origin of erector spinae. The dorsal rami of upper 4 sacral spinal nerves reach the surface by piercing multifidus and erector spinae muscles.
- 30. LATERAL SURFACES The rough area behind the auricular surface gives attachment to strong interosseous sacroiliac joint. The lower narrow part of lateral surface opposite the inferolateral angle gives attachment to 4 structures. From behind forward these are: a) Gluteus maximus b) Sacrotuberous ligament c) Sacrospinous ligament d) Coccygeus
- 32. OSSIFICATION The ossification of sacrum is not of much clinical interest. Ossification of sacrum is complicated. Sacrum is a composite bone formed by the fusion of 5 sacral vertebrae. It is ossifies by multiple centres.
- 33. APPLIED ASPECT Sacralization : The term sacralization means incorporation of the 5th lumbar or 1st coccygeal vertebrain the sacrum. Lumbarization : In this condition, the 1st sacral vertebra is separated from the sacrum and fused with the 5th lumbar vertebra.
- 34. Thank you