Signs and Symptoms of Genitourinary diseases 20Diseases.pptx
- 1. Symptoms and signs of Genitourinary diseases Prof J E Mensah
- 2. Objective • To stimulate your interest in Urology
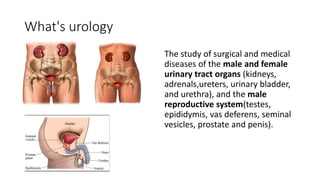
- 3. What's urology The study of surgical and medical diseases of the male and female urinary tract organs (kidneys, adrenals,ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra), and the male reproductive system(testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis).
- 4. Renal functions 1. Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis 2. Excretion of drugs and the waste products of metabolism 3. Endocrine function 4. Acid–base balance
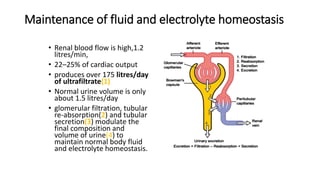
- 5. Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis • Renal blood flow is high,1.2 litres/min, • 22–25% of cardiac output • produces over 175 litres/day of ultrafiltrate(1) • Normal urine volume is only about 1.5 litres/day • glomerular filtration, tubular re-absorption(2) and tubular secretion(3) modulate the final composition and volume of urine(4) to maintain normal body fluid and electrolyte homeostasis.
- 6. Excretion of drugs and the waste products of metabolism • Urea - protein • Creatinine - muscle • Bilirubin - haemoglobin • Uric acid-nucleic acid • Water soluble drugs
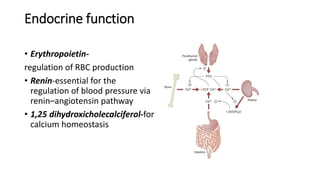
- 7. Endocrine function • Erythropoietin- regulation of RBC production • Renin-essential for the regulation of blood pressure via renin–angiotensin pathway • 1,25 dihydroxicholecalciferol-for calcium homeostasis
- 8. Symptoms and signs of renal failure Renal Function 1. Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis 2. Excretion of waste products of metabolism 3. Endocrine function- 4. Acid–base balance Renal failure • ↑abdominal girth • Pedal edema/Puffy face • Malaise • Anorexia • Headaches • Weight gain • Fatigue • Anaemia • ETC
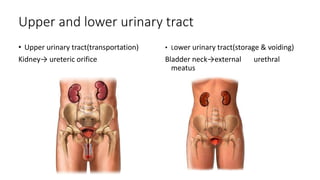
- 9. Upper and lower urinary tract • Upper urinary tract(transportation) Kidney→ ureteric orifice • Lower urinary tract(storage & voiding) Bladder neck→external urethral meatus
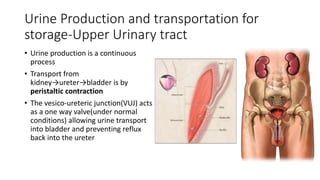
- 10. Urine Production and transportation for storage-Upper Urinary tract • Urine production is a continuous process • Transport from kidney→ureter→bladder is by peristaltic contraction • The vesico-ureteric junction(VUJ) acts as a one way valve(under normal conditions) allowing urine transport into bladder and preventing reflux back into the ureter
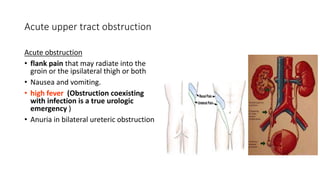
- 11. Acute upper tract obstruction Acute obstruction • flank pain that may radiate into the groin or the ipsilateral thigh or both • Nausea and vomiting. • high fever (Obstruction coexisting with infection is a true urologic emergency ) • Anuria in bilateral ureteric obstruction
- 12. Physiology of urine storage and voiding 1. bladder filling and urine storage • Relaxation of the detrusor muscles to accommodate increasing volumes of urine at a low intravesical pressure • Concomitant contraction of the sphincters to close the bladder outlet(S2-S4) 2. bladder emptying • coordinated contraction of the detrusor muscles • Concomitant relaxation the smooth and striated sphincter • Absence of anatomic obstruction
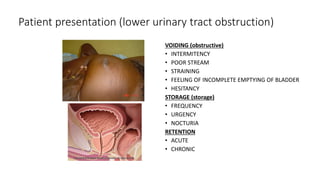
