Training on php by cyber security infotech (csi)
- 1. Training on PHP by Cyber security Infotech (csi) http://www.csinfotech.org/
- 2. About the company Cs-infotech is one of the best cyber security and website development company in India. we also provide Network security, software development, Cyber security corporate training and SEO and SMO services. Our services are Employee Monitoring System, Employee Monitoring Software, Website Audit, Network Security, Network Audit and Information Security.
- 3. What we'll cover A short history of php Parsing Variables Arrays Operators Functions Control Structures External Data Files
- 4. Background PHP is server side scripting system PHP stands for "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor" Syntax based on Perl, Java, and C Very good for creating dynamic content Powerful, but somewhat risky! If you want to focus on one system for dynamic content, this is a good one to choose
- 5. History Started as a Perl hack in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf (to handle his resume), developed to PHP/FI 2.0 By 1997 up to PHP 3.0 with a new parser engine by Zeev Suraski and Andi Gutmans Version 5.2.4 is current version, rewritten by Zend (www.zend.com) to include a number of features, such as an object model Current is version 5 php is one of the premier examples of what an open source project can be
- 6. About Zend A Commercial Enterprise Zend provides Zend engine for PHP for free They provide other products and services for a fee Server side caching and other optimizations Encoding in Zend's intermediate format to protect source code IDE-a developer's package with tools to make life easier Support and training services Zend's web site is a great resource
- 7. PHP 5 ArchitectureZend engine as parser (Andi Gutmans and Zeev Suraski) SAPI is a web server abstraction layer PHP components now self contained (ODBC, Java, LDAP, etc.) This structure is a good general design for software (compare to OSI model, and middleware applications)
- 8. PHP ScriptsTypically file ends in .php--this is set by the web server configuration Separated in files with the <?php ?> tag php commands can make up an entire file, or can be contained in html--this is a choice…. Program lines end in ";" or you get an error Server recognizes embedded script and executes Result is passed to browser, source isn't visible <P> <?php $myvar = "Hello World!"; echo $myvar; ?> </P>
- 9. Parsing We've talk about how the browser can read a text file and process it, that's a basic parsing method Parsing involves acting on relevant portions of a file and ignoring others Browsers parse web pages as they load Web servers with server side technologies like php parse web pages as they are being passed out to the browser Parsing does represent work, so there is a cost
- 10. Two WaysYou can embed sections of php inside html: Or you can call html from php: <BODY> <P> <?php $myvar = "Hello World!"; echo $myvar; </BODY> <?php echo "<html><head><title>Howdy</title> … ?>
- 11. What do we know already? Much of what we learned about javascript holds true in php (but not all!), and other languages as well $name = "bil"; echo "Howdy, my name is $name"; echo "What will $name be in this line?"; echo 'What will $name be in this line?'; echo 'What's wrong with this line?'; if ($name == "bil") { // Hey, what's this? echo "got a match!"; }
- 12. VariablesTyped by context (but one can force type), so it's loose Begin with "$" (unlike javascript!) Assigned by value $foo = "Bob"; $bar = $foo; Assigned by reference, this links vars $bar = &$foo; Some are preassigned, server and env vars For example, there are PHP vars, eg. PHP_SELF, HTTP_GET_VARS
- 13. phpinfo() The phpinfo() function shows the php environment Use this to read system and server variables, setting stored in php.ini, versions, and modules Notice that many of these data are in arrays This is the first script you should write…
- 14. Variable Variables Using the value of a variable as the name of a second variable) $a = "hello"; $$a = "world"; Thus: echo "$a ${$a}"; Is the same as: echo "$a $hello"; But $$a echoes as "$hello"….
- 15. OperatorsArithmetic (+, -, *, /, %) and String (.)Arithmetic (+, -, *, /, %) and String (.) Assignment (=) and combined assignmentAssignment (=) and combined assignment $a = 3; $a += 5; // sets $a to 8; $b = "Hello "; $b .= "There!"; // sets $b to "Hello There!"; Bitwise (&, |, ^, ~, <<, >>)Bitwise (&, |, ^, ~, <<, >>) $a ^ $b (Xor: Bits that are set in $a or $b but not both are set.) ~ $a (Not: Bits that are set in $a are not set, and vice versa.) Comparison (==, ===, !=, !==, <, >, <=, >=)Comparison (==, ===, !=, !==, <, >, <=, >=)
- 16. Coercion Just like javascript, php is loosely typed Coercion occurs the same way If you concatenate a number and string, the number becomesa string
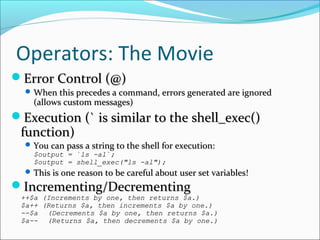
- 17. Operators: The Movie Error Control (@)Error Control (@) When this precedes a command, errors generated are ignoredWhen this precedes a command, errors generated are ignored (allows custom messages)(allows custom messages) Execution (` is similar to the shell_exec()Execution (` is similar to the shell_exec() function)function) You can pass a string to the shell for execution:You can pass a string to the shell for execution: $output = `ls -al`;$output = `ls -al`; $output = shell_exec("ls -al");$output = shell_exec("ls -al"); This is one reason to be careful about user set variables!This is one reason to be careful about user set variables! Incrementing/DecrementingIncrementing/Decrementing ++$a (Increments by one, then returns $a.)++$a (Increments by one, then returns $a.) $a++ (Returns $a, then increments $a by one.)$a++ (Returns $a, then increments $a by one.) --$a--$a (Decrements $a by one, then returns $a.)(Decrements $a by one, then returns $a.) $a--$a-- (Returns $a, then decrements $a by one.)(Returns $a, then decrements $a by one.)
