Understanding Marketing Processes and Consumer Behavior
- 1. Understanding Marketing Processes and Consumer Behavior
- 2. What Is Marketing? Process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational objectives
- 3. What Is a Marketing Plan? Detailed strategy for focusing marketing efforts on consumer needs and wants
- 4. Who Are Marketing Managers? Manager who plans and implements the marketing activities that result in the transfer of products or services from producer to consumer
- 5. Marketing: Providing Value and Satisfaction Value and Benefits Value is the relative comparison of a product’s benefits versus its costs Benefits include the functions of the product and the emotional satisfaction associated with owning, experiencing or possessing it
- 6. Marketing: Providing Value and Satisfaction Value and Utility Utility is the ability of a product to satisfy a human want or need. Four kinds: Time Utility Place Utility Ownership Utility Form Utility
- 7. What Is Relationship Marketing? Marketing strategy that emphasizes lasting relationships with customers and suppliers
- 8. Marketing: Goods, Services and Ideas Consumer goods are products purchased by consumers for personal use Industrial goods are products used by companies to produce other products Services are intangible products that can be purchased
- 9. The Marketing Environment External environment is the combination of outside factors that influence marketing programs by posing opportunities and threats. Five environmental factors: Political–Legal Environment Social–Cultural Environment Technological Environment Economic Environment Competitive Environments
- 10. The External Marketing Environment
- 11. Competitive Environment Substitute products differ from those of competitors but can fill the same need
- 12. Competitive Environment Brand competition occurs between similar products
- 13. Competitive Environment International competition matches domestic products against foreign products e.g. Tapal vs Lipton
- 14. What Is the Marketing Mix (or the “Four P’s”)? Combination of product, pricing, promotion and distribution (place) strategies used to market products
- 15. What Is a Product? A product is a good, service or idea designed to fill a consumer need or want.
- 16. What Is a Product? Product differentiation is the creation of a product feature or product image that differs enough from competing products to attract consumers How do they differentiate themselves?
- 17. What Is Pricing? Pricing is the process of selecting the best price at which to sell a product. Prices must support a variety of costs Prices must be competitive Low- and high-price strategies can be effective in different situations
- 18. What Is Distribution (Place)? Distribution is part of the marketing mix concerned with getting products from producers to consumers. Decisions about warehousing, inventory control and transportation options Decisions about channels
- 19. What Is Promotion? Promotion is the techniques for communicating information about products. There are different promotional tools e.g. Advertising Personal Selling Sales Promotions Public Relations
- 20. What Is Target Marketing and Market Segmentation? Target markets are groups of people with similar wants and needs Market segmentation is the process of dividing a market into categories of customer types
- 21. Identifying Market Segments Geographic variables are geographical units e.g. provinces, cities etc. Demographic variables are characteristics of populations e.g. Age, Gender, Education, Income, Occupation, Marital Status, Parental Status etc.
- 22. Identifying Market Segments Psychographic variables are consumer characteristics such as lifestyles, personality and attitudes Behavioral variables are consumer characteristics based on the use of a product, benefits sought from it, reasons for its purchase and brand loyalty Toothpaste with: -Whiteners -Fluoride -Mouth Freshener - Medicaments
- 23. What Is Brand Loyalty? Pattern of regular consumer purchasing based on satisfaction with a product
- 24. What Is Marketing Research? Study of consumer needs and wants and the ways in which sellers can best meet them
- 25. The Research Process . Study the current situation . Select a research method . Collect data Secondary data is already available from previous research Primary data is collected through new research . Analyze the data . Prepare a report
- 26. Research Methods Observation involves watching and recording consumer behavior Survey uses a questionnaire which serves as the basis of interviews
- 27. Research Methods Focus group involves a small gathering of people who are presented with an issue and asked to discuss it in depth Experimentation compares the responses of the same or similar people under different circumstances under a controlled environment
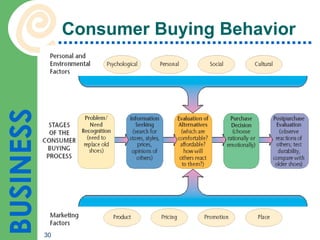
- 28. What Is Consumer Behavior? Study of the decision process by which people buy and consume products
- 29. Influences on Consumer Behavior Psychological influences : individual’s motivations, perceptions and attitudes Personal influences: lifestyle, personality and economic status Social influences : family, opinion leaders and reference groups Cultural influences : culture, subculture and social class