Shared Memory Programming with Pthreads and OpenMP
- 1. 1 Shared Memory Programming with Pthreads & OpenMP Dilum Bandara Dilum.Bandara@uom.lk Slides extended from An Introduction to Parallel Programming by Peter Pacheco
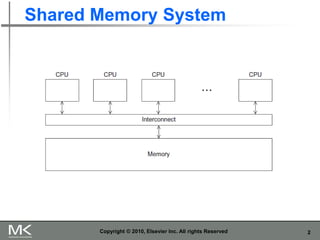
- 2. 2 Shared Memory System Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 3. 3 POSIX® Threads Also known as Pthreads Standard for Unix-like operating systems Library that can be linked with C programs Specifies an API for multi-threaded programming Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 4. 4 Hello World! Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Declares various Pthreads functions, constants, types, etc.
- 5. 5 Hello World! (Cont.) Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 6. 6 Hello World! (Cont.) Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 7. 7 Compiling a Pthread program Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved gcc −g −Wall −o pth_hello pth_hello.c −lpthread Link Pthreads library
- 8. 8 Running a Pthreads program Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved . /pth_hello <number of threads> . /pth_hello 1 Hello from the main thread Hello from thread 0 of 1 . /pth_hello 4 Hello from the main thread Hello from thread 0 of 4 Hello from thread 3 of 4 Hello from thread 2 of 4 Hello from thread 1 of 4
- 9. 9 Running the Threads Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Main thread forks & joins 2 threads
- 10. 10 Global Variables Can introduce subtle & confusing bugs! Use them only when they are essential Shared variables Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 11. 11 Starting Threads Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved pthread.h pthread_t int pthread_create ( pthread_t* thread_p, /* out */ const pthread_attr_t* attr_p, /* in */ void* (*start_routine) (void), /* in */ void* arg_p); /* in */ One object for each thread We ignore return value from pthread_create
- 12. 12 Function Started by pthread_create Function start by pthread_create should have following prototype void* thread_function ( void* args_p ) ; Void* can be cast to any pointer type in C So args_p can point to a list containing one or more values needed by thread_function Similarly, return value of thread_function can point to a list of one or more values Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 13. 13 Stopping Threads Single call to pthread_join will wait for thread associated with pthread_t object to complete Suspend execution of calling thread until target thread terminates, unless it has already terminated Call pthread_join once for each thread int pthread_join( pthread_t* thread /* in */ , void** ret_val_p /* out */ ) ; Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 14. 14 Matrix-Vector Multiplication in Pthreads Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 15. 15 Serial Pseudo-code Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 16. 16 Using 3 Pthreads Assign each row to a separate thread Suppose 6x6 matrix & 3 threads Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Thread 0 General case
- 17. 17 Pthreads Matrix-Vector Multiplication Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 18. 18 Estimating π Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 19. 19 Thread Function for Computing π Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 20. 20 Using a dual core processor Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved As we increase n, estimate with 1 thread gets better & better 2 thread case produce different answers in different runs Why?
- 21. 21 Pthreads Global Sum with Busy-Waiting Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Shared variable
- 22. 22 Mutexes Make sure only 1 thread in critical region Pthreads standard includes a special type for mutexes: pthread_mutex_t Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 23. 23 Mutexes Lock To gain access to a critical section Unlock When a thread is finished executing code in a critical section Termination When a program finishes using a mutex Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 24. 24 Global Sum Function Using a Mutex Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 25. 25 Global Sum Function Using a Mutex (Cont.) Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 26. 26 Busy-Waiting vs. Mutex Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Run-times (in seconds) of π programs using n = 108 terms on a system with 2x4-core processors
- 27. 27 Semaphores Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Semaphores are not part of Pthreads; you need to add this
- 28. 28 Read-Write Locks While controlling access to a large, shared data structure Example Suppose shared data structure is a sorted linked list of ints, & operations of interest are Member, Insert, & Delete Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 29. 29 Linked Lists Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 30. 30 Linked List Membership Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 31. 31 Inserting New Node Into a List Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 32. 32 Inserting New Node Into a List (Cont.) Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 33. 33 Deleting a Node From a Linked List Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 34. 34 Deleting a Node From a Linked List (Cont.) Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 35. 35 Multi-Threaded Linked List To share access to the list, we can define head_p to be a global variable This will simplify function headers for Member, Insert, & Delete Because we won’t need to pass in either head_p or a pointer to head_p: we’ll only need to pass in the value of interest Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 36. 36 Simultaneous Access by 2 Threads Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 37. 37 Solution #1 Simply lock the list any time that a thread attempts to access it Call to each of the 3 functions can be protected by a mutex Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved In place of calling Member(value).
