Unsteady radial flow in a confined aquifer Nonequilibrium well pumping equation
- 1. D . N A R E S H K U M A R A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G D E P A R T M E N T S T . M A R T I N ’ S E N G I N E E R I N G C O L L G E E L UNSTEADY RADIAL FLOW IN A CONFINED AQUIFER
- 2. Nonequilibrium well pumping equation When a well penetration an extensive confined aquifer is pumped at a constant rate, the influence of the discharge extends outward with time. The rate of decline of head times the storage coefficient summed over the area of influence equals the discharge. Because the water must come from a reduction of storage within the aquifer, the head will continue to decline as long as the aquifer is effectively infinite; therefore, unsteady, or transient, flow exists. The rate of decline, however, decreases continuously as the area of influence expands The applicable differential equation in plane polar coordinates is (4.4.2)
- 3. Where h is head, r is radial distance from the pumped well, S is the storage coefficient, T is transmissivity, and t is the time since beginning of pumping. Theis obtained a solution for equation based on the analogy between groundwater flow and heat conduction. By assuming that the well is replaced by a mathematical sink of constant strength and imposing the boundary conditions the solution
- 4. Is obtained, where s is drawdown, Q is the constant well discharge, and. Equation 4.4.2 is known as the nonequilibrium or Theis equation. The integral is a function of the lower limit u and is known as an exponential integral. It can be expanded as a convergent series as shown in equation and is termed the well function W(u). Alternatively, using customary units (gallon day foot system where s is in ft, Q is in gpm, T is in gpd/ft, u is in ft, and t is in days we have
- 5. The nonequilibrium equation permits determination of the formation constants S and T by means of pumping tests of wells. The equation is widely applied in practice and is preferred over the equilibrium equation because 1. A value for S can be determined 2. Only one observation well is required 3. A shorter period of pumping is generally necessary and 4. No assumption of steady state flow condition is required
- 6. The assumptions inherent in equation 4.4.2 should be emphasized because they are often overlooked in applying the nonequilibrium equation and thereby can lead to erroneous results the assumption in clude: 1. The aquifer is homogeneous, isotopic, of uniform thickness, and infinite areal extent. 2. Before pumping, the piezometric surface is horizontal 3. The well is pumped at a constant discharge rate. 4. The pumped well penetrates the entire aquifer, and flow is everywhere horizontal within the aquifer to the well 5. The well diameter is infinitesimal so that storage within the well can be neglected 6. Water removed from storage is discharged instantaneously with decline of head
- 7. Seldom if ever, are these assumptions strictly satisfied, but recognition of them can create an awareness of the approximations involved for employing the nonequilibrium equation under field conditions. Average values of S and T can be obtained in the vicinity of a pumped well by measuring in one or more observation wells the change in drawndown with time under the influence of a constant pumping rate. Because of the mathematical difficulties encountered in applying equation 4.4.2 or its equivalent
- 8. Theis method of solution
- 10. Copper-Jacob method of solution
- 12. Chow method of solution
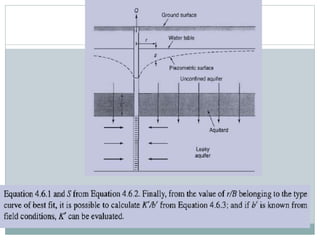
- 13. UNSTEADY RADIAL FLOW IN A LEAKY AQUIFER
- 17. THE END