Sulfonamides
- 1. SULFONAMIDES AND COTRIMOXAZOLE
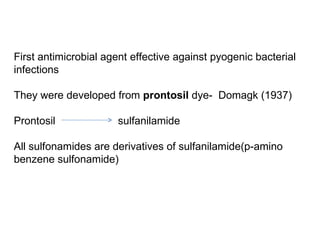
- 2. First antimicrobial agent effective against pyogenic bacterial infections They were developed from prontosil dye- Domagk (1937) Prontosil sulfanilamide All sulfonamides are derivatives of sulfanilamide(p-amino benzene sulfonamide)
- 3. Classification Short acting (4-8hr) Sulfadiazine,sulfadiamidine 2. Intermediate acting (8-12hr) sulfamethoxazole,sulfamoxole 3. Long acting (7 days) sulfadoxine,sulfamethopyrazine 4. Special purpose sulfonamides sulfacetamide sod.,sulfasalazine, mafenide,silver sulfadiazine
- 4. Classification according to therapeutic use Topically applied sulfonamides for eye infection- sulfacetamide(10%,20% & 30%) for skin infection- silver sulfadiazine,mefanide acetate GIT Infections succinylsulfathaizole,phthalylsulfathiazole, sulfaguanidine Meningitis sulfadiazine,sulfadimidine UTI infections sulfioxazole,sulfamethopyrazine
- 5. 5 . Respiratory tract infections sulfaphenazine,cotrimoxazole Leprosy dapsone,solapsone 7. Drugs for bowel disinfection sulfasalazine,pthalylsulfathiazole 8 . Malaria sulfadoxine+pyrimethamine 9. Nocardiosis sulfadiazine,sulfisoxazole
- 6. BACTERIAL SPECTRUM Staphylococcus pneumonia S. Pyogenes H. Influenzae H. Ducrey Nocardia Actinomycin
- 7. Pteridine + PABA dihydropteroate synthetase Dihydroteroic acid glutamate Dihydrofollic acid dihydrofollate reductase Tetrahydrofollic acid sulfonamides (-) trimethoprim (-)
- 8. Resistance Due to increased amount of PABA If folate synthetase has low affinity for sulfonamides alternate path for folate metabolism Increased capacity to destroy drug Gonococci,pneumococci,stapylococci,E.coli
- 9. PHARMACOKINETICS A- GIT D- plasma protein bound 10-95% M- N 4 acetylated sulfonamide E- urine,feaces,bile & milk
- 10. ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS Crystalluria Nausea,vomiting kernicterus
- 11. COTRIMOXAZOLE sulfamethoxazole + trimethoprim (diaminopyrimidine) Trimethoprim is selective inhibitor of bacterial DHFR Individually they both are bacteriostatic but the combination is bacteroicidal
- 12. OPTIMAL SYNERGY sulfamethoxazole : trimethoprim 20 : 1 BBB & placenta- trimethoprim crosses both sulfamethoxazole does not PPB Trimethoprim- less 40% sulfamethoxazole- more 65% MIC trimethoprim- 3µg sulfamethoxazole-0.3µg Combination - Trimethoprim-1µg sulfamethoxazole-0.05µg
- 13. RESISTANCE decreases because resistance to one component may still be killed by other. Resistance to trimethoprim is mostly through mutational or plasmid mediated acquisition of DHFRase having lower affinity for the inhibitor. SPECTRUM Salmonella typhii Enterobacter Yersinia Pneumocystis carinii
- 14. PHARMACOKINETICS A- Trimethoprim is more rapidly absorbed peak blood concentration of T- 2hrs & S- 4hrs. D - V d of trimethoprim is 9 times that of sulfamethoxazole E - T- 60% excreted in 24 hrs S- 25-50% in 24 hrs
- 15. ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS Nausea, vomiting & headache Folate deficiency Blood dyscrasias Patient with renal disease –uremia In elderly-greater risk of bone marrow toxicity
- 16. USES UTI RTI Typhoid Chancroid Bacterial diarrhoeas & dysentery Granuloma inguinale Pneumocystis carinii