SURGICAL ANATOMY OF DEEP NECK SPACES
- 1. Dr. Ajay Manickam MS (ENT) JUNIOR RESIDENT R.G.Kar Medical College
- 2. Extension Anteriorly from lower border of mandible to upper surface of manubrium of sternum Posteriorly from superior nuchal line on occipital bone of skull to c7 and t1 vertebrae Introduction
- 3. Skin – cervical dermatome Muscles – cervical myotomes The branchial apparatus Developmental Anatomy
- 4. 4 compartments provide longitudinal organisation Visceral compartment – anterior – digestive, respiratory & endocrine glands Vertebral compartment – posterior – cervical vertebrae, spinal cord, cervical nerves and muscles 2 vascular compartments – lateral – major blood vessels and vagus nerve Compartments
- 5. Fascia Superficial Deep 1.Superficial layer 2.Middle layer 3. Deep laayer Fascial layers
- 6. Thin sheet of muscle platysma, begins in superficial fascia of thorax, attaches to mandible and blend with muscles of face Penetrated by blood vessel that supply neck skin Subplatysmal flap protects blood supply to the skin Facial nerve- cervical branch Superficial fascia
- 7. Superficial layer Arises from ligamentum nuchaeand spinous process of cervical vertebrae Splits to enclose trapezius,omohyoid,sternocleidomastoid,strap muscles and parotid gland Deep cervical fascia
- 8. Middle layer Derived from superior layer of deep cervical fascia encircles trachea, thyroid, esophagus A. Investing Layer B. Muscular Pretracheal Layer C. Visceral Pretracheal Layer D. Prevertebral Layer Deep cervical fascia
- 9. Deep layer Arise from ligamentum nuchaeand spinous process of cervical vertebra Splits to enclose postvertebral muscles, form layer over vertebrae Floor of post triangle Allows pharynx to glide during deglutition Extends in lower region of neck to axilla – axillary sheath Deep cervical fascia
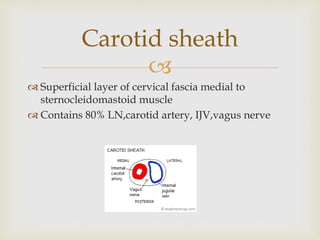
- 10. Superficial layer of cervical fascia medial to sternocleidomastoid muscle Contains 80% LN,carotid artery, IJV,vagus nerve Carotid sheath
- 12. Fascial spaces Between the fascial layers in the neck are spaces that may provide conduit for the spread of infections They contain loose areolar fascia
- 13. Deep Neck Spaces are described in relation to the Hyoid bone. A. Entire length of the neck. B. Suprahyoid. C. Infrahyoid. Classification of neck spaces
- 14. 1. Superficial neck space 2. Deep neck spaces Retropharyngeal space Danger space of Gillette Pre vertebral space Involving entire length of neck
- 15. Sub mental space Submandibular space -Sublingual space -Sub maxillary space Peri tonsillar space Parotid space Para pharyngeal space Masticator space Supra-hyoid
- 16. Pretracheal space Infra hyoid
- 17. Extends from base of skull to tracheal bifurcation Between two parapharyngeal space Superior – skull base Anterior – musculature of pharynx Posteror limit – prevertebral fascia Communicates with – mediastinum It is divided into two lateral compartments space of gillete by fibrous raphe Retropharyngeal space
- 18. There are a group of inconsistent nodes in the retropharyngeal space known as the Glands of Henle which regresses by 5 yrs of age. Suppuration of these nodes result in Ac. Retropharyngeal abscess and thus commoner in children. There is also a constant group of nodes called the Rouvier’s nodes which are the first nodes to enlarge in cases of nasopharyngeal and posterior sinus malignancies. Retropharyngeal space
- 19. Base of skull to diaphragm Located between the pre vertebral fascia and alar fascia Retro pharyngeal space proper is in front of alar fascia This is called danger space because of easy route of mediastinitis Danger space
- 20. Potential space between cervical vertebra posteriorly and the prevertebral fascia anteriorly Extends from base of skull to coccyx Tuberculosis of spine, penetrating traumas chief source of infections Prevertebral space
- 21. Midline space between anterior bellies of digastric muscles Contents – areolar tissue, lymphnode, ant jugular vein Submental space
- 22. Includes submaxillary + sublingual, divided by mylohyoid muscle Superficial boundary – submandibular gland & digastric muscle Deep boundary – mylohyoid muscle Lies between mucous membrane of floor of mouth& tongue on oneside & superficial layer of deep cervical fascia, from mandible to hyoid bone Comunicates with floor of the mouth Submandibular space
- 23. Between capsule of tonsil & superior constrictor Located lateral to the tonsils Infection source is mainly tonsillar crypts Communicates with retropharyngeal & parapharyngeal space Peritonsillar space
