SCABIES CASE PRESENTATION
- 1. PRESENTED BY: VARSHA R WADNERE (PD328)
- 9. SOAP ANALYSIS • Patient Details: Name- xxx (HEALTHCARE PROVIDER) •Age-34yrs old •Sex-Male
- 10. SUBJECTIVE DATA • CHIEF COMPLAINTS: Patient suffering from dry, itchy rash on his lower legs(during night) from last 2 weeks.
- 11. OBJECTIVE DATA
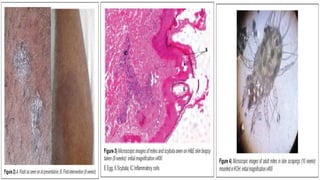
- 13. ASSESSMENT • PROVISIONAL DIAGNOSIS: Intestinal Worm Infection. • FINAL DIAGNOSIS: Atypical Nosocomial Scabies{HOSPITAL ACQUIRED INFECTION}.
- 14. HISTORY • Disease History: Peptic Ulcer. • Medication History: No medication history. • Family History: No relevant family history. • Social History: No social history.
- 15. GOALS OF TREATMENT • PATIENT SPECIFIC: 1. To treat lesions. 2. To reduce swelling in the skin. 3. To relieve symptoms of itching, rashes. 4. To treat multiple erythrematopapulus from the affected area. • DISEASE SPECIFIC: 1. To treat scabies. 2. To treat peptic ulcer. 3. To stop the progression of any symptoms and disease. 4. Prevent complications. 5. Preventing recurrence.
- 16. ASSESSMENT OF CURRENT THERAPY During the first 7 days of symptom presentation, the patient was de-wormed with 400 mg Albendazole for 3 days. As this provided no relief, he was referred to the dermatology clinic a week later, where based on his initial laboratory results, he was administered Benzyl Penicillin 2.4 mg IM stat, 0.0127% topical Hydrocortisone and a 10 day course of 10 mg oral Cetirizine. Two weeks later, he developed angioedema, which responded to 100 mg IM Hydrocortisone Succinate stat and topical Betamethasone Valerate (BV) 0.1%. He was also started on triple therapy for H. pylori infection (250 mg Azithromycin, 40 mg Pantoprazole and 250 mg Amoxicillin for 2 weeks) and advised to clean out his clothing and beddings. Finally, during the 10th week, he was administered a single dose of oral Ivermectin at 200 mcg/Kg, followed by topical Benzyl Benzoate which appeared to clear the rash and alleviate the persistent itch.
- 17. 1).Albendazole -400mg(3 days). INDICATION-This medication is used to treat certain tapeworm infections (such as neurocysticercosis and hydatid disease). ADR- Vomiting, Dizziness, increased liver enzyme, nausea loss of appetite. DRUG INTERACTION- Estradiol, Tibolone, Estriol, carbamazepine. CONTRAINDICATIONS- Anaemia, low levels of a type of white blood cell called neutrophils, liver problems. Abnormal liver function tests, pregnancy. MOA- The principal mode of action for albendazole is by its inhibitory effect on tubulin polymerization which results in the loss of cytoplasmic microtubules.
- 18. 2).BENZYL PENICILLIN-2.4mg IM. INDICATION- For use in the treatment of severe infections caused by penicillin G-susceptible microorganisms when rapid and high penicillin levels are required such as in the treatment of septicaemia, meningitis, pericarditis, endocarditis and severe pneumonia. SIDE EFFECT- Injection site reactions (swelling, bruising, or irritation),twitching or muscle spasm, overactive reflexes, mild skin rash, nausea, vomiting, upset stomach, diarrhoea. CONTRAINDICATIONS- arthralgia, prostration, haemolytic anaemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. DRUG INTERACTION- Cholera vaccine, typhoid vaccine, methotrexate, oxytetracycline, sarecycline. MOA- By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, penicillin- G inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that penicillin-G interferes with an autolysin inhibitor
- 19. 3).Topical hydrocortisone-0.0127%. INDICATION- It is a steroid the is used to treat inflammation and itching caused by skin conditions that respond to steroid medication. SIDE-EFFECT- Blistering, crusting, dryness, or flaking of the skin irritation, thinning, weakness, or wasting away of the skin. Drug interaction- Aspirin, furosemide, albuterol, esomeprazole. Contraindications- Inactive tuberculosis. herpes simplex infection of the eye.an infection due to a fungus. intestinal infection caused by the roundworm, Strongyloides pheochromocytoma condition with low thyroid hormone levels. diabetes. insufficiency of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. MOA- Hydrocortisone binds to the glucocorticoid receptor leading to downstream effects such as inhibition of phospholipase A2, NF-kappa B, other inflammatory transcription factors, and the promotion of anti- inflammatory genes.
