Session 11
- 1. Distribution Strategies Distribution Strategies Channel Mix & Logistic Management
- 2. International Marketing Mix Decisions International Channel-of-Distribution Alternatives Home Country Foreign Country The foreign marketer or producer sells to or through Foreign Domestic producer consumer or marketer sells to or through Open distribution via Foreign agent Foreign domestic wholesale Exporter Importer or merchant retailer middlemen wholesalers s Export management company or company sales force
- 3. Channel Objectives Marketing channels exist to create utility for customers Place utility Time utility Form utility Information utility
- 4. Direct involvement – the company establishes its own sales force or operates its own retail stores Indirect involvement – the company utilizes independent agents, distributors, and/or wholesalers
- 5. The process of shaping international channels to fit overall company objectives is constrained by several factors: Customer characteristics Product characteristics Middleman characteristics
- 6. Distribution Channels: Terminology and Structure Distribution is the physical flow of goods through channels Channels are made up of a coordinated group of individuals or firms that perform functions that add utility to a product or service
- 7. Distribution Channels: Terminology and Structure Distributor – wholesale intermediary that typically carries product lines or brands on a selective basis Agent – an intermediary who negotiates transactions between two or more parties but does not take title to the goods being purchased or sold
- 9. Consumer product Door-to-door selling Manufacture owned store Franchise operations Combination structures
- 11. Working with Channel Intermediaries Select distributors – don’t let them select you Look for distributors capable of developing markets, rather than those with a few good customer contacts Treat local distributors as long-term partners, not temporary market-entry vehicles
- 12. Working with Channel Intermediaries Support market entry by committing money, managers, and proven marketing ideas From the start, maintain control over marketing strategy Make sure distributors provide you with detailed market and financial performance data Build links among national distributors at the earliest opportunity
- 13. Global Retailing Hypermarkets (200,000 sq ft) Discount store (70,000 sq ft) Supermarkets(30,000- 50,000 sq ft)
- 14. Global Retailing Top 25 Global Retailers in 2002, sales in Millions
- 15. Global Retailing Environmental Factors Saturation in the home country market Recession or other economic factors Strict regulation on store development High operating costs Critical Question What advantages do we have relative to the local competition?
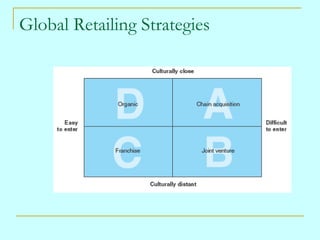
- 16. Global Retailing Strategies Organic Franchise Appropriate strategy when barriers to entry are low yet the market is culturally distant in terms of consumer behavior or retailing structures
- 17. Global Retailing Strategies Chain Acquisition A market entry strategy that entails purchasing a company with multiple existing outlets in a foreign country Joint Venture This strategy is advisable when culturally distant, difficult-to-enter markets are targeted
- 19. Innovation in Global Retailing Innovation takes place only in the most highly developed systems The ability of a system to successfully adapt innovations is directly related to its level of economic development Even when the economic environment is conducive to change, the process of adaptation may be either hindered or helped by local demographic factors, geographic factors, social mores, government action, and competitive pressures The process of adaptation can be greatly accelerated by the actions of aggressive individual firms
- 20. Supply Chain Definitions Supply Chain Includes all the firms that perform support activities by generating raw materials, converting them into components or finished products and making them available to customers Logistics The management process that integrates the activities of all companies to ensure tan efficient flow of goods through the supply chain
- 21. Physical Distribution, Supply Chains, and Logistics Management Order Processing includes order entry in which the order is actually entered into a company’s information system; order handling, which involves locating, assembling, and moving products into distribution; and order delivery Warehousing Warehouses are used to store goods until they are sold Distribution centers are designed to efficiently receive goods from suppliers and then fill orders for individual stores or customers
- 22. Physical Distribution, Supply Chains, and Logistics Management Inventory Management Ensures that a company neither runs out of manufacturing components or finished goods nor incurs the expense and risk of carrying excessive stocks of these items. Transportation the method or mode a company should utilize when moving products through domestic and global channels; the most common modes of transportation are rail, truck, air, and water
- 23. Transportation Channel Strategy – analyzing each shipping mode to determine which mode, or combination of modes, will be both effective and efficient in a given situation
Editor's Notes
- #7: Although channels for consumer products and industrial products are similar, there are also some distinct differences. In business-to-consumer marketing (b-to-c or B2C), consumer channels are designed to put products in the hands of people for their own use; as participants in a process known as business to- business marketing (b-to-b or B2B) , industrial channels deliver products to manufacturers or other types of organizations that use them as inputs in the production process or in day-to-day operations.