- 18. Son of the Valley of Operators Logical $a and $b And True if both $a and $b are true. $a or $b Or True if either $a or $b is true. $a xor $b Xor True if either $a or $b is true, but not both. ! $a Not True if $a is not true. $a && $b And True if both $a and $b are true. $a || $b Or True if either $a or $b is true. The two ands and ors have different precedence rules, "and" and "or" are lower precedence than "&&" and "||" Use parentheses to resolve precedence problems or just to be clearer
- 19. Control Structures Wide Variety available if, else, elseif while, do-while for, foreach break, continue, switch require, include, require_once, include_once
- 20. Control Structures Mostly parallel to what we've covered already in javascript if, elseif, else, while, for, foreach, break and continue
- 21. Switch Switch, which we've seen, is very useful These two do the same things…. if ($i == 0) { echo "i equals 0"; } elseif ($i == 1) { echo "i equals 1"; } elseif ($i == 2) { echo "i equals 2"; } switch ($i) { case 0: echo "i equals 0"; break; case 1: echo "i equals 1"; break; case 2: echo "i equals 2"; break; }
- 22. Nesting Filesrequire(), include(), include_once(), require_once() are usedrequire(), include(), include_once(), require_once() are used to bring in an external fileto bring in an external file This lets you use the same chunk of code in a number ofThis lets you use the same chunk of code in a number of pages, or read other kinds of files into your programpages, or read other kinds of files into your program Be VERY careful of using these anywhere close to userBe VERY careful of using these anywhere close to user input--if a hacker can specify the file to be included, that fileinput--if a hacker can specify the file to be included, that file will execute within your script, with whatever rights yourwill execute within your script, with whatever rights your script has (readfile is a good alternative if you just want thescript has (readfile is a good alternative if you just want the file, but don't need to execute it)file, but don't need to execute it) Yes, Virginia, remote files can be specifiedYes, Virginia, remote files can be specified
- 23. Example: A Dynamic Table I hate writing html tables You can build one in php This example uses pictures and builds a table with pictures in one column, and captions in another The captions are drawn from text files I'm using tables, but you could use css for placement easily…
- 24. ArraysYou can create an array with the array function, or use the explode function (this is very useful when reading files into web programs…) $my_array = array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); $pizza = "piece1 piece2 piece3 piece4 piece5 piece6"; $pieces = explode(" ", $pizza); An array is simply a variable representing a keyed list A list of values or variables If a variable, that var can also be an array Each variable in the list has a key The key can be a number or a text label
- 25. ArraysArrays are lists, or lists of lists, or list of lists of lists, you get the idea--Arrays can be multi-dimensional Array elements can be addressed by either by number or by name (strings) If you want to see the structure of an array, use the print_r function to recursively print an array inside of pre tags
- 26. Text versus KeysText keys work like number keys (well, really, it's the other way around--number keys are just labels) You assign and call them the same way, except you have to assign the label to the value or variables, eg: echo "$my_text_array[third]"; $my_text_array = array(first=>1, second=>2, third=>3); echo "<pre>"; print_r($my_text_array); echo "</pre>";
- 27. Walking ArraysUse a loop, eg a foreach loop to walk through an array while loops also work for arrays with numeric keys--just set a variable for the loop, and make sure to increment that variable within the loop $colors = array('red', 'blue', 'green', 'yellow'); foreach ($colors as $color) { echo "Do you like $color?n"; }
- 28. 05_arrays.phpYou can't echo an array directly… You can walk through an echo or print() line by line You can use print_r(), this will show you the structure of complex arrays--that output is to the right, and it's handy for learning the structure of an array Array ( [1] => Array ( [sku] => A13412 [quantity] => 10 [item] => Whirly Widgets [price] => .50 ) [2] => Array ( [sku] => A43214 [quantity] => 142 [item] => Widget Nuts [price] => .05 )
- 29. Multidimensional ArraysA one dimensional array is a list, a spreadsheet or other columnar data is two dimensional… Basically, you can make an array of arrays $multiD = array ( "fruits" => array("myfavorite" => "orange", "yuck" => "banana", "yum" => "apple"), "numbers" => array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), "holes" => array("first", 5 => "second", "third") ); The structure can be built array by array, or declared with a single statement You can reference individual elements by nesting: echo "<p>Yes, we have no " . $multiD["fruits"]["yuck"] . " (ok by me).</p>";
- 30. Getting Data into arrays You can directly read data into individual array slots via a direct assignment: $pieces[5] = "poulet resistance"; From a file: Use the file command to read a delimited file (the delimiter can be any unique char): $pizza = file(./our_pizzas.txt) Use explode to create an array from a line within a loop: $pieces = explode(" ", $pizza);
- 31. The Surface The power of php lies partially in the wealth of functions---for example, the 40+ array functions array_flip() swaps keys for values array_count_values() returns an associative array of all values in an array, and their frequency array_rand() pulls a random element array_unique() removes duppies array_walk() applies a user defined function to each element of an array (so you can dice all of a dataset) count() returns the number of elements in an array array_search() returns the key for the first match in an array
- 32. Using External Data You can build dynamic pages with just the information in a php script But where php shines is in building pages out of external data sources, so that the web pages change when the data does Most of the time, people think of a database like MySQL as the backend, but you can also use text or other files, LDAP, pretty much anything….
- 33. Standard data filesNormally you'd use a tab delimited file, but you can use pretty much anything as a delimiter Files get read as arrays, one line per slot Remember each line ends in n, you should clean this up, and be careful about white space Once the file is read, you can use explode to break the lines into fields, one at a time, in a loop….
- 34. Standard data filesYou can use trim() to clean white space and returns instead of str_replace() Notice that this is building an array of arrays $items=file("./mydata.txt");$items=file("./mydata.txt"); foreach ($items as $line)foreach ($items as $line) {{ $line = str_replace("n", "", $line);$line = str_replace("n", "", $line); $line = explode("t", $line);$line = explode("t", $line); // do something with $line array// do something with $line array }}
- 35. Useful string functions str_replace() trim(), ltrim(), rtrim() implode(), explode() addslashes(), stripslashes() htmlentities(), html_entity_decode(), htmlspecialchars() striptags()
- 36. 06_more_arrays.php This is a simple script to read and process a text file The data file is tab delimited and has the column titles as the first line of the file
- 37. How it works The script uses the first line to build text labels for the subsequent lines, so that the array elements can be called by the text label If you add a new column, this script compensates Text based arrays are not position dependent… This script could be the basis of a nice function There are two version of this, calling two different datafiles, but that's the only difference
- 38. 06a_more_arrays.php This version shows how to dynamically build a table in the html output
- 39. Alternative syntax Applies to if, while, for, foreach, and switch Change the opening brace to a colon Change the closing brace to an endxxx statement <?php if ($a == 5): ?> A is equal to 5 <?php endif; ?> <?php if ($a == 5): echo "a equals 5"; echo "..."; else: echo "a is not 5"; endif; ?>

























![Text versus KeysText keys work like number keys (well, really, it's
the other way around--number keys are just labels)
You assign and call them the same way, except you
have to assign the label to the value or variables, eg:
echo "$my_text_array[third]";
$my_text_array = array(first=>1, second=>2, third=>3);
echo "<pre>";
print_r($my_text_array);
echo "</pre>";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingonphpbycybersecurityinfotechcsi-151130074614-lva1-app6891/85/Training-on-php-by-cyber-security-infotech-csi-26-320.jpg)

![05_arrays.phpYou can't echo an array
directly…
You can walk through an
echo or print() line by
line
You can use print_r(),
this will show you the
structure of complex
arrays--that output is to
the right, and it's handy
for learning the structure
of an array
Array
(
[1] => Array
(
[sku] => A13412
[quantity] => 10
[item] => Whirly Widgets
[price] => .50
)
[2] => Array
(
[sku] => A43214
[quantity] => 142
[item] => Widget Nuts
[price] => .05
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingonphpbycybersecurityinfotechcsi-151130074614-lva1-app6891/85/Training-on-php-by-cyber-security-infotech-csi-28-320.jpg)
![Multidimensional ArraysA one dimensional array is a list, a spreadsheet or other columnar
data is two dimensional…
Basically, you can make an array of arrays
$multiD = array
(
"fruits" => array("myfavorite" => "orange", "yuck" =>
"banana", "yum" => "apple"),
"numbers" => array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6),
"holes" => array("first", 5 => "second", "third")
);
The structure can be built array by array, or declared with a
single statement
You can reference individual elements by nesting:
echo "<p>Yes, we have no " . $multiD["fruits"]["yuck"] . "
(ok by me).</p>";
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingonphpbycybersecurityinfotechcsi-151130074614-lva1-app6891/85/Training-on-php-by-cyber-security-infotech-csi-29-320.jpg)
![Getting Data into arrays
You can directly read data into individual array slots
via a direct assignment:
$pieces[5] = "poulet resistance";
From a file:
Use the file command to read a delimited file (the
delimiter can be any unique char):
$pizza = file(./our_pizzas.txt)
Use explode to create an array from a line within a loop:
$pieces = explode(" ", $pizza);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trainingonphpbycybersecurityinfotechcsi-151130074614-lva1-app6891/85/Training-on-php-by-cyber-security-infotech-csi-30-320.jpg)








