Uterine polyps
- 3. POLYPS: • Abnormal tissue growth on a mucous membrane. OR A polyp is a tumor attached by a pedicle.
- 4. Two types of polyps are commonly seen ; 1. Mucoid polyp. Fibroid polyp. 1) MUCOID POLYP: Mucoid type of polyp arises from the body of uterus or from the cervix.The pedicle may at times be long enough to make the polyp protrude from the cervix or reach up to the
- 5. CAUSES RISK FACTORS: Increasing age. Obesity. Use of tamoxifen. Hypertension. Increasing the level of estrogen in the blood.
- 6. CLINICAL FEATURES: There may not be any symptom.Polyps are usually discovered during speculum examination ,hysteroscopy or hysterosalpingography. Irregular uterine bleeding is seen either in pre or post menopausal. Contact bleeding (If polyp is outside the cervix). Excessive vaginal discharge. On speculum examination ,the polyp looks reddish in colour ,attached usually by a slender pedicle. The size may be about
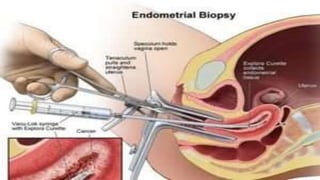
- 7. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION: TRANSVAGINAL ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION: A slender ,wand like device placed in vagina emits sound waves and creates an image of uterus ,including its interior. HYSTEROSCOPY: Inserting a thin ,flexible lighted telescope (hysteroscope) through vagina and cervix into the uterus. ENDOMETRIAL BIOPSY: Use a suction catheter inside the uterus to collect a specimen for lab testing. HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAPHY: An x-ray performed after pushing dye through the cervix into endometrial cavity.
- 12. MANAGEMENT: • Small polyps such as mucus polyps are removed by twisting ,after catching it with an ALLI”s forceps or tissue forceps. • Certain hormonal medications Progestins. Gonadotropin. Polyps with thick pedicle are removed by placing a trans fixation suture in the pedicle and then cutting it distal to the ligature. Big polyps lying in the vagina is removed by morcellation (piecemeal). Hysteroscopy.
- 14. 2)FIBROID POLYP: • The fibroid polyp may arise from the body of the uterus or from the cervix. It is an extrusion of a submucosal fibroid from the uterine cavity. The polyp is usually single and of varying sizes. There may be infection ,necrosis and hemorrhage at the tip
- 15. •CAUSES RISK FACTORS Increasing age. Obesity. Use of tamoxifen. Hypertension. Increasing the level of estrogen in the blood
- 16. CLINICAL FEATURES Intermenstrual bleeding. Colicky pain in lower abdomen. Excessive vaginal discharge ,which may be offensive. Sensation of something coming down when the polyp becomes big distending the vulva. Uterus may feel bulky. Pale or hemorrhage polyp can be visualized on speculum examination.
- 17. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION TRANSVAGINAL ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION: A slender ,wand like device placed in vagina emits sound waves and creates an image of uterus ,including its interior. HYSTEROSCOPY: Inserting a thin ,flexible lighted telescope (hysteroscope) through vagina and cervix into the uterus. ENDOMETRIAL BIOPSY: Use a suction catheter inside the uterus to collect a specimen for lab testing. HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAPHY: An x-ray performed after pushing dye through the cervix into endometrial cavity.
- 18. MANAGEMENT: • Small polyps such as mucus polyps are removed by twisting ,after catching it with an ALLI”s forceps or tissue forceps. • Certain hormonal medications Progestins. Gonadotropin. Polyps with thick pedicle are removed by placing a trans fixation suture in the pedicle and then cutting it distal to the ligature. Big polyps lying in the vagina is removed by morcellation (piecemeal). Hysteroscopy.
- 19. COMPLICATION •Infertility. •damageinjury to the cervix.
- 21. BIBLIOGRAPHY TEXT BOOK NAME: A COMPPREHENSIVE TEXTBOOK OF MIDWIFERY AND GYNECOLOGICAL NURSING. AUTHOR NAME : ANNAMMA JACOB. PUBLISHED BY : JAYPEE BROTHRS EDITION : 5TH EDITION. PAGE NO: 637~ 638.