- 24. Boundaries The space is circumscribed by the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia superior margin: external auditory canal; apex of the mastoid process inferior margin: inferior mandibular margin (although the parotid tail can extend further inferiorly below the angle of the mandible) anterior margin: masticator space contents parotid glands parotid lymph nodes facial nerve (CN VII) external carotid artery retromandibular vein Fascial layer is very thick superficially , very thin on deep side of gland- burst to parapharyngeal space- mediastinum Parotid space
- 25. Inverted pyramid shaped Para pharyngeal space
- 26. Located between superficial layer of deep cervical fascia & muscles of mastication Extends from base of skull to lower border of mandible Contents muscles of mastication ramus and body of mandible inferior alveolar nerve,vein,artery mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V3) enters the masticator space via the foramen ovale Masticator space
- 27. Anterior and lateral to thyroid cartilage Contains delphian node Communicates – superior mediastinum Pretracheal space
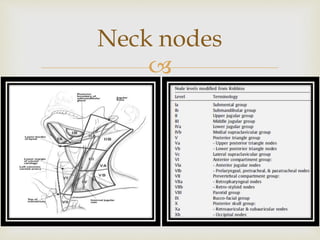
- 28. Neck nodes
- 29.
- 31. Rare, but life threatening infection,that causes progressive necrosis of the subcutaneous fat and fascia and causes secondary necrosis of the overlying skin. ETIOLOGY - Odontogenic infections - Tonsillar infections - As a complication of other DNSI Necrotizing fascitis
- 32. Cellulitis with disproportionate pain. Reduced skin sensation of the involved areas. Outer zone- Erythema Intermediate zone- Tender ecchymosis Central zone- Vesiculation Soft tissue crepitus due to gas formation. Hypocalcemia , Hyponatremia , Dehydration Necrotizing fascitis
- 33. Early correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalance. I.V Penicillin and I.V Metronidazole are the mainstays of the antimicrobial therapy. Surgical debridement of all necrotic areas is the key to successful treatment of the patient. Skin grafting after wound debridement Necrotizing fascitis
- 34. Life threatening infection URI, tuberculous lymphadenitis X-Ray soft tissue neck lateral view, CT Incision & drainage Retropharyngeal space infections
- 35. Children <3yDysphagia and difficulty in breathing. Stridor and Croupy cough maybe present,Torticollis,Bulge in the posterior pharyngeal wall. The child is febrile and adopts a peculiar posture with the neck flexed and the head extended. Straightening of the cervical spine known as Ramrod Spine Radiographic picture of the lateral view of neck (soft tissue) shows widening of the prevertebral space and even the presence of gas shadows(air fluid levels). Acute retropharyngeal abscess
- 36. Incision and Drainage of abscess is done,usually without anaesthesia as there is risk of rupture during intubation.[the child is kept supine with head low and mouth opened with a gag.A vertical incision is given in the most fluctuant area.Suction should always be available to prevent aspiration] Systemic Antibiotics-Broad spectrum antibiotics like Ceftriaxone and Metronidazole may be used. Tracheostomy in airway obstruction Acute retropharyngeal abscess
- 37. TB Spine(Pott’s Spine) where the pus collects in the prevertebral space. TB of retropharyngeal lymph nodes present in the retropharyngeal space proper. Post traumatic-vertebral fracture. Spread from Parapharyngeal abscess Chronic retropharyngeal abscess
- 38. Discomfort in the throat,mild dysphagia. Pain is absent due to cold abscess. Bulge in the posterior pharyngeal wall either centrally or laterally. Neck may show Tubercular lymph nodes. Treatment - Incision and drainage of abscess is done through a vertical incision along the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid for low abscesses, or along its posterior border for high abscesses. Full course of anti-Tubercular therapy is given Retropharyngeal space infections
- 39. Odontogenic infection – submandibular space – submental region Mandibular fractures Cutaneous infection Treatment- I&D Sub mental abscess
- 40. Drooling, trismus, dysphagia, stridor caused by laryngeal edema, and elevation of the posterior tongue against the palate , fever, tachycardia. Aerobe, anaerobe Maintanence of airway Needle aspiration USG or CT guided Submandibular space infection
- 41. Toothache, fever, odynophagia, drooling. SUBLINGUAL space infection -floor of mouth swelling. -tongue elevation. SUBMAXILLARY space infection -brawny/woody tender swelling below the chin. Trismus. Stridor- due to falling back of tongue, laryngeal edema. Initially there is cellulitis which is followed by abscess formation. Submandibular space infection
