reliability.pdf
- 1. 2/10/2016 1 Presented by: Vikash K Giri PGDM (Marketing) Batch: 2014-16
- 3. Definition Reliability - The ability of an item to perform a required function under stated conditions for a stated period of time. It is usually denoted as probability or as a success . 2/10/2016 3
- 4. Type of reliability Inherent reliability- predicted by product design. Achieved reliability- observed during use 2/10/2016 4
- 5. Reliability is related to the safety of a system. Deals with the estimation and management of high levels of lifetime engineering uncertainty and risks of failure. Failure – The termination of ability of an item to perform a required function. 2/10/2016 5
- 6. Type of failure Functional failure- failure that occurs that at the start of a product life due to manufacturing material defect. Reliability failure- failure after some period of time. 2/10/2016 6
- 7. Reliability measurement Failure rate – number of failure per unit time. Alternative measures 1. Mean time to failure 2. Mean time between failure 2/10/2016 7
- 8. Observed Failure Rate – For a stated period in life of an item, the ratio of the total number of failures in a sample to the cumulative of the time on that sample. The observed failure rate is associated with particular and stated time intervals(or summation of intervals) in the life of the item and under stated conditions. For example, an automobile's failure rate in its fifth year of service may be many times greater than its failure rate during its first year of service. 2/10/2016 8
- 10. In the given graph, the 'bathtub curve' hazard function (blue, upper solid line) is a combination of a decreasing hazard of early failure (red dotted line) and an increasing hazard of wear-out failure (yellow dotted line), plus some constant hazard of random failure (green, lower solid line). It comprises of 3 parts: 1. The first part is a decreasing failure rate, known as early failures. 2. The second part is a constant failure rate, known as random failures. 3. The third part is an increasing failure rate, known as wear- out failures. 2/10/2016 10
- 11. Advantages of reliability Focuses on costs of failure caused by system downtime, cost of spares, repair equipment, personnel and cost of warranty claims. For defense product and system, reliability is the differentiating factor determining mission success or loss of life. For industrial system and plants, reliability directly influences inherent availability and return on investment. For commercial product, high reliability provide a supplier with competitive advantage, resulting increase in market share and higher profit. 2/10/2016 11
- 12. Advantages of reliability The capacity of a designed, produced or maintained item to perform as required over time The capacity of a population of designed, produced or maintained items to perform as required over specified time The resistance to failure of an item over time The probability of an item to perform a required function under stated conditions for a specified period of time The durability of an object. 2/10/2016 12
- 13. Maintainability The probability that a system or a product can be retained in, or one that has failed can be restored . 2/10/2016 13
- 14. Advantages of maintainability Correct defects or their cause Prevent unexpected breakdowns Maximize a product's useful life Maximize efficiency, reliability and safety Make future maintenance easier 2/10/2016 14
- 15. Design for Maintainability Repairable Interchangeability. Accessibility. 2/10/2016 15
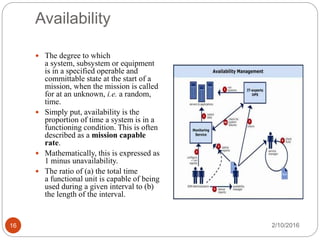
- 16. Availability The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at an unknown, i.e. a random, time. Simply put, availability is the proportion of time a system is in a functioning condition. This is often described as a mission capable rate. Mathematically, this is expressed as 1 minus unavailability. The ratio of (a) the total time a functional unit is capable of being used during a given interval to (b) the length of the interval. 2/10/2016 16
- 17. Name Definition Guarantee An assurance given by the manufacturer to the vendor that the product will work without failure for a stated period of time Warranty A written guarantee given to the purchaser of a new appliance, automobile, or other item by the manufacturer or dealer, usually specifying that the manufacturer will make any repairs or replace defective parts free of charge for a stated period of time. Maintainability The measure of the ability of an item to be retained in or retained in or restored to a specified condition when maintenance is performed by personnel having specified skill levels, using prescribed procedures and resources Applies to a major tasks where many repetitions are expected and where considerable time is required Availability A tool for measuring the percent of time an item or system is in a state of readiness where it is operable and can be committed to use when called upon. Availability ceases because of a downing event that causes the item/to system become unavailable to initiate a mission when called upon Availability=MTBF/(MTBF+MTTR) Reliability The ability of an item to perform a required function under stated conditions for a stated period of time. It is usually denoted as probability or as a success . 2/10/2016 17
- 18. What is reliability engineering Manufacturers often suffer high costs of failure under warranty Reliability is usually concerned with failures in the time domain. This distinction marks the difference between traditional quality control and reliability engineering Whether failures occur or not and their times to occurrence can seldom be forecast accurately .reliability is therefore an aspect of engineering uncertainty Whether an item will work for a particular period is a question which can be answered as a probability. Ultimately reliability engineering is effective management of engineering 2/10/2016 18
- 19. Reliability centered maintenance A process to ensure that systems continue to do what their users require in their present operating context. It is used to achieve improvements in fields such as the establishment of safe minimum levels of maintenance, changes to operating procedures and strategies and the establishment of capital maintenance regimes and plans. It regards maintenance as the means to maintain the functions a user may require of machinery in a defined operating context. 2/10/2016 19
- 20. RCM offers five principal options among the risk management strategies: Predictive maintenance tasks Preventive Restoration or Preventive Replacement maintenance tasks Detective maintenance tasks Run-to-Failure One-time changes to the "system" (changes to hardware design, to operations, or to other things) 2/10/2016 20
- 21. Why engineering items failed? The design might be inherently incapable, the more complex the design ,more the difficult to overcome the problem The item might be overstressed in some way Failures can be caused by wear out. Sufficiently strong at the start of the life and become weaker with age Failures can be caused by other time dependent mechanism such as battery run down, creep in turbine caused simultaneously by high temperature and tensile stress 2/10/2016 21
- 22. MISSION RELIABILITY Mission reliability is defined as the ability of an item to perform its required functions for the duration of a specified “mission profile.” Mission reliability thus defines the probability of non-failure of the system for the period of time required to complete a mission. The probability is a point on the reliability function corresponding to a time equal to the mission length. 2/10/2016 22
- 23. BAUXITE SL H/C U/F AIR CLUTCH MOTOR GEAR BOX TROMMEL SCREEN MSP Ball mill in NALCO 2/10/2016 23
- 24. CONCLUSION Reliability is like a preventive measures to avoid failures. Reliable product will give consistent output for a longer period of time. Failure occurs if a product is not reliable. So, maintenance is required. Maintainability is restoring the failed parts to working condition. Availability is when a product is in committable state and available in specific time or random time. 2/10/2016 24
- 25. 2/10/2016 25
- 26. 2/10/2016 26