Taeniasis.ppt
- 1. Cestods
- 2. common features of Class Cestoda 1. Adult worm is flattened ribbon-like, without body cavity. 2. The body is composed of a head, neck and segmented strobilus . The head has suckers, rostellum and hooklets or sucking grooves. The neck is the budding zone from which segments are formed. The strobilus consists of immature, mature and pregnant proglottides. 3. They are hermaphroditic. There is a set of female and male reproductive organs in every mature proglottid. 4. Digestive tract is absent. Nutrition is absorbed by villi of body surface. 5. They are biohelminths. Intermediate hosts are indispensable.
- 3. 6. All adult worms parasitize digestive tracts of mammals. 7. The developing stages in intermediate hosts are called metacestode , such as cysticercus , hydatid cyst , cysticercoid , procercoid , plerocercoid. 8. Tapeworms are classified into two orders: Cyclophyllidea : The head is spherical with suckers, hooklets. The uterus has no opening. One intermediate host is required. The eggs contain an oncosphere . They are medically important, such as Taenia solium , Taenia saginata and Echinococcus granulosus Pseudophyllidea : The head is spear-like with sucking grooves. The uterus has an opening. Two or more intermediate hosts are required. The eggs contain a coracidium and have to get into water to develop. Human being occasionally get infection. This worms include Spirometra mansoni and Diphyllobothrium latum.
- 4. Taenia solium(pork tapeworm) Adult worms live in human small intestine causing taeniasis . The larval stage (Cysticercus cellulose lives in pig or human tissues causing human cysticercosis.
- 5. I. Morphology 1. Adult is flattened ribbon-like, creamy write in color, measures about 2-4 m and has 700-1000 proglottides. scolex : global, 1mm. With 4suckers, 1rostellum and 25-50 hooklets arranged in a double crown It consists of neck: it’s the narrowest part of the body and budding zone containing germinative tissue immature proglottides:width>length strobila mature proglottides: width=length gravid proglottides: width<length
- 6. Immature proglottides are transverse rectangle, located in the anterior part of the body and inner organs are developing. Mature proglottides are square in shape and located in the mid part of the body and have 150-200 testes, a centrally straight uterus and 3 lobes of ovary . Pregnant(gravid) proglottides are longitudinal rectangle, located in the posterior part of the body and contain a branched uterus filled with eggs. The number of main branches on each side of the uterus stem is 7-13.
- 8. scolex
- 10. India Ink Technique Note : less than 13 lateral uterine branches (one side).
- 11. 2. Egg, The eggs of Taenia saginata and T. solium are indistinguishable morphologically. The eggs are spherical, diameter 31 to 43 µm, with a thick radially striated brown embryophore . Inside each is an oncosphere with 6 hooklets. t
- 12. 3.Cysticercus cellulose. It is a semitransparent and elliptic bladder, like a white pomegranate seed about 0.6- 1cm. There is fluid and a white scolex with 4 suckers and hooklets in the bladder.
- 13. Under stimulation of bile The scolex invaginates in the bladder The scolex evaginates
- 16. II. Life cycle 1. final host: man, 2. Intermediate host: pig (or man), 3. Infective stage: cysticercus and egg, 4. Infective mode: eating raw bean-pork, 5. Site of inhabitation: adult in small intestine; cysticercus in tissues, 6. Infective mode of cysticercosis: endogenous, exogenous auto-infection and foreign source; 7. Life span: more than 25 years; cysticercus can survives 5-6 years in human body.
- 18. Life Cycle of Taenia solium Attach to intestinal mucosa scolex evaginates adults grivad proglottides develop into fall off duodenum In human small intestine and are 2-3 months discharged in feces man eats cysticercus in raw pork ───────────────────────────── Pig ingests eggs In intermediate hosts man gets infection 60-70days develop into cysticercus onchosphere hatch in all parts of the body larval migration in duodenum penetrate intestinal wall into blood stream
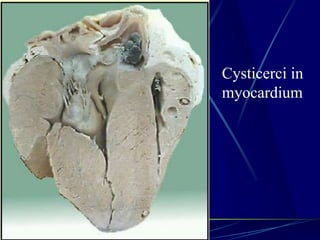
- 19. III. Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestations 1. Taeniasis: It is caused by the adult residing in small intestine of the man. The adult irritates the small intestine causing discomforts, such as abdominal pain, anorexia, chronic indigestion, diarrhea, emaciation, eosinophilia and etc. The patient is usually no obvious symptom, only complaining passing proglottides. 2. Cysticercosis: It is caused by the cysticerci living in human tissues. The manifestations vary with the number of cysticerci and the tissues and organs involved. Cysticercosis is divided into three types.
- 20. The subcutaneous nodules are usually found in head, limbs, neck, abdomen and back. They are movable and painless. (1) Subcutaneous type:
- 21. Note this cysticercus in the tongue
- 22. The cysticercus is usually found in the vitreous body or subretina. Visual disturbance often occurs. The died body of worm may provokes local inflammation causing blindness. (2) Ocular type:
- 23. (3) Brain type: The symptoms are related to the site of infection. The patients may manifest headache, nausea, vomiting, epilepsy ( 癫 痫 ), paralysis ( 瘫 痪 ), weakness in limbs, diplopia(复视), dizziness, mental disorder. Epilepsy is the most frequent symptoms of brain cysticercosis.
- 24. Brain type
- 25. IV. Diagnosis 1.Taeniasis: Confirmative diagnosis of taeniasis is made by finding gravid proglottides or egg in stool. (1) direct fecal smear (2) brine floatation technique **(3) cellophane-tape technique 2. Cysticercosis: Biopsy of subcutaneous nodules, X- ray ,CT 0r MR are used for the diagnosis of brain type and ophthalmoscope examination is used for ocular form. 3. Immunological tests are for reference only.
- 26. V. Treatment and prevention 1. Treatment of Taeniasis: (1)The recognition of a scolex in the patient’s stool after the application of taenifuge is important. When the entire worm has been expelled, the therapy is successful, otherwise the strobila regrow. (2) Praziquantel may be used.
- 27. 2. Treatment of cysticercosis: Surgical removal is required for ocular and superficial cysticercoses. Praziquantel may be used to treat brain cysticercosis , but the patients should take praziquantel in hospital. 3. Prevention: (1) Health education (2) Avoid eating raw bean-pork. (3)avoid pigs eating human stool. (4) sanitary inspection of slaughter and sanitary disposal of night soil. VI. Epidemiology This disease is prevalent all over the world except Muslim and Jew areas. The infection of T. solium is closely associated with the method of pig-raising and the sanitary condition.
- 28. Taenia saginata Adult worms live in human small intestine causing taeniasis. Larval stage (Cysticercus bovis) lives in cattle tissues. This disease is prevalent all over the world.
- 29. 1. Body length T. solium T. saginata Differences between T. solium and T. saginata
- 30. 2. scolex T. solium T. saganita
- 31. 3. Mature proglottid T. solium T. saginata
- 32. 4. Gravid proglottid . T. solium T. saginata
- 33. 5. cysticercus Cysticercus cellulose Cysticercus bovis
- 34. I. Morphology: 1. The biological differences between T. solium and T. saginata ______________________________________________________________________________ Adult T. solium T. saginata ______________________________________________________________________________ length 2-4 meters 4-8 meters scolex 1mm in diameter with 2mm in diameter, with 4 suckers and hooklets 4 suckers but no hooklets Number of segment 700 to 1000 1000 to 2000 Mature proglottid 3 lobes of ovary 2 lobes of ovary Gravid proglottid 7-13 uterine lateral 15-30 uterine lateral branches on one side branches on one side Number of gravid usually several segments usually single segment proglottid detached Mode of proglottids passively expelled actively migrate out of anus passing out Cysticercus scolex with hooklets no hooklets on scolex found in man and pig only found in cattle Disease caused in man taeniasis and cysticercosis taeniasis ______________________________________________________________________ 2. Egg: same as that of T solium
- 35. II. Life cycle The intermediate host is cattle and cysticercus bovis can not live in human. The others same as those of T. solium. III. Pathogenesis: Usually only single worm is present and the patient is no symptom. Some patients may complain of migrating proglottids from anus with pruritus at the perianal region. Abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea may occur.
- 36. IV. Diagnosis Finding of gravid proglottids or eggs at the perianal region by cellophane tape method. V. Epidemiology: T. saginata has a world-wide distribution. Human infection is acquired from consumption of raw beef containing the cysticercus bovis. Cattle become infected from grazing on the ground polluted by human feces containing the eggs of the parasite. It is important to have latrines and manure pits far away from the pastures. VI. Treatment: Same as tha of T. solium