Unit 1 ch 1 3
- 1. Warmup 8/30 Has the discovery of America been beneficial or harmful to the human race? Explain in at least 3-5 sentences.
- 2. Pre-Contact Americas, Discovery & ColonializationMs. JosephsonWoodrow Wilson Senior High SchoolAP US History
- 3. What is the significance of 1492? Discovery or holocaust?Uninhabited land or 50+ million people?Greater positives than negatives? Introduction of slave trade to new continent.Utopia (1518) Sir Thomas More Ideal society where crime, inustice don’t exist Hold all in common, scorn wealth but—slave labor?
- 5. Essential QuestionWhat causes people to leave their homes & explore new lands?
- 6. Causes of ExplorationWealth (spices, jewels, drugs, textiles, gold)MercantilismReligious motivesKnowledgeFor CountriesFrench = Forest, Fish and Firs (3 F’s)Spanish = Gold, God and Glory (3 G’s) Aiming for Asia & “found” AmericaCaravel & Portuguese exploration (Prince Henry the Navigator)Competition between European powers
- 7. EmpiresSpainAmerigo Vespucci – America named after him (mistake on map)Treaty of Tordesillas = Line of DemarcationPope Alexander VI divided new placesSpain gets all but Brazil to west of linePortugal gets AfricaVasco de Balboa –Isthmus of Panama to find Pacific OceanJuan Ponce de Leon- Florida & Fountain of YouthHernan Cortes-Aztec Empire-1519Ferdinand Magellan—Circumnavigates the globePizarro—Inca Empire-1530sHernando de Soto—Mississippi River looking for cities of goldFrancisco de Coronado—Grand Canyon (1539-1542) for gold7 Cities myth made up by Indians to avoid conversion/death
- 8. EmpiresEnglishCabot—Newfoundland—1497Sir Francis Drake &his ‘Sea Dogs’—Voyage around the globe—1577—why? Sir Walter Raleigh—Roanoke Island—1585—The Lost ColonyWhy so late to the party? FrenchGiovanni de Verrezano—Carolinas to Nova Scotia (1524)Jacques Cartier—St. Lawrence River (1524)Samuel de Champlain—Quebec founded 1608All looking for Northwest Passage
- 9. EmpiresDutchHenry Hudson (Dutch East India Company)—New Amsterdam aka New YorkFort Amsterdam (1614)New Amsterdam on Governors Island (1625)
- 10. The Black Legend16th Century—House of Habsburgs (Spain, Austria, Italy, Holland, New World)Protestant rebellions presentation of Spain as evil destructors of entire race of Indians, Bartolome de lasCasas solution = importation of African slavesStaple crops: Sugar, coffee, rice, indigoGives English “ideological sanction” to sieze ships, raid Spanish colonial cities & destroy Catholic hold over the New WorldSpanish Armada destroyed (1588) => no longer able to stop the English from entering the New World
- 11. First Permanent North American SettlementsEngland—1607—JamestownFrance—1608—Quebec—Fish & fursDutch—1614—Albany/New Amsterdam—Fish & fursSweden—1638—Deleware Valley—Fish & fursSpain—1749 (Laredo)—1769 (California)—Gold &livestock, Mestizos
- 12. Essential QuestionsWhy does one group succeed at colonization and another does not?
- 13. Reasons England Won+++Surplus population (enclosure & debt = English poor seek escape)Indentured servitudeReligious persecutionLarge variety in form of settlement/tradesBalanced sex ratio
- 14. JamestownVirginia Company of London—1607Algonquian Indians—30,000—Powhatan ConfederacyFood = greatest source of conflictResidents = aristocratsUnwilling to workMore interested in GOLD
- 15. Jamestown Fort
- 16. Captain John SmithThe Right Man for the Job?Farmer’s son & military adventurer President of Jamestown 1608-1609Encouraged trading & calm interactions with PowhatanPocahontas? Adoption ceremony?Marriage to John Rolfe
- 17. Chesapeake BayDo you see any geographic or environmental problems?
- 19. Jamestown Colonization Pattern: 1620-1660 Large plantations (>100acres)Spread > 5miles apartSee any problems there?
- 20. High Mortality RatesThe “Starving Time”:1607: 104 colonistsBy spring, 1608: 38 survived1609: 300 more immigrantsBy spring, 1610: 60 survived1610 – 1624: 10,000 immigrants1624 population: 1,200Adult life expectancy: 40 yearsDeath of children before age 5: 80%
- 21. Anglo-Powhatan Wars1610-1614 First Anglo-Powhatan WarDe La Warr Raided villages, burned houses, took supplies, burned cornfields.1614-1622-Peace sealed by Wolfe/Pochahontas1622—Great Powhatan Uprising1646—Indians defeated & removed from land
- 22. Essential QuestionsHow does the purpose or cause of a colony’s founding affect its ensuing society?
- 23. John Rolfe & Economic SuccessVirginia’s gold & silverTOBACCO1618 — Virginia produces 20,000 pounds of tobacco.1622- Virginia produces 60,000 pounds of tobacco.1627 — Virginia produces 500,000 pounds of tobacco.1629 — Virginia produces 1,500,000 pounds of tobacco.
- 24. Tobacco Prices: 1618-1710Why such a steep decline?
