pandas - Python Data Analysis
- 1. Python for Data Analysis Andrew Henshaw Georgia Tech Research Institute
- 2. • PowerPoint • IPython (ipython –pylab=inline) • Custom bridge (ipython2powerpoint)
- 3. • Python for Data Analysis • Wes McKinney • Lead developer of pandas • Quantitative Financial Analyst
- 4. • Python library to provide data analysis features, similar to: • R • MATLAB • SAS • Built on NumPy, SciPy, and to some extent, matplotlib • Key components provided by pandas: • Series • DataFrame
- 5. • One-dimensional array-like object containing data and labels (or index) • Lots of ways to build a Series >>> import pandas as pd >>> s = pd.Series(list('abcdef')) >>> s 0 a 1 b 2 c 3 d 4 e 5 f >>> s = pd.Series([2, 4, 6, 8]) >>> s 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8
- 6. • A Series index can be specified • Single values can be selected by index • Multiple values can be selected with multiple indexes >>> s = pd.Series([2, 4, 6, 8], index = ['f', 'a', 'c', 'e']) >>> >>> s f 2 a 4 c 6 e 8 >>> s['a'] 4 >>> s[['a', 'c']] a 4 c 6
- 7. • Think of a Series as a fixed-length, ordered dict • However, unlike a dict, index items don't have to be unique >>> s2 = pd.Series(range(4), index = list('abab')) >>> s2 a 0 b 1 a 2 b 3 >>> s['a] >>> >>> s['a'] 4 >>> s2['a'] a 0 a 2 >>> s2['a'][0] 0
- 8. • Filtering • NumPy-type operations on data >>> s f 2 a 4 c 6 e 8 >>> s[s > 4] c 6 e 8 >>> s>4 f False a False c True e True >>> s*2 f 4 a 8 c 12 e 16
- 9. • pandas can accommodate incomplete data >>> sdata = {'b':100, 'c':150, 'd':200} >>> s = pd.Series(sdata) >>> s b 100 c 150 d 200 >>> s = pd.Series(sdata, list('abcd')) >>> s a NaN b 100 c 150 d 200 >>> s*2 a NaN b 200 c 300 d 400
- 10. • Unlike in a NumPy ndarray, data is automatically aligned >>> s2 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index = ['c', 'b', 'a']) >>> s2 c 1 b 2 a 3 >>> s a NaN b 100 c 150 d 200 >>> s*s2 a NaN b 200 c 150 d NaN
- 11. • Spreadsheet-like data structure containing an ordered collection of columns • Has both a row and column index • Consider as dict of Series (with shared index)
- 12. >>> data = {'state': ['FL', 'FL', 'GA', 'GA', 'GA'], 'year': [2010, 2011, 2008, 2010, 2011], 'pop': [18.8, 19.1, 9.7, 9.7, 9.8]} >>> frame = pd.DataFrame(data) >>> frame pop state year 0 18.8 FL 2010 1 19.1 FL 2011 2 9.7 GA 2008 3 9.7 GA 2010 4 9.8 GA 2011
- 13. >>> pop_data = {'FL': {2010:18.8, 2011:19.1}, 'GA': {2008: 9.7, 2010: 9.7, 2011:9.8}} >>> pop = pd.DataFrame(pop_data) >>> pop FL GA 2008 NaN 9.7 2010 18.8 9.7 2011 19.1 9.8
- 14. • Columns can be retrieved as a Series • dict notation • attribute notation • Rows can retrieved by position or by name (using ix attribute) >>> frame['state'] 0 FL 1 FL 2 GA 3 GA 4 GA Name: state >>> frame.describe <bound method DataFrame.describe of pop state year 0 18.8 FL 2010 1 19.1 FL 2011 2 9.7 GA 2008 3 9.7 GA 2010 4 9.8 GA 2011>
- 15. • New columns can be added (by computation or direct assignment) >>> frame['other'] = NaN >>> frame pop state year other 0 18.8 FL 2010 NaN 1 19.1 FL 2011 NaN 2 9.7 GA 2008 NaN 3 9.7 GA 2010 NaN 4 9.8 GA 2011 NaN >>> frame['calc'] = frame['pop'] * 2 >>> frame pop state year other calc 0 18.8 FL 2010 NaN 37.6 1 19.1 FL 2011 NaN 38.2 2 9.7 GA 2008 NaN 19.4 3 9.7 GA 2010 NaN 19.4 4 9.8 GA 2011 NaN 19.6
- 16. >>> obj = pd.Series(['blue', 'purple', 'red'], index=[0,2,4]) >>> obj 0 blue 2 purple 4 red >>> obj.reindex(range(4)) 0 blue 1 NaN 2 purple 3 NaN >>> obj.reindex(range(5), fill_value='black') 0 blue 1 black 2 purple 3 black 4 red >>> obj.reindex(range(5), method='ffill') 0 blue 1 blue 2 purple 3 purple 4 red • Creation of new object with the data conformed to a new index
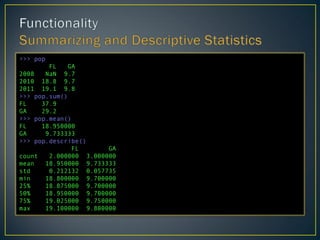
- 17. >>> pop FL GA 2008 NaN 9.7 2010 18.8 9.7 2011 19.1 9.8 >>> pop.sum() FL 37.9 GA 29.2 >>> pop.mean() FL 18.950000 GA 9.733333 >>> pop.describe() FL GA count 2.000000 3.000000 mean 18.950000 9.733333 std 0.212132 0.057735 min 18.800000 9.700000 25% 18.875000 9.700000 50% 18.950000 9.700000 75% 19.025000 9.750000 max 19.100000 9.800000
- 18. >>> pop FL GA 2008 NaN 9.7 2010 18.8 9.7 2011 19.1 9.8 >>> pop < 9.8 FL GA 2008 False True 2010 False True 2011 False False >>> pop[pop < 9.8] = 0 >>> pop FL GA 2008 NaN 0.0 2010 18.8 0.0 2011 19.1 9.8
- 19. • pandas supports several ways to handle data loading • Text file data • read_csv • read_table • Structured data (JSON, XML, HTML) • works well with existing libraries • Excel (depends upon xlrd and openpyxl packages) • Database • pandas.io.sql module (read_frame)
- 20. >>> tips = pd.read_csv('/users/ah6/Desktop/pandas talk/data/tips.csv') >>> tips.ix[:2] total_bill tip sex smoker day time size 0 16.99 1.01 Female No Sun Dinner 2 1 10.34 1.66 Male No Sun Dinner 3 2 21.01 3.50 Male No Sun Dinner 3 >>> party_counts = pd.crosstab(tips.day, tips.size) >>> party_counts size 1 2 3 4 5 6 day Fri 1 16 1 1 0 0 Sat 2 53 18 13 1 0 Sun 0 39 15 18 3 1 Thur 1 48 4 5 1 3 >>> sum_by_day = party_counts.sum(1).astype(float)
- 21. >>> party_pcts = party_counts.div(sum_by_day, axis=0) >>> party_pcts size 1 2 3 4 5 6 day Fri 0.052632 0.842105 0.052632 0.052632 0.000000 0.000000 Sat 0.022989 0.609195 0.206897 0.149425 0.011494 0.000000 Sun 0.000000 0.513158 0.197368 0.236842 0.039474 0.013158 Thur 0.016129 0.774194 0.064516 0.080645 0.016129 0.048387 >>> party_pcts.plot(kind='bar', stacked=True) <matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x6bf2ed0>
- 22. >>> tips['tip_pct'] = tips['tip'] / tips['total_bill'] >>> tips['tip_pct'].hist(bins=50) <matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x6c10d30> >>> tips['tip_pct'].describe() count 244.000000 mean 0.160803 std 0.061072 min 0.035638 25% 0.129127 50% 0.154770 75% 0.191475 max 0.710345
- 23. • Data Aggregation • GroupBy • Pivot Tables • Time Series • Periods/Frequencies • Operations with Time Series with Different Frequencies • Downsampling/Upsampling • Plotting with TimeSeries (auto-adjust scale) • Advanced Analysis • Decile and Quartile Analysis • Signal Frontier Analysis • Future Contract Rolling • Rolling Correlation and Linear Regression




