Varda Rotter - Weizmann Institute of Science.
- 1. Varda Rotter Department of Molecular Cell Biology, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel Can mutant p53 change faces into guardian of the genome?
- 3. Mutant p53: oncogenic gain of function Brosh and Rotter, Nature Cancer Rev 2009
- 4. Expression of mutant p53 in human colon carcinoma Rotter, V. (1983). p53, a transformation-related cellular encoded protein, can be used as a biochemical marker for the detection of primary tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 80:2613-2617
- 5. p53 somatic mutations: prevalence of appearance in cancer types 5
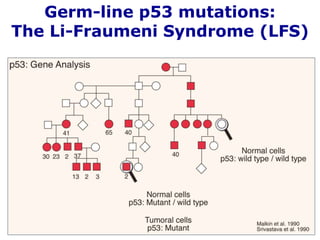
- 7. Germ-line p53 mutations: The Li-Fraumeni Syndrome (LFS)
- 8. • The Li-Fraumeni Syndrome (LFS): Human heterozygous carrier are born apparently normal developed variety of tumors later in life! • Mostly associated with LOH. • Connection to Cancer stem cell activityl!
- 9. Experimental model: p53 heterozygote mice develop normally Yet, develop tumors late in life
- 10. Experimental mouse stem cells models: wtp53, mutp53 and HZp53 • Adult stem cells: MSCs and C-FUCs multipotent; lower genomic fidelity; important for tissue regeneration and are associated with cancer development. UNDER GO LOH • Embryonic stem cells: iPSCs and ES pluripotent; important for development; high genomic fidelity. DO NOT UNDERGO LOH
- 12. What is the mechanism that suppress mutant p53 in mutp53 knock-in ES? Proteomic control??
- 13. Mutant p53 ES??
- 15. (human&mouse) (mouse) (human & mouse) WT p53 Mutant p53 Conformation specific antibodies:
- 16. Mutant p53 shifts into Wild type p53 conformation in ES
- 17. Identifying potential stabilizers of WT p53 conformation Mass Spectrometry Collaboration with T. Geiger at TAU
- 18. Binders bound to WT form in WT ESCs: Validation… WT p53 binds known Binders: MDM2, MDM4, p53BP1, Trim24 Mass Spectometry:
- 19. Interactome network of binders: Mass Spectrometry: binders of WT conformation of Mut p53 Post- translational modifications Ubiquitin- related Chaperones Other binders
- 20. Mutant p53 shifts into Wild type p53 conformation in ES
- 21. Conclusion: Mutant p53 protein is “refolded” into a wild type p53 protein conformation in embryonic stem cells Rivlin et al., PNAS 2014
- 22. p53 based therapy: Small peptide
- 23. Development of p53 based therapy Develop a ways to “convert” mutant p53 into wild type p53 Dr. Perry Tal Prof. Varda Rotter Prof. Moshe Oren 23
- 24. Conversion of mutant (M) p53 protein conformation into wild type (W) p53 protein conformation: Novel mutant p53-based personalized cancer therapy: for cancers that express a mutant p53 M M Treatment of various p53 mutant types with combinations of small peptides
- 25. Tumor suppressor Oncogenic Folded correctly Partially Denatured Binds to consensus DNA Does not bind DNA Low protein levels High protein levels MM p53 folding conformation is in a state of equilibrium An example of equilibrium state are p53 temperature sensitive mutations E285, V143 37°C 32°C p53 conformation equilibrium 25
- 26. Phage Display 26 Synthesis of DNA coding for a peptide library NEB PhD-7 and PhD-12 libraries each displaying 109-1011 peptides Packaging and display of the peptide library fused to pIII phage protein Reaction of phage with an immobilized target Elution of bound phageInfection of bacteria Washing of unbound phage Amplification of phage in bacteria Deep Sequencing
- 27. (human&mouse) (mouse) (human & mouse) WT p53 Mutant p53 Conformation specific antibodies:
- 28. Ab 1620 Peptide Phage Library screening Conformational shift of p53 28
- 29. Protocol for developing mutant p53 “conversion” • Screening of phage display peptide libraries for peptides capable of p53 modulation • Deep sequencing of pools of positive clones from the libraries • Computational deduction of optimized peptide sequences • Peptide synthesis • Functional validation in several in vitro assays • Functional validation in animal cancer models 29
- 30. Peptide Phage Library screening help identifying small peptides that can “educate” mutant p53 to function like the wild type p53 tumor suppressor!
