Streptococcus pneumoniae
- 2. INTRODUCTION Gram positive, lanceolate shaped diplococcus Pneumococci Normal inhabitants of the human upper respiratory tract Pneumonia and Otitis media in children Sinusitis, Bronchitis, Bacteremia, Meningitis
- 3. MORPHOLOGY Small, slightly elongated cocci One end broad or rounded and the other pointed Flame shamed or lanceolate Pairs with broad ends in apposition Capsulated Typical morphology may not occur in culture India ink preperation
- 4. CULTURAL CHARACTERISTICS Enriched media Aerobes and facultative anaerobes On Blood agar, colonies are small (0.5 – 1 mm), dome shaped and glistening with α haemolysis Colonies become flat with raised edges and central umbonation Concentric rings on surface when viewed from above Draughtsman or carrom coin appearance Large Mucoid clonies ( types 3 and 7)
- 6. CULTURAL CHARACTERISTICS ß haemolysis in anaerobic conditions due to oxygen labile Hemolysin O Glucose broth – uniform turbidity Autolysis Autolysis is enhanced by bile salts, Sodium lauryl sulphate and surface active agents Heat killed cultures do not undergo autolysis
- 7. BIOCHEMICAL REACTIONS Catalase and oxidase negative Hiss’s serum sugars Ferments Inulin Bile solubility test: If a few drops of 10% sodium deoxycholate are added to 1 mL of an overnight broth culture, the culture clears due to lysis of cocci. Autolytic amidase that cleaves the bond between alanine and muramic acid in the peptidoglycan Amidase is activated by bile salts
- 9. RESISTANCE 52° C for 15 minutes Cultures die on prolonged incubation due to accumulation of toxic peroxides Sensitive to beta lactam antibiotics Optochin (Ethyl hydrocuprein) sensitive
- 10. ANTIGENIC PROPERTIES Capsule Nucleoprotein antigen ‘C’ carbohydrate antigen C – reactive protein (CRP) acute phase protein ( Beta globulin) bacterial infections, inflammation, malignancy and tissue destruction
- 11. CAPSULE Capsular polysaccharide Specific Soluble Substance (SSS) 90 serotypes named 1, 2, 3 and so on Serotyping carried out by agglutination, Precipitation or Quellung reaction Nuefeld (1902) Suspension of S. pneumoniae is mixed on a slide with a drop of type specific antiserum and a loopful of methylene blue Capsule becomes swollen and refractile
- 13. VARIATION Smooth to rough (S – R) variation In the R form, cocci are non capsulated, autoagglutinable and avirulent Spontaneous mutants In tissues R mutants are eliminated by phagocytosis Rough S. pneumoniae of one serotype may be made to produce capsules of the same or different serotype, on treatment with DNA from the respective serotypes Transformation by Griffith
- 14. TOXINS AND VIRULENCE FACTORS Capsular Polysaccharide Protects the cocci from phagocytosis Surface phagocytosis Enhanced virulence of type 3 Non capsulated strains are avirulent Antibody to capsular polysaccharide is protective Pneumolysin Autolysin Oxygen labile hemolysin and leucocidin
- 15. PATHOGENICITY Fatal infection in mice & rabbits Colonise the human Nasopharynx Infection of middle ear, Paranasal sinuses and Respiratory tract Meningitis Bacteremia may lead to infection in the heart, peritoneum or joints Endgoenous infection Exogenous infection
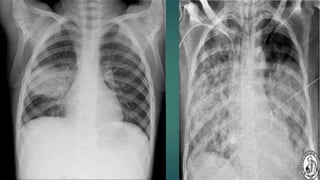
- 16. PATHOGENICITY Lobar and Bronchopneumonia Acute tracheobronchitis and Empyema Aspiration of nasopharyngeal secretions Bacteremia Bronchopneumonia is always a secondary infection in aged and debilitated patients Acute exacerbations in Chronic Bronchitis
- 18. Meningitis Secondary to Pneumonia, Otitis media, Sinusitis or conjunctivitis Occur at all ages Highly fatal 25% fatality even with antibiotic therapy
- 19. SUPPURATIVE LESIONS Empyema Pericarditis Otitis media Sinusitis Conjunctivitis Suppurative arthritis Peritonitis Keratitis and Dacryocystitis
- 20. EPIDEMIOLOGY S. pneumoniae occurs in the throats of 50% of human population Droplets Dissemination is facilitated by crowding Infection usually leads to pharyngeal carriage Disease results when host resistance is lowered by viral infection, stress, malnutrition, immunodeficiency or alcoholism Splenectomy and Sickle cell disease
- 21. Serotypes vary greatly in virulence Type 3 is the most virulent Common infections – Otitis media, Sinusitis Serotypes 6, 14, 19F and 23F are commonly seen in West In adults, type 1 – 8 are responsible for about 75% of Pneumonia In children type 6, 14, 19 and 23 are frequent causes Lobar pneumonia is sporadic Bronchopneumonia increases with an epidemic of Influenza Common in winter and affect the two extreme age groups
- 22. LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Specimen – Sputum, CSF, Blood and Urine Microscopy – Gram stain of rusty sputum Culture – Blood agar (5 – 10% CO2 ) Gentamicin (5 µg/Ml) Blood culture in Glucose broth Mouse inoculation (negative in type 14 strain)
- 23. ANTIGEN DETECTION SSS in CSF can be detected by Precipitation or Latex agglutination test Capsular polysaccharide can be demonstrated by counterimmunoelectrophoresis Immunochromatography CRP Procalcitonin PCR
- 24. PROPHYLAXIS Immunity is type specific 7- valent conjugate vaccine CRM 197 protein of Corynebacterium diptheriae Children from 2 months to 2 years Polyvalent polysaccharide vaccine
- 25. POLYVALENT POLYSACCHARIDE VACCINE Capsular antigens of the 23 most prevalent serotypes 80 – 90 % protection Not meant for general use Absent or Dysfunctional spleen Sickle cell disease Chronic heart, renal, lung and celiac disease Diabetes mellitus HIV
- 26. TREATMENT Parental Penicillin Amoxycillin Alteration in Penicillin Binding Protein Third generation cephalosporins vancomycin
- 27. THANK U