- 20. 4).Cetirizine-10mg/oral for 10 days. Indication- It is an antihistamine that reduces the natural chemical histamine in the body. SIDE-EFFECT- Fast, pounding, or uneven heartbeat; weakness, tremors (uncontrolled shaking), or sleep problems (insomnia);severe restless feeling, hyperactivity; confusion; problems with vision; or urinating less than usual or not at all. DRUG INTERACTION- Diphenhydramine, pregabalin. CONTRAINDICATIONS- Glaucoma increased pressure in the eye, liver problems decreased kidney function an inability to completely empty the bladder. MOA- A metabolite of hydroxyzine, is an antihistamine; its principal effects are mediated via selective inhibition of peripheral H1 receptors. It also possesses some mast cell stabilizing properties.
- 21. 5).Hydrocortisone Sod Succinate-100mg IM after 2 weeks. INDICATION-This medication is used to treat various conditions such as arthritis, severe allergies, blood diseases, breathing problems, certain cancers, eye diseases, intestinal disorders, and skin diseases. SIDE-EFFECT- Stomach upset, headache, dizziness, trouble sleeping, appetite changes, menstrual period changes, acne, or pain/redness/swelling at the injection site may occur. DRUG INTERACTION- aldesleukin, mifepristone, clopidogrel, NSAIDs, ibuprofen, naproxen warfarin, dabigatran. CONTRAINDICATIONS- inactive tuberculosis, herpes simplex infection of the eye, an infection due to a fungus, intestinal infection caused by the roundworm, Strongyloides pheochromocytoma. A condition with low thyroid hormone levels, diabetes. MOA- Hydrocortisone binds to the glucocorticoid receptor leading to downstream effects such as inhibition of phospholipase A2, NF-kappa B, other inflammatory transcription factors, and the promotion of anti- inflammatory genes.
- 22. 6).Betamethasone Valerate Ointment 0.1%. INDICATION- This medication is used to treat a variety of skin conditions (e.g., eczema, dermatitis, allergies, rash). Betamethasone reduces the swelling, itching, and redness that can occur in these types of conditions. SIDE-EFFECT- Stinging, burning, itching, irritation, dryness, or redness of the skin may occur when this medication is first applied to the skin. DRUG INTERACTION- prednisone. CONTRAINDICATIONS- insufficiency of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland MOA- Betamethasone binds to specific intracellular glucocorticoid receptors and subsequently binds to DNA to modify gene expression.
- 23. 7).Azithromycin- 250mg(for H.pylori). INDICATION- it is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. SIDE-EFFECT-Stomach upset, diarrhoea/loose stools, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. DRUG INTERACTION- amiodarone, chloroquine, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, hydroxychloroquine, ibutilide, pimozide, procainamide, quinidine, sotalol. CONTRAINDICATIONS- diarrhoea from an infection with Clostridium difficile bacteria, low amount of magnesium in the blood, low amount of potassium in the blood, myasthenia gravis. A skeletal muscle disorder, hearing loss torsade's de pointes. A type of abnormal heart rhythm. MOA- Azithromycin prevents bacteria from growing by interfering with their protein synthesis. It binds to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, thus inhibiting translation of mRNA. Nucleic acid synthesis is not affected
- 24. 8).Pantoprazole-40mg INDICATION- Pantoprazole is used to treat certain stomach and oesophagus problems (such as acid reflux). SIDE EFFECT- headache, diarrhoea. DRUG INTERACTION- ampicillin, atazanavir, erlotinib, nelfinavir, pazopanib, rilpivirine, certain azole antifungals itraconazole, ketoconazole, Posaconazole. Contraindications- Diarrhoea from an infection with Clostridium difficile bacteria, inadequate vitamin B12,Low amount of magnesium in the blood, type of kidney inflammation called interstitial nephritis. subacute cutaneous lupus erythematous, systemic lupus erythematous-an autoimmune disease. MOA- Inhibit the final step in gastric acid production. In the gastric parietal cell of the stomach, pantoprazole covalently binds to the H+/K+ ATP pump to inhibit gastric acid and basal acid secretion. The covalent binding prevents acid secretion for up to 24 hours and longer.