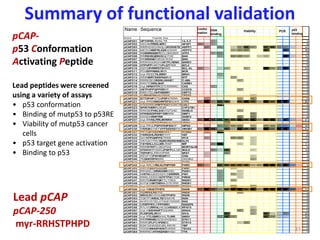
- 31. N ame P eptide Seq pCAP201 HPTHPIRLRDNLTR 14-3-3 3 3 pCAP202 DEDAKFRIRILMRR APAF1 3 2 3 8 pCAP203 RRRHDSCHNQLQNYDHSTE ASPP1 3 2 4 6 4 6 6 4 4 42 pCAP204 MSTESNMPRLIQNDDRRR ASPP2 2 4 4 5 5 20 pCAP205 RCRNRKKEKTECLQKESEK ATF3 2 5 pCAP206 RRRSHSQENVDQDTDE BAK 3 3 2 1 2 6 19 pCAP207 RRSRSNEDVEDKTEDE BAK 0 pCAP208 RRIRSGGKDHAWTPLHENH BARD1 0 pCAP209 HTPHPPVARTSPLQTPRR BCL2 0 pCAP210 DEFERYRRFSTSRRR BCL-XL 3 2 2 2 6 3 3 6 29 pCAP211 PDSEPPRMELRRR BCR 0 pCAP212 myr-REEETILIIRRR BRG1 3 pCAP213 RRIKMIRTSESFIQHIVS BTF 3 5 pCAP214 RRRESEQRSISLHHHST C-ABL 2 2 pCAP215 RRDTFDIRILMAF CARM1 0 pCAP216 myr-HFNHYTFESTCRRRRC CAS 2 2 pCAP217 HSTPHPPQPPERRR CCDC8 2 2 pCAP218 RREVTELHHTHEDRR CEP72 0 pCAP219 SYRHYSDHWEDRRR CETD2 1 1 pCAP220 STTHPHPGTSAPEPATRRR CHD6 2 2 2 6 pCAP221 myr-RRKHNKHRPEPDSDER CTF2 3 5 3 4 2 5 6 5 2 5 4 6 6 60 pCAP222 RYEENNGVNPPVQVFESRTR CUL7 4 pCAP223 SPWTHERRCRQR CYP27B1 0 pCAP224 RRKSEPHSLSGGYQTGAD DIABLO 2 2 pCAP225 HTIHSISDFPEPPDRRRR DMP1 3 3 pCAP226 DDSDNRIIRYRR G3BP2 3 3 6 pCAP227 myr-RRKILFIRLMHNKH GAS2 4 6 5 5 5 6 5 6 3 5 5 3 4 67 pCAP228 DEDAAHSTGHPHNSQHRRRRHIPK1 3 0 pCAP229 myr-PRVLPSPHTIHPSQYP HIPK2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 29 pCAP230 RKRGKSYAFFVPPSESKERW HMGB1 3 5 5 4 3 6 5 5 2 6 4 6 6 63 pCAP231 HRTQSTLILFIRRGRET HTRA2 3 9 pCAP232 RSRSSHLRDHERTHT HZF 0 pCAP233 SHYHTPQNPPSTRRR IFI16 3 3 3 2 11 pCAP234 HRTGHYTRCRQRCRSRSHNRHKLF4 2 2 pCAP235 RSYSKLLCLLERLRISP MIF 2 2 2 11 pCAP236 RRRSTNTFLGEDFDQ MORTALIN 0 pCAP237 HTIHVHYPGNRQPNPPLILQR MULE 3 5 2 12 pCAP238 TSPHPSLPRHIYPRR NFAT 2 4 6 pCAP239 REGFYGPWHEQRRR OGA 2 2 4 pCAP240 TEQHHYIPHRRR OSGIN2 3 3 pCAP241 LIGLSTSPRPRIIR PAR3 0 pCAP242 myr-RRLIVRILKLPNPPER PARC 4 3 6 6 6 6 3 4 6 6 5 6 6 pCAP243 RRCRSILPLLLLSR PERP 2 2 pCAP244 RRVSELQRNKHGRKHEL PIAS1 2 5 pCAP245 NHITNGGEEDSDCSSRRRRL PIN1 3 2 8 pCAP246 RRRLDDEDVQTPTPSEYQN PIRH2 2 5 pCAP247 RRITEIRGRTGKTTLTYIED RAD51 3 6 pCAP248 EIYGESGKTDEHALDTEYRR RAD51 0 pCAP249 myr-DERTGKTRRYIDTRDIRR RAD51 3 3 6 pCAP250 myr-RRHSTPHPD RAD9 4 6 5 5 5 5 5 6 3 6 6 6 6 72 pCAP251 RLRRVILRSYHE RAD9 3 3 pCAP252 RRVILRSYDGGHSTPHPD RAD9 0 pCAP253 TGKTFVKRHLTEFEKKYR RAN 0 pCAP254 NHFDYDTIELDTAGEYSRRR RAS 0 pCAP255 DPEPPRYLPPPPERR RASSF5 0 pCAP256 RTLHGRRVILHEGGHSISDLK RPA70 2 2 pCAP257 myr-HSSHHHPTVQHRR SIN3A 4 4 8 pCAP258 FLIGPDRLIRSR SIVA 6 4 5 2 2 4 23 pCAP259 myr-RTLIGIIRSHHLTLIRR SMG1 5 4 5 3 2 2 25 pCAP260 RRTFIRHRIDSTEVIYQDED