- 42. Ludwig’s angina Xray showing supraglottic swelling
- 43. Systemic antibiotics- Ceftriaxone/Cefuroxime and Metronidazole/Clindamycin. Tracheostomy if airway is compromised after unsuccessful attempts at oral/nasal intubations. Incision and Drainage of Abscess: intraoral—sublingually localised infection. extraoral—submaxillary infection. A transverse incision extending from one angle of mandible to the other is made with vertical opening of midline musculature of tongue with a blunt haemostat Ludwig’s angina
- 44. Quinsy Tonsillitis Odynophagia, hot potato voice Complication – ludwig’s angina, adjacent spaces Needle aspiration I&D Peri tonsillar space infection
- 45. Peritonsillar abscess is opened at the point of maximum bulge above the upper pole or just lateral to the point of junctionof anterior pillar and a horizontal line drawn through the base of the uvula Interval Tonsillectomy maybe done 4 to 6 weeks after an attack of Quincy. Abscess/Hot Tonsillectomy are preffered by some instead of Incision and drainage. This has the risk of abscess rupture during anaesthesia and excessive bleeding at the time of operation. Incision & drainage
- 46. Acute/Chronic infections of tonsils and adenoid, bursting of the peritonsillar abscess. Dental infection usually from the lower last molar. From Bezold abscess or Petrositis. Infections of parotid, retropharyngeal and submaxillary spaces. Penetrating injuries of neck, injection of L.A for mandibular nerve block or for tonsillectomy. Parapharyngeal space infections
- 47. More common in adults Infective process of upper aerodigestive tract, Trismus, pyrexia, tonsil may be medially displaced USG, CT, needle aspiration under CT or USG guidance Small loculated – conservatively Large collections – external approach, medial to carotid sheath, isertion of a drain Parapharyngeal space infections
- 48. Incision and Drainage -Usually done under G.A. -Pre-op tracheostomy if trismus is marked. -Drained by a horizontal incision made 2-3 cms below the angle of the mandible.Blunt dissection is done along the inner surface of the medial pterygoid towards styloid process and the abscess is evacuated and a drain is inserted. [Transoral drainage should never be done due to the danger of the great vessels which pass through this space.] Parapharyngeal space infection
- 49. Causes Ascent of bacterial infection(Staphylococcus, Streptococcus,Haemophilus) to a dehydrated parotid via Stenson’s duct from oral cavity. Suppuration of intra-parotid LNs. Spread of infection from the auditory canal via the cartlaginous fissures of Santorini or the bony foramen of Huschke. Parotid space infection
- 50. Symptoms Spontaneous onset of painful parotid enlargement followed by fever and cellulitis which then turns into fluctuant parotid abscess. Pain and induration over the parotid. Pitting edema over the parotid area differentiates parotid abscess from simple parotitis Parotid massage expresses pus into the oral cavity via the Stenson’s duct ,opposite the upper 2nd molar. Parotid space infection
- 51. Treatment:- Maintainence of oral hygiene, IV antibiotics Incision and Drainage:- -Blair’s incision made. -Multiple incisions made through fascia parallel to branches of the facial nerve. -Blunt dissection done to evacuate the pus. -Drains are placed. Parotid space
- 52.

































![
Incision and Drainage of abscess is done,usually without
anaesthesia as there is risk of rupture during intubation.[the child
is kept supine with head low and mouth opened with a gag.A
vertical incision is given in the most fluctuant area.Suction should
always be available to prevent aspiration]
Systemic Antibiotics-Broad spectrum antibiotics like Ceftriaxone
and Metronidazole may be used.
Tracheostomy in airway obstruction
Acute retropharyngeal
abscess](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anatomyofdeepneckspacesanditssurgical-160619103705/85/SURGICAL-ANATOMY-OF-DEEP-NECK-SPACES-36-320.jpg)











![
Incision and Drainage
-Usually done under G.A.
-Pre-op tracheostomy if trismus is marked.
-Drained by a horizontal incision made 2-3 cms below
the angle of the mandible.Blunt dissection is done along
the inner surface of the medial pterygoid towards styloid
process and the abscess is evacuated and a drain is
inserted.
[Transoral drainage should never be done due to the
danger of the great vessels which pass through this
space.]
Parapharyngeal space
infection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anatomyofdeepneckspacesanditssurgical-160619103705/85/SURGICAL-ANATOMY-OF-DEEP-NECK-SPACES-48-320.jpg)