- 13. Patient presentation (lower urinary tract obstruction) VOIDING (obstructive) • INTERMITENCY • POOR STREAM • STRAINING • FEELING OF INCOMPLETE EMPTYING OF BLADDER • HESITANCY STORAGE (storage) • FREQUENCY • URGENCY • NOCTURIA RETENTION • ACUTE • CHRONIC
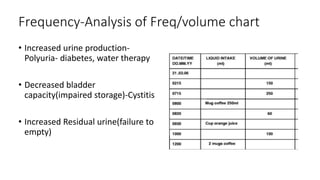
- 14. Frequency-Analysis of Freq/volume chart • Increased urine production- Polyuria- diabetes, water therapy • Decreased bladder capacity(impaired storage)-Cystitis • Increased Residual urine(failure to empty)
- 15. Impact of symptoms on patient's QOL • Urgency • Straining • Nocturia and frequency • Hesitancy • Feeling of incomplete emptying • Poor stream
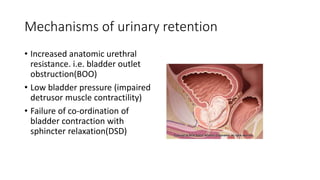
- 16. Mechanisms of urinary retention • Increased anatomic urethral resistance. i.e. bladder outlet obstruction(BOO) • Low bladder pressure (impaired detrusor muscle contractility) • Failure of co-ordination of bladder contraction with sphincter relaxation(DSD)
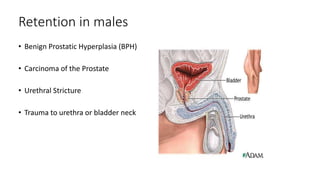
- 17. Retention in males • Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) • Carcinoma of the Prostate • Urethral Stricture • Trauma to urethra or bladder neck
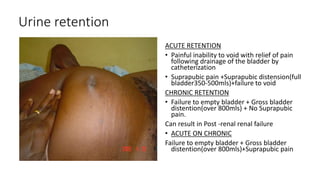
- 18. Urine retention ACUTE RETENTION • Painful inability to void with relief of pain following drainage of the bladder by catheterization • Suprapubic pain +Suprapubic distension(full bladder350-500mls)+failure to void CHRONIC RETENTION • Failure to empty bladder + Gross bladder distention(over 800mls) + No Suprapubic pain. Can result in Post -renal renal failure • ACUTE ON CHRONIC Failure to empty bladder + Gross bladder distention(over 800mls)+Suprapubic pain
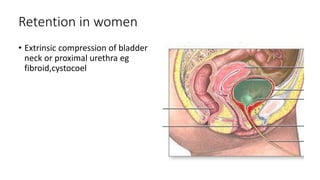
- 19. Retention in women • Extrinsic compression of bladder neck or proximal urethra eg fibroid,cystocoel
- 20. PAIN
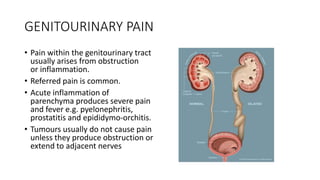
- 21. GENITOURINARY PAIN • Pain within the genitourinary tract usually arises from obstruction or inflammation. • Referred pain is common. • Acute inflammation of parenchyma produces severe pain and fever e.g. pyelonephritis, prostatitis and epididymo-orchitis. • Tumours usually do not cause pain unless they produce obstruction or extend to adjacent nerves
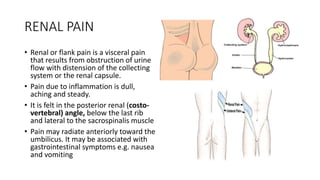
- 22. RENAL PAIN • Renal or flank pain is a visceral pain that results from obstruction of urine flow with distension of the collecting system or the renal capsule. • Pain due to inflammation is dull, aching and steady. • It is felt in the posterior renal (costo- vertebral) angle, below the last rib and lateral to the sacrospinalis muscle • Pain may radiate anteriorly toward the umbilicus. It may be associated with gastrointestinal symptoms e.g. nausea and vomiting
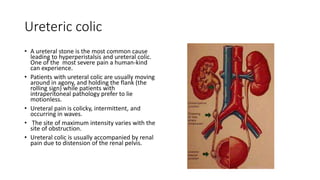
- 23. Ureteric colic • A ureteral stone is the most common cause leading to hyperperistalsis and ureteral colic. One of the most severe pain a human-kind can experience. • Patients with ureteral colic are usually moving around in agony, and holding the flank (the rolling sign) while patients with intraperitoneal pathology prefer to lie motionless. • Ureteral pain is colicky, intermittent, and occurring in waves. • The site of maximum intensity varies with the site of obstruction. • Ureteral colic is usually accompanied by renal pain due to distension of the renal pelvis.
- 24. Ureteric Colic • The nerve supply of the upper ureter is by T 10; hence pain starts at costo-vertebral angle and radiate around the trunk into the lower quadrant of the abdomen, or possibly into the anterior aspect of upper thigh and testicle(simulates torsion) or labium • Pain in mid-ureter simulates appendicitis or diverticulitis. • In the distal ureter ,the Pain is felt as suprapubic discomfort with LUTS (urgency, frequency) and radiates along urethra to tip of penis.(simulates cystitis) • Often associated with restlessness, nausea, vomiting, sweating, and collapse. • Associated fever chills and haematuria may exist
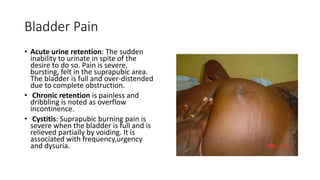
- 25. Bladder Pain • Acute urine retention: The sudden inability to urinate in spite of the desire to do so. Pain is severe, bursting, felt in the suprapubic area. The bladder is full and over-distended due to complete obstruction. • Chronic retention is painless and dribbling is noted as overflow incontinence. • Cystitis: Suprapubic burning pain is severe when the bladder is full and is relieved partially by voiding. It is associated with frequency,urgency and dysuria.
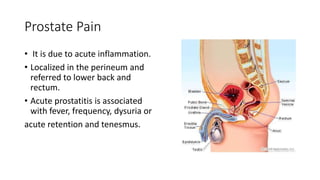
- 26. Prostate Pain • It is due to acute inflammation. • Localized in the perineum and referred to lower back and rectum. • Acute prostatitis is associated with fever, frequency, dysuria or acute retention and tenesmus.
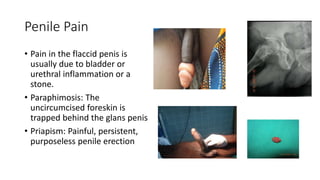
- 27. Penile Pain • Pain in the flaccid penis is usually due to bladder or urethral inflammation or a stone. • Paraphimosis: The uncircumcised foreskin is trapped behind the glans penis • Priapism: Painful, persistent, purposeless penile erection
- 28. Testicular/Scrotal pain • Primary pain is due to acute epididymo-orchitis, torsion of the testis or trauma. • In patients with testicular discomfort and a normal scrotal examination, renal or retroperitoneal disease should be considered. • Referred pain in renal or ureteric colic. • Hydrocele, varicocele and testicular tumour may be associated with scrotal discomfort
- 29. Urethral Pain • Burning or scalding during micturition is usually due to inflammation(gonococcal urethritis) or a stone. • Dysuria is pain or burning sensation during micturition usually caused by inflammation.
- 30. Haematuria-Blood in Urine • 5-25% of patients with haematuria have urologic malignancies
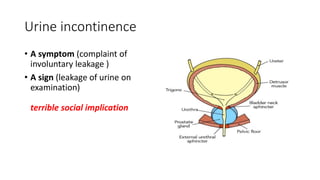
- 31. Urine incontinence • A symptom (complaint of involuntary leakage ) • A sign (leakage of urine on examination) terrible social implication
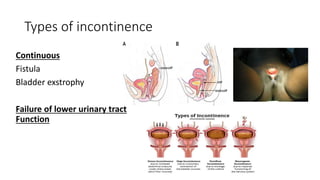
- 32. Types of incontinence Continuous Fistula Bladder exstrophy Failure of lower urinary tract Function
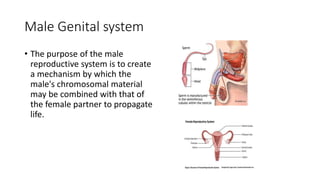
- 33. Male Genital system • The purpose of the male reproductive system is to create a mechanism by which the male's chromosomal material may be combined with that of the female partner to propagate life.
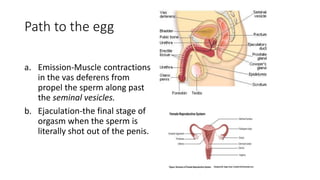
- 34. Path to the egg a. Emission-Muscle contractions in the vas deferens from propel the sperm along past the seminal vesicles. b. Ejaculation-the final stage of orgasm when the sperm is literally shot out of the penis.
- 35. Priapism • Prolonged erection (>6hrs) in the absence of sexual stimulation and not relieved by orgasm. • Priapism is an emergency • Hypoxia leading to erectile dysfunction
- 36. Erectile dysfunction Definition • consistent inability to achieve and maintain a penile erection sufficient to permit satisfactory sexual intercourse. Requirements for a GOOD erection • Good mood(libido) • Good nerves • Good vessels • Good penis
- 37. An Erection Requires a Coordinated Interaction of Multiple Organ Systems • Psychological • Endocrine-DM • Vascular-Cardiovascular System • Neurologic-
- 38. Ejaculatory disorders • Premature ejaculation is persistent occurrence of ejaculation with minimal sexual stimulation before or shortly(LESS THAN 1 min) after penetration. • Retrograde ejaculation is backflow of semen into the bladder due to Anatomic causes e.g. incompetent bladder neck e.g. after bladder neck and prostatic surgery, neurological e.g. spinal cord injuries
- 39. Take Home Message • Always try to understand the anatomical and physiological basis of every symptom and sign • Read Your Books-BAJA • Google