STK11 0 pCAP261 RRRQPLPSAPENEE STK15 2 3 5 pCAP262 ESKTGHKSEEQRLRRYR TBP 0 pCAP263 YDDEHNHHPHHSTHRRR TSC22 0 pCAP264 RRRREVHTIHQHGIVHSD TTK 0 4 3 3 3 4 6 3 5 2 5 3 3 6 4 4 2 3 2 3 3 2 Name Sequence Confor mation DNA binding Viability PCR p53 binding pCAP- p53 Conformation Activating Peptide Lead peptides were screened using a variety of assays • p53 conformation • Binding of mutp53 to p53RE • Viability of mutp53 cancer cells • p53 target gene activation • Binding to p53 Lead pCAP pCAP-250 myr-RRHSTPHPD Summary of functional validation 31
- 32. 4-10 lead peptides were identified as functionally effective in a verity of assays; p53 conformation Binding of mutp53 to p53RE Viability of mutp53 cancer cells p53 target genes activation Binding to p53 pCAP- p53 Conformation Activating Peptide Lead pCAPs pCAP-250 myr-RRHSTPHPD pCAP-227 myr-RRKILFIRLMHNKH pCAP-325 myr-RRIRDPRILLLHFD pCAP-242 myr-RRLIVRILKLPNPPER pCAP-144 SFILFIRRGRLGRRRRRRRRR Peptides functional screening summary Tal P, Eizenberger S, Cohen E, Goldfinger N, Pietrokovski S, Oren M, Rotter V. Oncotarget. 2016
- 33. Predicted model of peptide pCAP-250 and p53 binding “Anchor-Dock” algorithm produced a model of pCAP-250 peptide folding and its interaction with p53 33Avi Ben-Shimon
- 34. TP53 Mutations in the Genome Era Exonic mutation frequencies from WES/WGS studies (COSMIC v65) SomaticMutation Frequency TP53 M. Olivier IARC 34
- 35. In vitro Lead pCAP-250 effect on apoptosis and p53 targets Ovarian Cancer model ES2 cells p53S241F Time treatment pCAP-250 FoldmRNAexpression Time treatment pCAP-250 Btg2/GAPDH FoldmRNAexpression Time treatment pCAP-250 p21/GAPDH Annexin-PI assay (pCAP-250 12μg/ml) p53 target genes expression FoldmRNAexpression Time treatment pCAP-250 PUMA/GAPDH FoldmRNAexpression CD95/GAPDH Apoptosis Growth arrest Peptid e
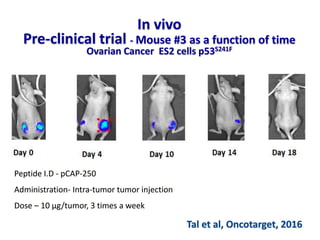
- 36. In vivo Pre-clinical trial - Mouse #3 as a function of time Ovarian Cancer ES2 cells p53S241F Peptide I.D - pCAP-250 Administration- Intra-tumor tumor injection Dose – 10 μg/tumor, 3 times a week Tal et al, Oncotarget, 2016
- 37. Intra tumor (IT) injection of 10μg/tumor 3 times a week Control peptide pCAP-250 Day 27 Control peptide pCAP-250 p - 0.014 8.4E+06 5.1E+07 1.8E+08 4.8E+08 9.7E+08 1.7E+09 2.7E+09 4.0E+09 4.9E+09 0.E+00 2.E+09 4.E+09 6.E+09 0 3 7 10 13 17 20 24 27 Time (Days) Con peptide n=10 pCAP-250 n=10 8.4E+06 6.0E+07 2.1E+08 5.8E+08 4.3E+08 2.8E+08 1.9E+08 1.2E+08 9.6E+07 0.E+00 5.E+08 1.E+09 2.E+09 2.E+09 0 3 7 10 13 17 20 24 27 Time (Days) Con peptide n=10 pCAP-250 n=10 ES2 cells Luminescence over time (in-vivo) Treatment IVISRead(photons) Ovarian Cancer Animal Model: ES2 cells p53S241F 28