![• One-dimensional
array-like object
containing data
and labels (or
index)
• Lots of ways to
build a Series
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> s = pd.Series(list('abcdef'))
>>> s
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 d
4 e
5 f
>>> s = pd.Series([2, 4, 6, 8])
>>> s
0 2
1 4
2 6
3 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-5-320.jpg)
![• A Series index can be
specified
• Single values can be
selected by index
• Multiple values can be
selected with multiple
indexes
>>> s = pd.Series([2, 4, 6, 8],
index = ['f', 'a', 'c', 'e'])
>>>
>>> s
f 2
a 4
c 6
e 8
>>> s['a']
4
>>> s[['a', 'c']]
a 4
c 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-6-320.jpg)
![• Think of a Series as a
fixed-length, ordered
dict
• However, unlike a dict,
index items don't have
to be unique
>>> s2 = pd.Series(range(4),
index = list('abab'))
>>> s2
a 0
b 1
a 2
b 3
>>> s['a]
>>>
>>> s['a']
4
>>> s2['a']
a 0
a 2
>>> s2['a'][0]
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-7-320.jpg)
![• Filtering
• NumPy-type operations
on data
>>> s
f 2
a 4
c 6
e 8
>>> s[s > 4]
c 6
e 8
>>> s>4
f False
a False
c True
e True
>>> s*2
f 4
a 8
c 12
e 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-8-320.jpg)

![• Unlike in a NumPy
ndarray, data is
automatically aligned
>>> s2 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3],
index = ['c', 'b', 'a'])
>>> s2
c 1
b 2
a 3
>>> s
a NaN
b 100
c 150
d 200
>>> s*s2
a NaN
b 200
c 150
d NaN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-10-320.jpg)

![>>> data = {'state': ['FL', 'FL', 'GA', 'GA', 'GA'],
'year': [2010, 2011, 2008, 2010, 2011],
'pop': [18.8, 19.1, 9.7, 9.7, 9.8]}
>>> frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
>>> frame
pop state year
0 18.8 FL 2010
1 19.1 FL 2011
2 9.7 GA 2008
3 9.7 GA 2010
4 9.8 GA 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-12-320.jpg)

![• Columns can be retrieved
as a Series
• dict notation
• attribute notation
• Rows can retrieved by
position or by name (using
ix attribute)
>>> frame['state']
0 FL
1 FL
2 GA
3 GA
4 GA
Name: state
>>> frame.describe
<bound method DataFrame.describe
of pop state year
0 18.8 FL 2010
1 19.1 FL 2011
2 9.7 GA 2008
3 9.7 GA 2010
4 9.8 GA 2011>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-14-320.jpg)
![• New columns can be
added (by computation
or direct assignment)
>>> frame['other'] = NaN
>>> frame
pop state year other
0 18.8 FL 2010 NaN
1 19.1 FL 2011 NaN
2 9.7 GA 2008 NaN
3 9.7 GA 2010 NaN
4 9.8 GA 2011 NaN
>>> frame['calc'] = frame['pop'] * 2
>>> frame
pop state year other calc
0 18.8 FL 2010 NaN 37.6
1 19.1 FL 2011 NaN 38.2
2 9.7 GA 2008 NaN 19.4
3 9.7 GA 2010 NaN 19.4
4 9.8 GA 2011 NaN 19.6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-15-320.jpg)
![>>> obj = pd.Series(['blue', 'purple', 'red'],
index=[0,2,4])
>>> obj
0 blue
2 purple
4 red
>>> obj.reindex(range(4))
0 blue
1 NaN
2 purple
3 NaN
>>> obj.reindex(range(5), fill_value='black')
0 blue
1 black
2 purple
3 black
4 red
>>> obj.reindex(range(5), method='ffill')
0 blue
1 blue
2 purple
3 purple
4 red
• Creation of new
object with the
data conformed
to a new index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-16-320.jpg)
![>>> pop
FL GA
2008 NaN 9.7
2010 18.8 9.7
2011 19.1 9.8
>>> pop < 9.8
FL GA
2008 False True
2010 False True
2011 False False
>>> pop[pop < 9.8] = 0
>>> pop
FL GA
2008 NaN 0.0
2010 18.8 0.0
2011 19.1 9.8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-18-320.jpg)

![>>> tips = pd.read_csv('/users/ah6/Desktop/pandas
talk/data/tips.csv')
>>> tips.ix[:2]
total_bill tip sex smoker day time size
0 16.99 1.01 Female No Sun Dinner 2
1 10.34 1.66 Male No Sun Dinner 3
2 21.01 3.50 Male No Sun Dinner 3
>>> party_counts = pd.crosstab(tips.day, tips.size)
>>> party_counts
size 1 2 3 4 5 6
day
Fri 1 16 1 1 0 0
Sat 2 53 18 13 1 0
Sun 0 39 15 18 3 1
Thur 1 48 4 5 1 3
>>> sum_by_day = party_counts.sum(1).astype(float)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-20-320.jpg)

![>>> tips['tip_pct'] = tips['tip'] / tips['total_bill']
>>> tips['tip_pct'].hist(bins=50)
<matplotlib.axes.AxesSubplot at 0x6c10d30>
>>> tips['tip_pct'].describe()
count 244.000000
mean 0.160803
std 0.061072
min 0.035638
25% 0.129127
50% 0.154770
75% 0.191475
max 0.710345](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-130614111704-phpapp01/85/pandas-Python-Data-Analysis-22-320.jpg)
