Trematodes
- 2. Trematodes : Flukes • 1) INTRODUCTION • Unsegemented helminthes • Leaf of tree or flatfish (fluke) • Trematode (suckers with hole in middle) • Trematode : (trema : hole and eidos : appearance)
- 3. • I) Habitat classification :
- 4. 3) General characters • 1)Morphology : adult worm , egg and larva • i) Adult worm: unsegmented , Flattened dorsoventrally. • A) size : 1mm to 6mm • B) suckers: oral (mouth) and ventral suckers • SEX NOT SEPERATE (EXCEPT SCHISTOSOMES)
- 6. SCHISTOSOMES MALE AND FEMALE
- 7. • Ii)Egg: oviparous(egg larva) • All operculated except schistosome (nonoperculated –urine (spine) • enviroment
- 8. • III) Larvae : 5-larval (miracidium , sporocyst , redia, cercaria and metacerceria)
- 9. 4)Lifecycle • i) Definitive host :Mammals , humans or animals • Ii) Intermediate host : freshwater molluscs or snail • Second intermediate host : Fish or Crab (encystment) • Schistosomes not need 2nd intermediate host
- 10. Rediae : 2nd generation No rediae in schistosomes
- 11. Difference in life cycle of other trematodes and schistosomes Metacerceria larvae (I.F in s.i.h -fish) human by ingestion lung, liver, intestine, bile duct Adult worm self fertilized (egg) feses and sputum miracidium larvae Ingested by snail (1st i.h) sporocyte redia(1st & 2nd ) infective to man cercaria metacercaria S.i.h (fish) cerceria larvae (water) Human Skin penetration Enter venus circulation intestine &kidney Adult worm Cross fertilized Egg in urine and stool Miracisium in water Snail (1st i.h) Sporocyte (1st and 2nd ) Cercaria in water Clonorchis & opisthorchis
- 12. 5)MODE OF INFECTION • i) Ingestion (cercaeria): • A) Vegetables: F.Hepatica , F.buski , W.watsoni • B) fish: C.cinensis , H.heterophyes , M.yokogawai • C) fish of crab or crayfish: P.westermani • Ii) skin penetration: S.haematobium , S.mansoni , S.japonicum
- 13. 6) Blood Flukes • A) Schistosomes : • Sex seperate (dioecious) • Schistossommiasis (water born disease) • Africa , Latin America and Asia • Schistosoma haematobium, S. japonicum, S. mansoni , S. mekongi and S. intercalatum
- 14. • B) Order :strigeida • C) Superfamily : schistosomatoidea • D) Family : schistosomatidae • E) Morphology: : adult worm , egg and larva •
- 15. • Ii) eggs: • 1) 70-180 micro m X 40-73 breadth • 2) non operculated with spine • S.haematobium :terminal • S.mansoni: lateral • S.japonicum: lateral rudimentary spine
- 16. • Iii) larva:miracidium , sporocyts (1st & 2nd ) & cercaria (infective form )
- 19. Egg cell: not acidfast Miracidium larvae in egg :acid fast Egg shell : acid fast Egg shell : acid fast
- 20. f) Mechanism of Egg Expulsion LAID • EGG LAID enter into vesicle wall by spine Small venus and pelvic pelvic plexus , (mescentric portal system ,pulmonary arteries ) Release : lytic substance passes Lumen of urinary bladder Discharged : urine Skin –local tissue irritation Egg –in feces
- 21. g) Life cycle of schistosomiasis
- 22. i) Antigen from egg stimulate HMI Immune complex and serum sikness (c/d katyama fever) h) Pathogenesis and clinical features Cercariae (skin penetration ) dermatitis , pruritis Lung :cough with fever
- 23. • a) urogenital disease : (s.hematobium) • Symptomatic after 3 months • EGG: pathogenic • Egg urinary bladder (dysuria and hematuria) D.Hypersensitivity Urinary bladder Granuloma of macrophage , lymphocyte etc Granuloma join together Granular metaplasia Heavy infection Elephanthasis of scrotum and penis Important pathogen in HIV ii) Chronic schistosomiasis
- 24. • iii) Obstructive utropathies : (s.hematobium) • Fibrosis • iv) Bladder carcinoma: (s.hematobium) due to metaplastic change • i) predisposing factor : • Diet containing nitroso compound (cheese , beans etc) • Secondary bacterial infection Obstruction in lower ureters Hydroureter and hydronephrosis
- 25. v) vi) Hepatosplenic disese : (S.Mansoni & japonicum) Granuloma formation and fibrosis in liver (symmers pipestem fibrosis) Hypension , hepatomegaly , splenomegaly
- 26. • vii) cerebral schistosomiasis : s.japonicum • 2-4% of cases • Symptoms : jacksonian convulsion and grand male fever
- 27. j) LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Urine microscopy : urine and stool (rarely) for nonoporculated egg Collection time : 12pm to 3pm Histopathology : egg in bladder mucosa biopsy Ab detection in serum IgE & igG4 : I) HAMA – FALCON ASSAY SCREENING TEST –ELISA II) HAMA –EITB (ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOTRANSFER BLOT 1) ANTIGEN DETECTION : A) Circulating cathodic antige (CCA) in serum and urine by ELISA B) ELISA based specific monocolonal AB against (M Ab – SEA)
- 28. h) TREATMENT • A) Praziquantel : 20 mg /kg/dose , two dose in single day • B) Metrifonate : inhibits acetylcholine receptor on adult male worm . Multiple dose for a week
- 29. 7)Liver flukes • 1)Fasciola hepatica and F.gigantica • 2)Colonorchis sinensis • 3)Opisthorichis species • 4)Dicrocoelium dendriticum
- 30. 1)Fasciola hepatica • i) largest and most common in human(Greater liver fluke) • Ii) Sheep (sheep liver fluke) • Iii) G.D : Egypt • Iv) host: Herbivorous animals and accidently man • V)Habitat :liver and bile duct • Vi) Disease: Fascioliasis(Liver Rot)
- 31. • Vii) Morphology : • A) Adult: • Leaf • length 30mm long and 15mm broad. • Anteriorly (conical) and posteriorly (round) • Testes: Two • Ovary: One
- 32. • B) Eggs: • 140umx80um • Oval • Operculated • immature embryo • Bile stained
- 33. • C) larva: • metacercaria (infective form) • Miracidia • Rediae • Sporocyst
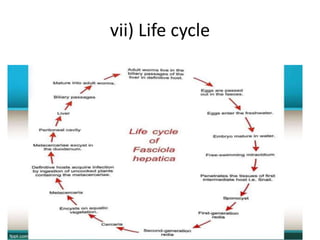
- 34. vii) Life cycle
- 36. viii) Pathogenesis, clinical and complications • 2 phages • i) Acute or invasive phase: fever , right upper quandrant pain , hepatomegaly and eosinophilia • symptoms appear 2 weeks after the infection • due to: • Mechanical injury. • Parasite toxin. • Allergy to parasite ex-product • Anemia and dyspepsia
- 37. • Ii) Chronic stage: • maturing worm in the bile duct • A) Ectopic fascioliasis • In lung • Subcutaneous tissue • Rare central nervous system(rare) Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis ,Jaundice , Liver fibrosis
- 38. • B) Halzoun (marrare sybdrome) • Uncooked meat of sheep goat • form of acute laryngopharyngitis.
- 40. 2)
- 41. • Eggs : • flask shaped • Operculum (prominent shoulder and common shaped knob)
- 42. • Larvae : • metacercaria (infective form) • Miracidia • Rediae • Sporocyst
- 43. • Mode of transmission • Eating of frozen, dried or pickled fish (metacercariae).
- 44. Life cycle
- 46. Pathogenesis • cholangitis. • Cholangiocarcinoma. • Calculus formation. • Few cases : • Biliary cirrhosis. • Portalhypertension.
- 47. • Clinical Picture : • Fever • epigastric pain • diarrhea • tender hepatomegaly • biliary colic • obstructive jaundice.
- 49. INTESTINAL FLUKES PROPERTIES F.BUSKI Habitat Jejunum and duodenum (man & pig) Epidermiology U.P , bihar , west bengal Assam and maharastra Adult worm 2-7.5 cm Cephalic cone Absent Suckers Oral and ventral egg Biled stained Larvae Metacerceria (I.F) Host D.H-PIG /MAN , 2 I.H- SNAIL , PLANT
- 50. PATHOGRNESIS MALABSORPTION WITH YELLOWISH GREEN COLOUR STOOL
- 51. LAB DIAGNOSIS • STOOL : oporculated egg
- 52. Lung fluke (paragonium westermani/oriental lung fluke) Properties paragonium westermani Epidermiology Manipur , north east states of india Habitat Paranchyma of lung Adult worm Reddish brown , broad anterior end , Excretory bladder : divided body into 2 part egg Oval , golden brown, 80-120 micro m X 45- 65 micro m larvae Metacerceria (I.F) , Host D.H- (Man , dog , cat) , 2 I.H – (Snail , crab)
- 55. Pathogenesis Intestinal complication Pulmonary paragonimiasis Extrapulmonary paragonimiasis Abdominal tederness Initially : eosinophilic granulomatous inflamation Cerebral paragonimiasis : fever , headeche vomiting and motor weakness Nausea Cyst surrounding worm Cutaneous paragonimiasis : subcutaneous nodule Vomiting Cyst (blood & fluid ) Cyst break into bronchioles Expectoration of brownish blood sputum with offensive fishy order Bronchitis, bronchiectasis ,pneumonia and lung abscess
- 56. Laboratory diagnosis 1) Sputum microscopy : early morning sample mount with saline (operculated egg) 2) Formal ether method 3) Stool microscope in children (sputum difficult to collect) Serology : 1) Ab detection : a) Rapid test : dot immunogold filtration assay , ELISA (IgG or IgE) 2) Antigen detection : dot ELISA (ACTIVE INFECTION) MRI , CT scan (cyst in CNS)