- 38. Ovarian cancer ES2 cells: daily SC injections of pCAP 38 Con pCAP SC 0.05mg/day 14 days Average 9.12 108 pCAP-250 SC 0.05mg/day 14 days Average 3.54 108 2 5 9 12 15 2 5 9 12 15 Control SC pCAP 250 SC 0.00E+000 1.00E+009 2.00E+009 Time Days Time Days
- 39. Programmable release 1d-6weeks 2 µg/ml IC50 ES2 Cells 4 – 6 µg/ml 20mg/Kg0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Plasmaconcentration(ng/ml) Time (day) pCAP 250 @ 3 mg/kg sc (minipump) pCAP 250 @ 10 mg/kg sc (minipump) pCAP-250 PK sub-cutaneous release by ALZET mini-pump Peptide Controlled release with ALZET mini-pump
- 40. pCAP-250 ALZET pump 20mg/Kg 14 Days 1.0E+07 2.8E+07 6.8E+07 1.3E+08 6.9E+08 8.2E+08 1.1E+09 1.7E+09 2.0E+09 2.3E+09 1.5E+08 5.8E+08 9.7E+08 7.9E+08 4.5E+08 2.7E+08 2.2E+08 2.1E+08 4.6E+07 0.0E+00 5.0E+08 1.0E+09 1.5E+09 2.0E+09 2.5E+09 3.0E+09 0 4 7 10 14 17 21 24 28 32 Time (Days) Control peptide n=10 pCAP-250 mini-pumps n=10 pCAP-250 intra-tumor n=10 pCAP-250 intra-tumor 10µg/tumor 3 times/week Treatment IVISRead(photons) 105 cells injection Control intra-tumor 10µg/tumor 3 times/week Control ALZET pump 20mg/Kg 14 Days Peptide delivery in-vivo ALZET mini-pumps Ovarian Cancer ES2 cells Luminescence over time (in-vivo)
- 41. Breast cancer animal model MDA-MB231 cells p53E280K triple negative Day 18 Day 29 Day 18 Day 29 Intra tumor injection 6μg/tumor 3 times a week pCAP- 250,154,242 Control 41
- 42. Control peptides pCAP Treatment Day 34 Day 35 IVISRead(photons) 5*105cells injection Treatment Intra tumor injection 6μg/tumor 3 times a week Colon carcinoma SW-480 p53R273H SW-480 cells Luminescence over time (in-vivo) 42 2.23E+07 2.79E+08 9.25E+08 1.76E+09 2.41E+09 3.27E+09 3.58E+09 4.22E+09 4.44E+09 4.67E+09 1.07E+09 1.06E+09 9.91E+08 7.52E+08 3.11E+08 2.30E+08 7.81E+07 0.E+00 2.E+09 4.E+09 6.E+09 0 4 8 11 15 19 23 27 31 34 Time (Days) Con peptides n=10 pCAP-325,250,154 n=10
- 43. • The p53 pCAPs “convert” mutant p53 conformation
- 44. Acknowledgments: Alina Molchadsky Noa Rivlin* Yoav Shetzer Gabriela Koiefman Meital Charni Yan Stein Hilla Solomon Giusepo Lonetto Tom Kaufman Perry Tal* Shay Eizenberger* Naomi Goldfinger Collaborators: Moshe Oren Tami Geiger