- 25. 9).Amoxicillin-250mg for 2 weeks. INDICATION- Amoxicillin is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. Side effects- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhoea. Drug interaction- methotrexate. Contraindications- mononucleosis-the kissing disease. Liver problems, blockage of normal bile flow, severe renal impairment. MOA- Amoxicillin is in the class of beta-lactam antimicrobials. Beta-lactams act by binding to penicillin- binding proteins that inhibit a process called transpeptidation (cross-linking process in cell wall synthesis), leading to activation of autolytic enzymes in the bacterial cell wall.
- 26. 10).Ivermectin-200 mcg/Kg in 10th week Indication-This medication is used to treat certain parasitic roundworm infections. Side-effect-Headache, dizziness, muscle pain, nausea, or diarrhoea. Drug interaction- barbiturates (such as phenobarbital, butalbital), benzodiazepines (such as clonazepam, lorazepam), sodium oxybate (GHB), valproic acid. Contraindications- Infection by the worm Loa loa, abnormal liver function tests. MOA- Glutamate-gated chloride channel Ivermectin binds with high affinity to glutamate-gated chloride channels which occur in invertebrate nerve and muscle cells, causing an increase in the permeability of the cell membrane to chloride ions with hyperpolarization of the nerve or muscle cell. Hyperpolarization results in paralysis and death of the parasite.
- 27. 11).Benzyl benzoate Indication- It is used to treat lice and scabies infections. Side effect- Difficulty in urinating, jerking movements. Contraindications: In patient with known hypersensitivity to benzyl benzoate. MOA: Act on nervous system of the parasite, causing paralysis and death.
- 29. PLANNING • MONITOR SYMPTOMS OF PATIENT. • MONITOR DRUG INTERACTIONS AND ADVERSE DRUG REACTION. • Management of oral ivermectin at 200 mcg/Kg body weight, followed a week later by topical benzyl benzoate appear to have provided symptomatic relief after almost 3 months. The preventative measure of cleaning out his wardrobe and beddings plus housing may have provided crucial disruption of a self-re- infection cycle. • Monitor abnormal lab parameters in regular interval of time.
- 31. POINT TO PATIENT
- 32. 1. Taking lukewarm baths. 2. Applying moisturizer within 3 minutes of bathing to "lock in" moisture. 3. Moisturizing every day. 4. Wearing cotton and soft fabrics, and avoiding rough, scratchy fibers and tight- fitting clothing. 5. Using a mild soap or a non-soap cleanser when washing. 6. Air drying or gently patting skin dry with a towel, rather than rubbing the skin dry after bathing. 7. Where possible, avoiding rapid changes of temperature and activities that make you sweat. 8. Using a humidifier in dry or cold weather. 9. Phototherapy: This involves exposure to ultraviolet A or B waves, alone or combined. The skin will be monitored carefully. This method is normally used to treat moderate dermatitis 10.Eat foods containing flavonoids-soyabeans, legumes, kale, berries, teas, apple, red grape, probiotics- yogurt, buttermilk, honey, flaxseed for curing ulcers.
- 33. REFERENCE • https://www.google.com/search?q=pathophysiology+of+scabies&rlz=1C1UEAD_enIN930IN930&sxsrf=ALeKk03zN0n- jE8CkMKdhLo_amKyIBm4HQ:1611304860324&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjL6Muukq_uAhVHfX0K HdI7Db4Q_AUoAXoECBUQAw&biw=1280&bih=578#imgrc=OMQiyWPohAL85M • https://www.pulsus.com/scholarly-articles/a-complicated-case-of-scabies-in-a-health-care-provider-4392.html • https://www.slideshare.net/smaxy/scabies-65809987 • https://www.pulsus.com/articles-images/journal-skin-skin-biopsy-2-1-7-g003.png • https://www.pulsus.com/articles-images/journal-skin-skin-scrapings-2-1-7-g004.png • https://www.pulsus.com/articles-images/journal-skin-Rash-2-1-7-g002.png • https://www.pulsus.com/articles-images/journal-skin-laboratory-investigations-2-1-7-g001.png
- 34. THANK YOU ANY QUESTIONS ?