- #9: This figure summarizes six channel structure alternatives for consumer products. The characteristics of both buyers and products have an important influence on channel design. The first alternative is to market directly to buyers via the Internet, mail order, various types of door-to-door selling, or manufacturer owned retail outlets. The other options utilize retailers and various combinations of sales forces, agents/brokers, and wholesalers. The number of individual buyers and their geographic distribution, income, shopping habits, and reaction to different selling methods frequently vary from country to country and may require different channel approaches. Product characteristics such as degree of standardization, perish-ability, bulk, service requirements, and unit price have an impact as well. Generally speaking, channels tend to be longer (require more intermediaries) as the number of customers to be served increases and the price per unit decreases. Bulky products usually require channel arrangements that minimize the shipping distances and the number of times products change hands before they reach the ultimate customer.
- #11: This figure summarizes marketing channel alternatives for the industrial- or business-products company. As is true with consumer channels, product and customer characteristics have an impact on channel structure. Three basic elements are involved: the manufacturer’s sales force, distributors or agents, and wholesalers. A manufacturer can reach customers with its own sales force, a sales force that calls on wholesalers who sell to customers, or a combination of these two arrangements. A manufacturer can sell directly to wholesalers without using a sales force, and wholesalers, in turn, can supply customers. Finally, a distributor or agent can call on wholesalers or customers for the manufacturer.
- #12: Channel decisions are important because of the number and nature of relationships that must be managed. Channel decisions typically involve long-term legal commitments and obligations to various intermediaries. Such commitments are often extremely expensive to terminate or change, so it is imperative for companies to document the nature of the relationship with the foreign partner. As the saying goes, “The shortest pencil is better than the longest memory.” At a minimum, the written agreement should include a definition of what constitutes “good cause” for termination. Harvard professor David Arnold offers seven specific guidelines to help prevent such problems from arising these are highlighted above and on the next slide.
- #14: Global retailing is any retailing activity that crosses national boundaries. Since the mid-1970s, there has been growing interest among successful retailers in expanding globally. However, this not a new phenomenon. For centuries, entrepreneurial merchants have ventured abroad both to obtain merchandise and ideas and to establish retail operations. During the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, British, French, Dutch, Belgian, and German trading companies established retailing organizations in Africa and Asia. International trading and retail store operation were two of the economic pillars of the colonial system of that era. In the twentieth century, Dutch retailer C&A expanded across Europe, and Woolworth crossed the Atlantic from the United States to the United Kingdom. Today’s global retailing scene is characterized by great variety. This slide offers a survey of some of the different forms retailing can take. Retail stores can be divided into categories according to the amount of square feet of floor space, the level of service offered, width and depth of product offerings, or other criteria.
- #16: A number of factors have prompted retailers to look overseas for new store development. Companies must ask themselves the critical question on the slide. If the answer to the question is, “Nothing,” when competition, local laws governing retailing practice, distribution patterns, or other factors are taken into account. However, a company may possess competencies that can be the basis for competitive advantage in a particular retail market. A retailer has several things to offer consumers. Some are readily perceived by customers, such as selection, price, and the overall manner in which the goods are offered in the store setting. The last includes such things as store location, parking facilities, in-store atmosphere, and customer service. Competencies can also be found in less visible value chain activities such as distribution, logistics, and information technology.
- #19: This slide provides students with the visual representation of the market entrance strategies.
- #20: Distribution channels around the world are highly differentiated. On the surface, it appears this differentiation can be explained only in terms of culture and the income level that exists in the market. However, the incidence and rate of retail innovation can be explained in terms of the four observations highlighted on this slide.
- #21: In Chapter 1, marketing was described as one of the activities in a firm’s value chain. The distribution “P” of the marketing mix plays a central role in a given firm’s value chain; because global companies create value by making sure their products are available where and when customers want to buy them. Physical distribution consists of activities involved in moving finished goods from manufacturers to customers. However, the value chain concept is much broader, for two basic reasons. First, the value chain is a useful tool for assessing an organization’s competence as it performs value-creating activities with a broader supply chain . Second, the particular industry in which a firm competes (for example, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, or consumer electronics) is characterized by a value chain. The specific activities an individual firm performs help define its position in the value chain.
- #24: This slide allows the professor to walk the students through discussion of channel strategy. They are encouraged to create a situation that will allow the class to utilize the table and determine the best channel strategy.