- 25. But who did all the work? Headright System:Each Virginian got 50 acres for each person whose passage they paid.Indenture Contract:5-7 years.Promised “freedom dues” [land, £]Forbidden to marry.1610-1614: only 1 in 10 outlived their indentured contracts!Indentured Contract, 1746
- 26. In-Class ActivityWhat was it like to be an indentured servant in Virginia?
- 27. The Child of TobaccoTobacco’s effect on Virginia’s economy:Vital role in putting VA on a firm economic footing.Ruinous to soil when continuously planted.Chained VA’s economy to a single crop.Tobacco promoted the use of the plantation system.Need for cheap, abundant labor.
- 28. Why was 1619 a pivotal year for the Chesapeake settlement?
- 29. Growing Political PowerThe House of Burgesses established in 1619 & began to assume the role of the House of Commons in EnglandControl over finances, militia, etc.By the end of the 17c, Virginia House of Burgesses was able to initiate legislation.A Council appointed by royal governorMainly leading planters.Functions like House of Lords.High death rates ensured rapid turnover of members.
- 30. Virginia Becomes a Royal ColonyJames I grew hostile to VirginiaHe hated tobacco.He distrusted the House of Burgesses which he called a seminary of sedition.1624-he revoked the charter of the bankrupt VA Company.Thus, VA became a royal colony, under the king’s direct control!
- 31. SlaveryEnglish Tobacco Label First Africans arrived in Jamestown in 1619.Their status was not clear-- perhaps slaves, perhaps indentured servants.Slavery not that important until the end of the 17c.
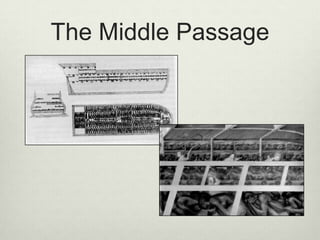
- 32. The Atlantic Slave Trade
- 33. Good Traded w/Africa for Slaves
- 35. Essential QuestionHow did slavery and indentured servitude diverge? Was slavery an economic institution or a racial institution?
- 36. Early Colonial SlaveryBeginning in 1662-- “Slave Codes”Made blacks [and their children] property, or chattel for life of white masters.In some colonies, it was a crime to teach a slave to read or write.Conversion to Christianity did not qualify the slave for freedom.
- 37. Frustrated Free White Men Late 1600 -- large numbers of young, poor, discontented men in the Chesapeake area.Little access to land or women for marriage.1670 --The Virginia Assembly disenfranchised most landless men!
- 38. Nathaniel Bacon’s Rebellion: 1676Led 1,000 Virginians in a rebellion against Governor BerkeleyRebels resented Berkeley’s close relations with Indians.Berkeley monopolized the fur trade with the Indians in the area.Berkley refused to retaliate for Indian attacks on frontier settlements.GovernorWilliam BerkeleyNathaniel Bacon
- 39. Bacon’s RebellionRebels attacked Indians, whether they were friendly or not to whites.Governor Berkeley driven from Jamestown.Rebels burned the capital & went on a rampage of plunderBacon suddenly died of fever.Berkeley brutally crushed the rebellion and hanged 20 rebels.
- 40. Results of Bacon’s RebellionIt exposed resentments between inland frontiersmen and landless former servants against gentry on coastal plantations.Socio-economic class differences/clashes between rural and urban communities would continue throughout American history.Upper class planters searched for laborers less likely to rebel -- BLACK SLAVES!!
- 41. The Settlement of MarylandA royal charter was granted to George Calvert, Lord Baltimore, 1632A proprietary colony created in 1634Heathier location than JamestownTobacco is to be main cropPlan was to govern as an absentee owner in a feudal relationship (tracts of land granted to his Catholic relatives.
- 42. A Haven for CatholicsColonists only willing to come to MD if they received landColonists = Catholic land barons surrounded by mostly Protestant small farmersConflict between the two led to Lord Baltimore’s loss of proprietary rights at the end of the 17th centuryLate 1600s—slave import beginsBaltimore allowed high degree of freedom of worship to prevent repeat of persecution of Cahtholics by ProtestantsProtestants feel threatened
- 43. Maryland Toleration Act of 1649Maryland Tolerations Act of 1649 Supported by Catholics in MDGuaranteed toleration to all CHRISTIANSDecreed death to those who denied the divinity of Jesus (like Jews, atheists, etc.)In a way—less tolerant than before the law was passed!
- 44. British Colonial Settlements by 1660
























![But who did all the work? Headright System:Each Virginian got 50 acres for each person whose passage they paid.Indenture Contract:5-7 years.Promised “freedom dues” [land, £]Forbidden to marry.1610-1614: only 1 in 10 outlived their indentured contracts!Indentured Contract, 1746](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1ch1-3-100904154356-phpapp01/85/Unit-1-ch-1-3-25-320.jpg)









![Early Colonial SlaveryBeginning in 1662-- “Slave Codes”Made blacks [and their children] property, or chattel for life of white masters.In some colonies, it was a crime to teach a slave to read or write.Conversion to Christianity did not qualify the slave for freedom.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1ch1-3-100904154356-phpapp01/85/Unit-1-ch-1-3-36-320.jpg)