- 38. 38 Issues Serializing access to the list If vast majority of our operations are calls to Member We fail to exploit opportunity for parallelism If most of our operations are calls to Insert & Delete This may be the best solution Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 39. 39 Solution #2 Instead of locking entire list, we could try to lock individual nodes A “finer-grained” approach Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 40. 40 Issues Much more complex than original Member function Much slower Because each time a node is accessed, a mutex must be locked & unlocked Addition of a mutex field to each node substantially increase memory needed for the list Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 41. 41 Pthreads Read-Write Locks Neither multi-threaded linked lists exploits potential for simultaneous access to any node by threads that are executing Member 1st solution only allows 1 thread to access the entire list at any instant 2nd only allows 1 thread to access any given node at any instant Read-write lock is somewhat like a mutex except that it provides 2 lock functions 1st locks the read-write lock for reading 2nd locks it for writing Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 42. 42 Pthreads Read-Write Locks (Cont.) Multiple threads can simultaneously obtain lock by calling read-lock function While only 1 thread can obtain lock by calling write-lock function Thus If any thread owns lock for reading, any thread that wants to obtain a lock for writing will be blocked If any thread owns lock for writing, any threads that want to obtain lock for reading or writing will be blocked Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 43. 43 Protecting Our Linked List Functions Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 44. 44 Linked List Performance Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved 100,000 ops/thread 99.9% Member 0.05% Insert 0.05% Delete 100,000 ops/thread 80% Member 10% Insert 10% Delete
- 45. 45 OpenMP Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
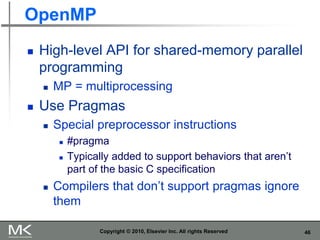
- 46. 46 OpenMP High-level API for shared-memory parallel programming MP = multiprocessing Use Pragmas Special preprocessor instructions #pragma Typically added to support behaviors that aren’t part of the basic C specification Compilers that don’t support pragmas ignore them Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 47. 47 Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 48. 48 Compiling & Running Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved gcc −g −Wall −fopenmp −o omp_hello omp_hello.c . / omp_hello 4 compiling running with 4 threads Hello from thread 0 of 4 Hello from thread 1 of 4 Hello from thread 2 of 4 Hello from thread 3 of 4 Hello from thread 1 of 4 Hello from thread 2 of 4 Hello from thread 0 of 4 Hello from thread 3 of 4 Hello from thread 3 of 4 Hello from thread 1 of 4 Hello from thread 2 of 4 Hello from thread 0 of 4 possible outcomes
- 49. 49 OpenMp pragmas Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved # pragma omp parallel Most basic parallel directive Original thread is called master Additional threads are called slaves Original thread & new threads called a team
- 50. 50 Clause Text that modifies a directive num_threads clause can be added to a parallel directive Allows programmer to specify no of threads that should execute following block Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved # pragma omp parallel num_threads ( thread_count )
- 51. 51 Be Aware… There may be system-defined limitations on number of threads that a program can start OpenMP standard doesn’t guarantee that this will actually start thread_count threads Most current systems can start hundreds or even 1,000s of threads Unless we’re trying to start a lot of threads, we will almost always get desired no of threads Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 52. 52 Mutual Exclusion Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved # pragma omp critical { global_result += my_result ; } only 1 thread can execute following structured block at a time
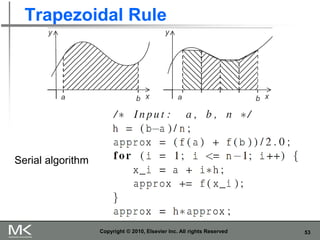
- 53. 53 Trapezoidal Rule Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved Serial algorithm
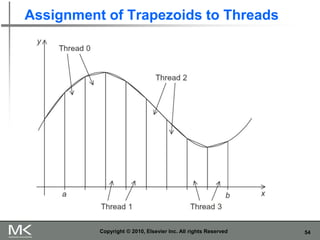
- 54. 54 Assignment of Trapezoids to Threads Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 55. 55 Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved
- 56. 56 Copyright © 2010, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved